Abstract
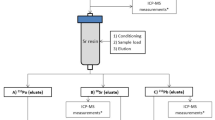
The present procedure for analysing 90Sr combines the use of a non radioactive carrier with high pressure ion chromatography separation, conductivity detection of the carrier and optimized external counting by liquid scintillation. This improvement with respect to traditional methods led to a more rapid and efficient purification stage. The present work proves that activities of 90Sr as low as 3 Bq/L can be measured in highly contaminated pressurized water reactor primary coolant matrix without any observed radiochemical interference. The approach shows promise for the analysis of other emitters of low energy radiation, or isotopes subject to high background or matrix effects in a PWR primary coolant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Tigeras et al., Understanding the radionuclide behaviour in PWR primary coolant: fuel failure detection and characterisation, Intern. Conf. on Water Chemistry of Nuclear Reactor Systems, Korea, 2006.
L. Lazare et al., On the use of alpha liquid scintillation for analysing primary coolant, Intern. Conf. on Water Chemistry of Nuclear Reactor Systems, EPRI, San Francisco, October 2004, p. 2222.
M. F. L’Annunziata, Handbook of Radioactivity Analysis, Academic Press, 1998.
AFNOR Norm NF M 60–316 — Technologie du combustible — Déchets: Détermination du 90Sr dans les effluents et déchets après séparation chimique préalable.
E. R. Tompkins, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 70 (1948) 3520.
U. P. Senaratne, W. A. Jester, C. D. Bleistein, Health Phys., 73 (1997) 601.
J. Cobb, P. Warwick, R. C. Carpenter, R. T. Morrison, Sci. Total Environ., 173–174 (1995) 179.
J. Cobb, P. Warwick, R. C. Carpenter, R. T. Morrison, Analyst, 119 (1994) 1759.
P. Desmartin et al., Environ. Monit. Assess., 44 (1997) 413.
R. A. Fjeld et al., J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 263 (2005) 635.
M. Betti, J. Chromatogr., 789 (1997) 369.
S. Möbius, T. L. Ramamonjisoa, W. Jongisook, R. Andriambolona, Sci. Total Environm., 173/174 (1995) 231.
M. F. L’Annunziata, Kessler , Radiotracer Liquid Scintillation Analysis, in: Handbook of Radioactivity Analysis, M. F. L’Annunziata (Ed.), Academic Press, 1998, p. 234.
ISO Norm 5667-3 June 2004: Water Quality — Sampling — Part 3: Guidance on the Preservation and Handling of Water Samples.
AFNOR Norm XP-T90-210 — Décembre 1999 — Protocole d’évaluation d’une méthode alternative d’analyse physico chimique quantitative par rapport à une méthode de référence.
AFNOR Norm XP-T90-220 — Qualité de l’eau — Protocole d’estimation de l’incertitude de mesure associée à un. résultat d’analyse pour les méthodes physico-chimiques.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lazare, L., Crestey, C. & Bleistein, C. Measurement of 90Sr in primary coolant of pressurized water reactor. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 279, 633–638 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-008-7298-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-008-7298-0