Abstract
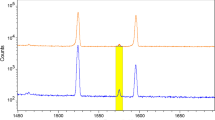
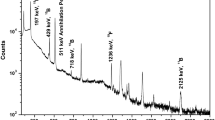
Phosphorus is an essential element for plants and animals, playing a fundamental role in the production of biochemical energy. Despite its relevance, phosphorus is not commonly determined by instrumental neutron activation analysis (INAA), because 32P does not emit gamma-rays in its decay. There are alternative methods for the determination of phosphorus by INAA, such as the use of beta counting or the measurement of bremsstrahlung originated from the high energy beta particle from 32P. Here the determination of phosphorus in plant materials by measuring the bremsstrahlung production was further investigated, to optimize an analytical protocol for minimizing interferences and overcoming the poor specificity. Eight certified reference materials of plant matrices with phosphorus ranging between 171 and 5,180 mg kg−1 were irradiated at a thermal neutron flux of 9.5 × 1012 cm−2 s−1 and measured with a HPGe detector at decay times varying from 7 to 60 days. Phosphorus solutions added to a certified reference material at three levels were used for calibration. Counts accumulated in the baseline at four different regions of the gamma-ray spectra were tested for the determination of phosphorus, with better results for the 100 keV region. The Compton scattering contribution in the selected range was discounted using an experimental peak-to-Compton factor and the net areas of all peaks in the spectra with energies higher than 218 keV, i.e. Compton edge above 100 keV. Amongst the interferences investigated, the production of 32P from sulfur, and the contribution of Compton scattering should be considered for producing good results.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Damsgaard E, Heydorn K (1987) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 113:267–273
Weginwar RG, Samudralwar DL, Garg AN (1989) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 133:317–324
Cunha IIL, Oliveira RM (1996) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 213:185–192
St-Pierre J, Kennedy G (1998) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 234:51–54
Garg AN, Kumar A, Choudhury RP (2007) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 271:481–488
Bajo S, Wyttenbach A (1988) Talanta 35:747–751
Porte N, Mauerhofer E, Denschlag HO (1997) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 220:3–7
Steinnes E (1967) Talanta 14:753–758
França EJ, Fernandes EAN, Bacchi MA (2003) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 257:113–115
Bacchi MA, Fernandes EAN (2003) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 257:577–582
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) for the financial support and to IPEN/CNEN for the irradiation of samples in the nuclear research reactor IEA-R1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsubara, T.C.M., Bacchi, M.A. & De Nadai Fernandes, E.A. Further investigating the determination of phosphorus in plants by INAA using bremsstrahlung measurement. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 291, 201–205 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-011-1282-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-011-1282-9