Abstract
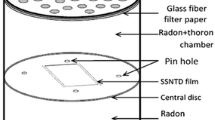
Radon and thoron have been identified as potential radiological health hazard and the dose estimation due to their exposure is an important task. Understanding their behavior in indoor environment helps in calculating the inhalation doses due to them. Present study aims at the distribution of radon and thoron concentrations in a typical Indian dwelling. Solid state nuclear track detectors are employed in the study. The concentration of radon is found to be invariant in indoor environment. The thoron concentration is found to decrease exponentially as a function of distance from the source (wall/floor). Solution of one dimensional diffusion equation is used for regression fittings for thoron variation, from which the diffusion constants and the exhalation rates were calculated. The diffusion constants varied from 0.00195 to 0.00540 m2 s−1.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruno RC (1983) Verifying a model of radon decay products behaviour indoors. Health Phys 45:471–480
Jacobi W (1972) Activity and potential α-energy of 222Rn and 220Rn daughter in different air atmospheres. Health Phys 22:441–450
Porstendörfer J, Wicke A, Schraub A (1978) The influence of exhalation, ventilation and deposition processes upon the concentration of radon, thoron and their decay products. Health Phys 34:465–473
Sreenath Reddy M (2003) Ph.D. thesis submitted to Osmania University, Hyderabad, India
Mayya YS, Eappen KP, Nambi KSV (1998) Methodology for mixed field inhalation dosimetry in monazite areas using a twin-cup dosimeter with three track detectors. Radiat Prot Dosim 77:177–184
Kubozoe T, Watanabe Y, Nakamura K, Kabeyama M, Aihara Y (1988) The vertical distribution of radon 222 in the atmosphere. In: Proceedings of the Seventh International Congress of International Radiation Protection Association, pp 881–884
Katase A, Matsumoto Y, Sakae T, Ishibashi K (1988) Indoor concentrations of Rn-220 and its decay products. Health Phys 54:283–286
Doi M, Fujimoto K, Kobayashi S, Yonehara H (1993) Spatial distribution of thoron and radon concentrations in the indoor air of a traditional Japanese wooden house. Health Phys 66:43–49
Guo Q, Iida T, Okamoto K (1995) Measurements of thoron concentration by passive cup method and its application to dose assessment. J Nucl Sci Tech 32:794–803
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Dr. A. Ramakrishna and Dr. A.R. Sundararajan of Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB), Mumbai, Dr. A.R. Reddy, former Director of D.R.D.O., New Delhi for their continued interest and encouragement. Financial support from AERB in the form of a research project No. AERB/SRP/23/05, dated 05.10.2001 is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, K.V.K., Reddy, M.S., Reddy, C.G. et al. Spatial and vertical distribution of radon and thoron in a typical Indian dwelling. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 292, 1089–1092 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-1655-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-1655-8