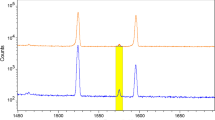
Abstract
Biological materials containing trace amounts of mercury and selenium were examined using neutron activation analysis. They were analyzed using Compton suppression and γ–γ coincidence counting. The 279 keV photopeak of activated mercury (203Hg) was analyzed in order to observe the mercury content in these samples. Selenium, an element found in many biological samples, interferes with the analysis of 203Hg when activated (75Se). Because the selenium interference comes from a cascading emission, Compton suppression was utilized to reduce this interference. In order to fully characterize the selenium content in the samples, γ–γ coincidence was used which reduced the background and eliminated bremsstrahlung interference produced from neutron activated phosphorous through the 31P(n, γ)32P reaction which is a pure beta emitter. As a result, we determined the mercury and selenium concentrations in three standard reference materials, which contain varying ratios of mercury to selenium concentrations. This study also showed that these types of concentrations can be determined from small (<500 mg) sample masses. Further work needs to be done on wet samples that require dehydration, as mercury can be lost through this process.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastos WR, Bernardi JVE, Lacerda LD, Silveira EG, Pfeiffer WC (2006) Sci Total Environ 368:344–351
FDA US Food and Drug Administration (2004) Food and Drug Administration. http://www.fda.gov/food/foodsafety/product-specificinformation/seafood/foodbornepathogenscontaminants/methylmercury/ucm115662.htm. Accessed 01 Mar 2011
Bourdineaud JP, Bellance N, Giovani Benard G et al (2005) Environ Sci Technol 43:2448–2454
Boudou A, Maury-Brachet R, Coquery M, Durrieu G, Cossa D (2005) Environ Sci Technol 39:2448–2454
Serfor-Armah Y, Nyarko BJB, Adote DK, Adomako D, Akaho EHK (2004) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 262:685–690
Pillay KKS, Thomas CC Jr, Sondel JA, Hyche CM (1971) Anal Chem 43:1419–1425
Rook HL, Gills TE, LaFleur PD (1972) Anal Chem 44:1114–1117
Orvini E, Gills TE, LaFleur PD (1974) Anal Chem 46:1294–1297
Spyrou NM, Kerr S (1979) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 48:169–183
Mcdowell LS, Giffen PR, Chatt A (1987) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 110:519–529
Wangen LE, Gladney ES, Hensley WK (1980) Anal Chem 52:765–767
Siddique N, Waheed S, Daud M, Rahman A, Ahmad S (2007) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 274:181–186
Jacimovic R, Horvat M (2004) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 259:385–390
Acknowledgments
This research was performed under the Nuclear Forensics Graduate Fellowship Program, which is sponsored by the US Department of Homeland Security: Domestic Nuclear Detection Office and the US Department of Defense: Defense Threat Reduction Agency. We would like to acknowledge all of the staff members at the Nuclear Engineering Teaching Laboratory for all of their hard work in helping us perform this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horne, S., Landsberger, S. Selenium and mercury determination in biological samples using gamma–gamma coincidence and Compton suppression. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 291, 49–53 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-011-1268-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-011-1268-7