Abstract
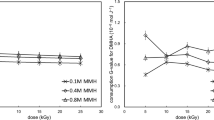
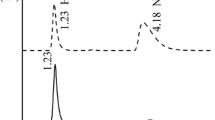
N,N-dimethylhydroxylamine (DMHA) is a novel salt-free reducing reagent used in the separation U from Pu and Np in the reprocessing of power spent fuel. This paper reports on the radiolysis of aqueous DMHA solution and its radiolytic liquid organics. Results show that the main organics in irradiated DMHA solution are N-methyl hydroxylamine, formaldehyde and formic acid. The analysis of DMHA and N-methyl hydroxylamine were performed by gas chromatography, and that of formaldehyde was performed by ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometry. The analysis of formic acid was performed by ion chromatography. For 0.1–0.5 mol L−1 DMHA irradiated to 5–25 kGy, the residual DMHA concentration is (0.07–0.47) mol L−1, the degradation rate of DMHA at 25 kGy is 10.1–30.1%. The concentrations of N-methylhydroxylamine, formaldehyde and formic acid are (8.25–19.36) × 10−3, (4.20–36.36) × 10−3 and (1.35–10.9) × 10−4 mol L−1, respectively. The residual DMHA concentration decreases with the increasing dose. The concentrations of N-methylhydroxylamine and formaldehyde increase with the dose and initial DMHA concentration, and that of formic acid increases with the dose, but the relationship between the concentration of formic acid and initial DMHA concentration is not obvious.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ochsenfeld W, Petrich G (1983) Sep Sci Technol 18:1685–1698
Choppin GR, Morgenstern A (2000) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 243(1):45–51
Choppin GR and Khankhasayev MKh (1999) Chemical separation technologies and related methods of nuclear waste management. Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands, pp 1–16
Koltunov VS, Baranov SM, Zharova TP et al (1993) Radiokhimiya 35:49–53 (in Russian)
Zhang AY, Li K, He H et al (2001) Chin J Appl Chem 18:180–183 (in Chinese)
Koltunov VS (1998) RECOD′98, pp 425–431
Sze YK, Gosselin JA (1983) Nucl Technol 63:431–441
Koltunov VS, Baranov SM, Zharova TP (1993) Radiokhimiya 35:79–84
Zhang AY, Hu JX, Zhang XY (1999) At Energy Sci Technol 33:97–103 (inChinese)
Wang JH, Wan Y, Wu MH et al (2008) Nucl Sci Technol 19(6):343–346
Wang JH, Wang Sh X, Bao BR et al (2008) Nucl Sci Technol 19(2):79–82
Wang JH, Bao BR, Wu MH et al (2004) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 262(2):451–453
Wang JH, Bao BR, Wu MH et al (2006) J Nucl Radiochem 28(4):249–252 (in Chinese)
Wang JH, Bao BR, Wu MH et al (2004) J Nucl Radiochem 26(2):103–107 (in Chinese)
Wang JH, Bao BR, Wu MH et al (2003) J Nucl Radiochem 25(4):244–247 (in Chinese)
Wang JH, Li Ch, Bao BR et al (2009) Radiat Phys chem 78:1145–1147
Wang JH, Wu MH, Bao BR et al (2007) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 273(2):371–373
Wang JH, Li Ch, Wu MH et al (2010) Nucl Sci Technol 21(4):233–236
Barbara BS, Robert AG (1979) J Phys Chem 83(13):1696–1701
Adamic K, Bowman DF, Gillan T et al (1971) J Amer Chem Soc 93(4):902–908
Wu JL, Qi ShCh (1993) Radiation Chemistry. Atomic Energy Publisher, Beijing, pp 183–187 (in Chinese)
Spinks JWT, Woods RJ (1976) An introduction to radiation chemistry 2nd ed a Wiley-Interscience Publication. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 317–321
Olszyna K, Heicklen J (1976) Sci Total Environ 5:223–230
Andrawes FF (1984) J Chromatogr 290:65–74
Guo L, Zhang GX, Mo AP (1990) China Public Sanitation 6(10):452–454 (in Chinese)
Wang XN, Chen GW (1999) Jiangsu Chem Ind 25(8):44–45 (in Chinese)
Wang HM, Chen JY (1997) Synth Chem 5(1):14–16 (in Chinese)
Ding YW, Fan Chzh, Wu Y et al (2002) J Mol Catal 16(3):175–179 (in Chinese)
Xia HB, Cui YQ, Yang PQ et al (1998) Shandong Chem Ind 5:46–47
Li GL, He H, Ch H et al. (2008) Chem Reag 30(7):515–517, 549
Wang JH, Wan Y, WU MH et al (2008) Nucl Sci Technol 19(6):100–103
Zhao XH, Sun JW, Yao L (2004) Anal Detect 5:124–126
Fan YQ, Zhou T, Li YP et al (2005) Mod Prev Med 32(10):1396–1397
Zhang SB, Xin ChB, Wang X (2000) Indu Water Treat 20(10):27–28
Zheng B, Chen WB, Xu XL (2006) J Zhejiang Ocean Univ (Nat Sci) 25(4):355–358
Chen YM (2006) Chin J Health Lab Tech 16(10):1265–1266
Zhao Sh Q, Zhang M, Zhang Gsh (2006) Hebei Chem Eng Ind 29(5):60–61
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to extend warm acknowledgement for the financial assistance of Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20771074, 40973073, 40830744) and Shanghai Leading Academic Disciplines (No. S 30109).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J.H., Li, Q., Wu, M.H. et al. Radiolysis of N,N-dimethylhydroxylamine and its radiolytic liquid organics. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 292, 249–254 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-011-1468-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-011-1468-1