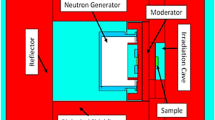
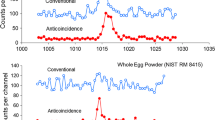
Abstract
Total body nitrogen (TBN) can be used to estimate total body protein, an important body composition component at the molecular level. A system using the associated particle technique in conjunction with prompt gamma neutron activation analysis has been developed for the measurement of TBN in vivo. The system uses a compact D, T neutron generator (~107 n/s) coupled to an internal alpha-particle detector, and a counting system with six bismuth germinate detectors. 14 Subjects were scanned from shoulders to hips (20 min scan time, <0.4 mSv dose) generating complex spectra dominated by signals from C, O, H, and N, with significant peak overlap. Fractional contributions from these elements to regions of interests (ROI) spanning a 4–8 MeV range were determined by algorithms comparing ratios of interrelated ROIs. In addition, multi-component least squares fitting was done to further resolve individual peak activities (MATLAB R2011b). Total body potassium (TBK) was also measured using a whole body gamma counter. Predicted TBN values, based on fat-free mass estimated from TBK, were compared to measured TBN results. Measured versus predicted results for all subjects were not statistically different. Separating subjects by gender also showed no difference between measured and predicted values. The associated particle system showed good agreement with predicted TBN values, but measurement precision was not better than that commonly seen in traditional prompt gamma thermal neutron activation analysis systems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nagai T, Fujii I, Muto H, Inouye T (1969) J Nucl Med 10:192–196
Wang ZM, Pierson RN Jr, Heymsfield SB (1992) Am J Clin Nutr 56:19–28
Hedley AA, Ogden CL, Johnson CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, Flegal KM (2004) JAMA 291:2847–2850
Chettle DR, Fremlin JH (1984) Phys Med Biol 29:1011–1043
Beddoe AH, Zuidmeer A, Hill GL (1984) Phys Med Biol 29:371–383
Dilmanian FA, Lidofsky LJ, Stamatelatos I, Kamen Y, Yasumura S, Vartsky D, Pierson RN, Weber DA, Moore RI, Ma R (1998) Phys Med Biol 43:339–349
Hollas CL, Ussery LE, Butterfield KB, Morgado RE (1990) Basic Life Sci 55:395–400
Gierlik M, Batsch T, Moszynski M, Szczesniak T, Wolski D, Klamra W, Perot B, Perret G (2006) IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 53:1737–1743
Gordon CM, Peters CW (1990) Int J Radiat Appl Instrum A 41:1111–1116
Mitra S, Wolff JE, Garrett R, Peters CW (1995) Phys Med Biol 40:1045–1055
Shypailo RJ, Ellis KJ (2005) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 263:759–765
Shypailo RJ, Ellis KJ (2008) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 276:71–77
Ellis KJ, Shypailo RJ (2008) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 276:79–83
Chichester DL, Simpson JD, Lemchak M (2007) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 271:629–637
Lim CS, Sowerby BD (2005) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 264:15–19
Shypailo RJ, Ellis KJ (2011) Phys Med Biol 56:2979–2997
Baur LA, Allen JR, Humphries IR, Gaskin KJ (2001) In: Jurimae T, Hills AP (eds) Body composition assessment in children and adolescents. Karger, Basel
Perot B, Carasco C, Bernard S et al (2008) Appl Rad Isotopes 66:421–434
ICRP (1975) Report of the task group on reference man. International commission of radiation protection publication 23. Pergamon, Oxford
Acknowledgments
This work is a publication of the USDA/ARS Children’s Nutrition Research Center, Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine, and Texas Children’s Hospital, Houston, TX. Funding has been provided from the USDA/ARS under Cooperative Agreement No. 58-6250-6-001. The contents of this publication do not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the USDA, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the US Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shypailo, R.J., Workeneh, B. & Ellis, K.J. Assessment of the associated particle prompt gamma neutron activation technique for total body nitrogen measurement in vivo. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 296, 143–148 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-2138-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-2138-7