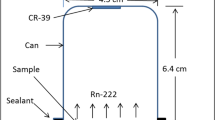
Abstract
Indoor radon and thoron concentrations were dominated with their exhalation rate from building materials. Thus, the evaluation of exhalation rate with highly precise is important. This paper presented a new technique to measure the dependence radon/thoron exhalation rate, from building materials used in Japan, on absolute humidity. The measurement technique consisted of a solid state alpha detector equipped a ventilation-type chamber and humidity control system in a flow through method. The exhalation rate of dried samples (Indian red granite and Japanese gray granite) was measured at various absolute humidity levels in the range of 1–20 g cm−3. It was found that exhalation rate increased exponential with increasing of absolute humidity for both samples. Furthermore, the dependence of radon emanation coefficient on building material’s temperature was also studied using an accumulation chamber equipped with scintillation cell alpha detector. The emanation coefficient of dry sample increased proportionally with increasing the material’s temperature with a correlation factor of 0.88.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
UNSCEAR, Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. Report to the General Assembly with Scientific Annexes, United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, New York, 2000
Yasuoka Y, Ishikawa T, Tokonami S, Takahashi H, Sorimachi A, Shiogi M (2009) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 279:885–891
The World Health Organization, Fact Sheet No.291: Radon and Cancer, June 2005. Available on http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs291/en/index.html access: 8 May 2009
Sasaki T, Gunji Y, Okuda T (2004) J Nucl Sci Technol 41:142–151
Nazaroff WW (1992) Rev Geophys 30:137–160
Hosoda M, Sorimachi A, Yasuoka Y, Ishikawa T, Sahoo S, Furukawa M, Hassan NM, Tokonami S, Uchida S (2009) J Radiat Res 50:333–343
Schery SD, Wilkening MH, Hart KP, Hill SD (1989) J Geophys Res 94:8567–8576
Stranden E, Kolstad AK, Lind B (1984) Health Phys 47:480–485
Markkanen M, Arvela H (1992) Radiat Prot Dosim 45:269–272
Morawska L, Phillips CR (1993) Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57:1783–1797
Iskandar D, Yamazawa H, Iida T (2004) Appl Radiat Isot 60:971–973
Hosoda M, Shimo M, Sugino M, Furukawa M, Fukushi M (2007) J Nucl Sci Technol 44:664–672
Koarashi J, Amano H, Andoh M, Iida T (2000) Radiat Prot Dosim 87:121–131
Kojima H, Nagano K (2005) J Atoms Elect 25:1–9
Hosoda M, Yamamoto Y, Harada K, Kori T, Fukushi M, Shimo M (2007) Jpn J Health Phys 42:89–97
Tuccimei P, Moroni M, Norcia D (2006) Appl Radiat Isot 64:254–263
Osmanlioglo AE (2006) Radiat Prot Dosim 121:325–329
Tokonami S, Yang M, Yonehara H, Yamada Y (2002) Rev Sci Instrum 73:69–72
De Martino S, Sabbarese C, Monetti G (1998) Appl Radiat Isot 49:407–413
Keller G, Schutz M (1988) Radiat Prot Dosim 24:43–46
Hosoda M, Ishikawa T, Sorimachi A, Hassan NM, Tokonami S, Uchida S (2010) J Nucl Sci Technol (in press)
Sorimachi A, Sahoo SK Tokonami S (2009) Rev Sci Instrum 80: 015104-1-4
Hassan NM, Ishikawa T, Hosoda M, Sorimachi A, Tokonami S, Fukushi M, Sahoo SK (2010) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 283:15–21
Faheem M, Matiullah (2008) Radiat Meas 43:1458–1462
Rogers VC, Nielson KK (1991) Health Phys 61:225–230
Cosma C, Dancea F, Jurcut T, Ristoiu D (2001) Appl Radiat Isot 54:467–473
Stranden E, Kolstad AK, Lind B (1984) Radiat Protect Dosim 7:55–58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, N.M., Tokonami, S. & Fukushi, M. A simple technique for studying the dependence of radon and thoron exhalation rate from building materials on absolute humidity. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 287, 185–191 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-010-0665-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-010-0665-7