Abstract
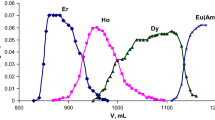
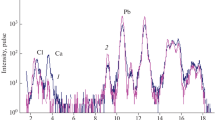
This paper describes the development of a separation method for americium from the effluents emanating from anion exchange column, used for the recovery of plutonium from analytical waste solutions. The waste contained uranium, sodium, calcium and iron as the major impurities as estimated by ICP-AES method. ~99% pure americium was obtained by three separation steps using solvent extraction and extraction chromatography techniques. In the first step, uranium was quantitatively separated by giving five contacts of equal volumes of 30% TBP in n-dodecane. Fe and Na were separated in the next step using 0.1 M TODGA + 0.5 M DHOA as the extractant. In the last step, Am was separated from the co-extracted Ca (about 76%) using CMPO loaded extraction chromatographic column. The overall recovery was >80% with decontamination factor (D.F.) from the impurities being >3000 while the purity of the product was 99%.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seaborg GT, Hobart DE (2001) IANCAS bulletin, chap I, p 3
Katz JJ, Seaborg GT, Morss LR (1986) The chemistry of the actinide elements, vol 1, 2nd edn. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 550–561
Michael KM, Kapoor SC, Mathur JN, Iyer RH (1996) Purification of americium from bulk quantities of plutonium loading effluent using trilaurylamine. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 213:431–439
Muscatello AC, Navratil JD (1988) Americium removal from nitric acid waste streams. J Radioanal Nucl Chem Lett 128:449–462
Mathur JN, Murali MS, Natarajan PR, Badheka LP, Banerji A, Michael KM, Kapoor SC, Dhumwad RK (1992) Tail-end purification of americium from plutonium loading effluents using a mixture of n-octyl (phenyl)-N,N-diisobutyl-carbamoylmethylphosphine oxide and tri-n-butyl phosphate. J Radioanal Nucl Chem Lett 165:219–227
Michel H, Barci-Funel G, Dalmasso J, Ardisson G (1999) One step ion exchange process for the radiochemical separation of americium, plutonium and neptunium in sediments. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 240:467–470
Michel H, Levent D, Barci V, Barci-Funel G, Hurel C (2008) Soil and sediment sample analysis for the sequential determination of natural and anthropogenic radionuclides. Talanta 74:1527–1533
Tavčar P, Jakopič R, Benedik L (2005) Sequential determination of 241Am, 237Np, Pu radioisotopes and 90Sr in soil and sediment samples. Acta Chim Slov 52:60–66
Moreno J, Vajda N, Danesi PR, Larosa JJ, Zeiller E, Sinojmeri M (1997) Combined procedure for the determination of 90Sr, 241Am and Pu radionuclides in soil samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 226:279–284
Wang JJ, Chen IJ, Chiu JH (2004) Sequential isotopic determination of plutonium, thorium, americium, strontium and uranium in environmental and bioassay samples. Appl Radiat Isotop 61:299–305
Lee YK, Bakhtiar SN, Akbarzadeh M, Lee JS (2000) Sequential; isotopic determination of strontium, thorium, plutonium, pranium, and americium in bioassay samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 243:525–533
Ansari SA, Pathak PN, Husain M, Prasad AK, Parmar VS, Manchanda VK (2005) N,N,N′,N′-tetraoctyl diglycolamide (TODGA): a promising extractant for actinide-partitioning from high-level waste (HLW). Solv Extr Ion Exch 23:463–479
Gupta KK, Manchanda VK, Subramanian MS, Singh RK (2000) Solvent extraction studies on U(VI), Pu(IV), and fission products using N,N-dihexyloctanamide. Solv Extr Ion Exch 18:273–286
Schulz WW, Horwitz EP (1988) TRUEX process and the management of liquid TRU waste. Sep Sci Technol 23:1191–1210
Mahajan GR, Prabhu DR, Manchanda VK, Badheka LP (1998) Substituted malonamides as extractants for partitioning of actinides from nuclear waste solutions. Waste Manage 18:125–133
Nair GM, Prabhu DR, Mahajan GR, Shukla JP (1993) Tetra-butyl and tetra-isobutyl malonamides as extractants for U(VI) and Pu(IV). Solv Extr Ion Exch 11:831–847
Mathur JN, Murali MS, Natarajan PR, Badheka LP, Banerji A, Ramanujam A, Dhami PS, Gopalakrishnan V, Dhumwad RK, Rao MK (1993) Partitioning of actinides from high-level waste streams of PUREX process using mixtures of CMPO and TBP in dodecane. Waste Manage 13:317–325
Zhu Z-X, Sasaki Y, Suzuki H, Suzuki S, Kimura T (2004) Cumulative study on solvent extraction of elements by N,N,N′,N′-tetraoctyl-3-oxapentanediamide (TODGA) from nitric acid into n-dodecane. Anal Chim Acta 527:163–168
Cuillerdier C, Musikas C, Hoel P, Nigond L, Vitart X (1991) Malonamides as new extractants for nuclear waste solutions. Separ Sci Technol 26:1229–1244
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sengupta, A., Adya, V.C., Mohapatra, P.K. et al. Separation and purification of americium from analytical waste solutions. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 283, 777–783 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-009-0420-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-009-0420-0