Summary
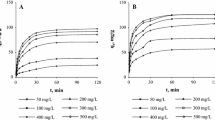
Studies on adsorption behavior of heavy radionuclides, present altogether in no-carrier-added state, e.g., 197-200Pb, 197-200Tl and 197Hg, have been carried out with calcium alginate beads. High lead (100%) and moderate thallium removal (~65%) was achieved in pH range 2-7. 100% mercury removal was also achieved at pH 2 and 4. Effort has been made to recover all three radionuclides adsorbed in the calcium alginate beads using various chemicals, such as HCl, thiourea, sodium acetate, sodium oxalate and sodium nitrite. It was found that 0.1M HCl and 0.1M thiourea could remove at pH 1 80-90% of adsorbed Pb. Tl recovery was possible by all chemicals mentioned above. Hg was also recovered by all chemicals except HCl.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nayak, D., Lahiri, S. Biosorption of toxic, heavy, no-carrier-added radionuclides by calcium alginate beads. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 267, 59–65 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-006-0009-9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-006-0009-9