Abstract
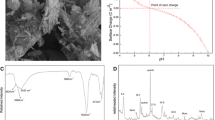
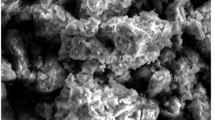
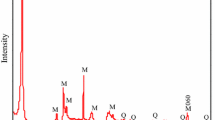
Attapulgite has been applied in the sorption of metal and radionuclide ions since its discovery. Herein, radionuclide Am(III) sorption onto attapulgite was carried out at 25 °C in 0.01 mol/L NaNO3 solutions. Effects of contact time, Am(III) initial concentration, pH, humic acid and temperature on Am(III) sorption onto attapulgite were investigated. The sorption of Am(III) increases with increasing contact time and reaches a maximum value within 24 h at different Am(III) initial concentration. The fast sorption velocity indicates that strong chemical sorption or strong surface complexation contributes to the sorption of Am(III) onto attapulgite under the experimental conditions. The experimental data can be described well by the pseudo-second-order rate model. The sorption of Am(III) onto attapulgite is strongly dependent on pH values and surface complexation is the main sorption mechanism. The presence of HA enhances the sorption of Am(III) onto attapulgite at pH < 8.5, whereas, at pH > 8.5, little effect of HA on Am(III) sorption is observed. The Langmuir, Freundlich and D-R models were used to simulate the sorption data at different pH values and the results indicated that Langmuir model simulates the experimental data better than Freundlich and D-R models. The thermodynamic parameters indicates that the sorption of Am(III) onto attapulgite is an endothermic and spontaneous process. The results suggest that the attapulgite is a suitable material as an adsorbent for preconcentration and immobilization of Am(III) from aqueous solutions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Das DK, Kumar S, Pathak PN, Tomar BS, Manchanda VK (2011) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 289:137–143
Lee MH, Jung EC, Song K, Han YH, Shin HS (2011) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 287:639–645
Dhami PS, Kannan R, Gopalakrishnan V, Ramanujam A, Salvi N, Udupa SR (1998) Biotechnol Lett 20:869–872
Wang XK, Chen CL, Du JZ, Tan XL, Xu D, Yu SM (2005) Environ Sci Technol 39:7084–7088
Wang XK, Chen CL, Hu WP, Ding AP, Xu D, Zhou X (2005) Environ Sci Technol 39:2856–2860
Pathak PN, Choppin GR (2007) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 274:517–523
Tripathi SC, Kannan R, Dhami PS, Naik PW, Munshi SK, Dey PK, Salvi NA, Chattopadhyay S (2011) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 287:691–695
Bradley WF (1940) Am Miner 25:405–410
Cao E, Bryant R, Williams DJA (1998) Colloid Polym Sci 276:842–846
Zhao YJ, Chen Y, Li MS, Zhou SY, Xue AL, Xing WH (2009) J Hazard Mater 171:640–646
Fan QH, Shao DD, Lu Y, Wu WS, Wang XK (2009) Chem Eng J 150:188–195
Chen H, Wang AQ (2009) J Hazard Mater 165:223–231
Huang JH, Wang XG, Jin QZ, Liu YF, Wang Y (2007) J Environ Manag 84:229–236
Huang JH, Liu YF, Wang XG (2008) J Hazard Mater 160:382–387
Fan QH, Shao DD, Hu J, Wu WS, Wang XK (2008) Surf Sci 602:778–785
Huang JH, Liu YF, Jin QZ, Wang XG, Yang J (2007) J Hazard Mater 143:541–548
Tan LQ, Jin YL, Chen J, Wu J, Cheng XC, Feng LD (2011) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 289:601–610
Tan LQ, Jin YL, Cheng XC, Wu J, Zhou W, Feng LD (2011) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 290:575–585
Tan XL, Wang XK, Geckeis H, Rabung T (2008) Environ Sci Technol 42(17):6532–6537
Tan XL, Fang M, Li JX, Lu Y, Wang XK (2009) J Hazard Mater 168:458–465
Fan QH, Shao DD, Lu Y, Wu WS, Wang XK (2009) Chem Eng J 150:188–195
Hu J, Shao DD, Chen CL, Sheng GD, Li JX, Wang XK, Nagatsu M (2010) J Phys Chem B 114:6779–6785
Kara M, Yuzer H, Sabah E, Celik MS (2003) Water Res 37:224–232
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) Process Saf Environ Prot 76:183–191
Hu J, Chen CL, Sheng GD, Li JX, Chen YX, Wang XK (2010) Radiochim Acta 98:421–429
Hu J, Xie Z, He B, Sheng GD, Chen CL, Li JX, Chen YX, Wang XK (2010) Sci China Ser B 53(6):1420–1428
Tan XL, Chen CL, Yu SM, Wang XK (2008) Appl Geochem 23:2767–2777
Mirajkar SP, Rao BS, Eapen MJ, Shiralkar VP (2001) J Phys Chem B 105:4356–4367
Yang ST, Zhao DL, Zhang H, Lu SS, Chen L, Yu XJ (2010) J Hazard Mater 183:632–640
Dubinin MM (1960) Chem Rev 60:235–241
Ozcan A, Oncu EM, Ozcan AS (2006) Colloids Surf A 277:90–97
Zhao GX, Zhang HX, Fan QH, Ren XM, Li JX, Chen YX, Wang XK (2010) J Hazard Mater 173:661–668
Ren XM, Wang SW, Yang ST, Li JX (2010) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 283:253–259
Lu SS, Guo ZQ, Zhang CC, Zhang SW (2011) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 287(2):621–628
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by Environmental research projects in Jiang Su province, Department of Finance (2010330) and Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation (BK2008195).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, W., Liu, X. & Tan, L. Effect of contact time, pH, humic acid and temperature on the sorption of radionuclide Am(III) onto attapulgite. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 292, 1173–1179 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-011-1573-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-011-1573-1