Summary
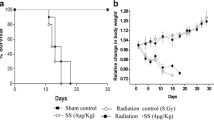
The aim of this study was to evaluate the potential radio-protective effects of different selenium supplement concentrations of 4, 8, 15 and 30 ppm in rats. Four groups of rats were administered different concentrations of selenium in drinking water for 30 days before irradiation starting from the ablactation which considered as day 0. The results showed that the sodium selenite of 4 ppm and 8 ppm enhance the 30-day survival of irradiated rats at 7 Gy (60Co source, whole body irradiation dose rate of 1 Gy . min-1) compared to the control group. The mean cumulated probability of survival of rats was 69%±6 (mean±S.E.) and 77%±6 in 4 and 8 ppm groups, respectively, versus 42%±9 for control group (P>0.001). Our data also indicated that sodium selenite with concentrations of 15 and 30 ppm had no significant reduction in mortality. The mean cumulated probability of survival of rats was 50%±12 (P=0.39) and 49%±14 (P=0.04), respectively. The toxic effects of selenium were observed at 15 ppm and 30 ppm, survivals after 30 days of selenium intake were 76% and 46%, respectively. We conclude that 4 and 8 ppm sodium selenite have a radio-protective effect. 15 and 30 ppm sodium selenite had no radio-protective effects in rats, this may be due to a synergism of toxicity and radiation effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakir, M., Alya, G., Mohammad, A. et al. Radio-protective effects of selenium in rats. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 266, 165–170 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0888-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0888-1