Abstract
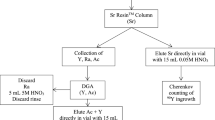
The activity concentrations of the Ra isotopes, 226Ra and 228Ra, as well as of 222Rn were measured in Austrian tap waters. Rn was extracted into a mineral oil cocktail not miscible with water and measured by liquid scintillation counting using pulse-shape analysis for α/β-separation. Ra isotopes were co-precipitated with BaSO4 or concentrated by filtration through an element specific filter. EDTA solution was used to redissolve the precipitate as well as to release the Ra from the filter. After mixing with a cocktail, the EDTA solution was measured by liquid scintillation counting, too. From our results the effective ingestion doses for adults and 3 months old babies were calculated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. T. Hess, J. Michel, T. R. Horton, H. M. Prichard, W. A. Coniglio, Health Phys., 48 (1985) 553.
P. T. King, J. Michael, W. S. Moore, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 46 (1982) 1173.
ICRP 68, Annales of the ICRP 24(4) (1994) 66.
WHO, Health Criteria and Other Supporting Information, Addendum to Vol. 2 in: Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, 2nd ed., World Health Organisation, Geneva, 1998.
US EPA, Proposed Drinking Water Standards, US EPA 65 FR 76707, US Environmental Protection Agency, December 7, 2000.
F. Schönhofer, Radiat. Prot. Dosim., 45 (1992) 123.
P. Vesterbacka, I. Mäkeläinen, H. Arvela, Radiat. Prot. Dosim., 113 (2005) 223.
G. Manjon, I. Vioque, H. Moreno, R. Garcia-Tenorio, M. Garcia-Leon, Appl. Radiation Isotopes. 48 (1997) 535.
A. S. Goldin, Anal. Chem., 33 (1961) 406.
G. Wallner, in: Intern. Conf. on Advances in Liquid Scintillation Spectrometry 2001, Karlsruhe, Germany, S. Möbius, J. E. Noakes, F. Schönhofer (Eds), Radiocarbon, Tucson USA, 2002, p. 269.
F. Schönhofer, G. Wallner, Radioact. Radiochem., 12 (2001) 33.
C. Katzlberger, G. Wallner, K. Irlweck, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 249 (2001) 191.
L. A. Currie, Anal. Chem., 40 (1968) 586.
UNSCEAR, 1993 Report: Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation, United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, New York, 1993.
Risk Assessment of Radon in Drinking Water, Committee on Risk Assessment of Exposure to Radon in Drinking Water, Board on Radiation Effects Research, Commission of Life Sciences, NRC (National Research Council). National Academic Press, Washington DC, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wallner, G., Steininger, G. Radium isotopes and 222Rn in Austrian drinking waters. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 274, 511–516 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-006-6939-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-006-6939-4