Abstract
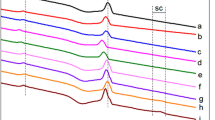
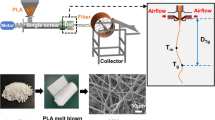
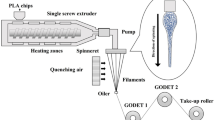
Biodegradable poly-lactic acid (PLA) with varying molecular weights of melt-blown nonwovens was successfully prepared through the method of melt spinning. The phase morphology, rheological behavior, hydrophobicity, and crystalline characteristics of the melt-blown nonwovens have been investigated. The thermal and crystallization behavior revealed that PLA samples with low molecular weights, resulted in a higher degree of crystallinity, meanwhile, the polarized optical microscopy (POM) analysis demonstrates that the large spherical crystal size was obtained with low molecular weights within the same crystallization time. For another, the storage modulus (G′), loss modulus (G′′), and complex viscosity |η*| were increased with the increase in molecular weight from rheological measurement. The morphologies of fiber were observed by SEM, the average diameter increased from 11.86 to 21.07 μm. Furthermore, the water contact angle (WCA) of nonwoven decreased from 128.9° to 114.9° due to an increase in viscosity led to an increase in the distribution of fiber diameters.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Zhu F, Su J, Wang M, Hussain M, Yu B, Han J (2018) Study on dual-monomer melt-grafted poly(lactic acid) compatibilized poly(lactic acid)/polyamide 11 blends and toughened melt-blown nonwovens. J Ind Text 49(6):748–772. https://doi.org/10.1177/1528083718795913
Sun H, Zhang H, Zhen Q, Wang S, Hu J, Cui J, Qian X (2022) Large-scale preparation of polylactic acid/polyethylene glycol micro/nanofiber fabrics with aligned fibers via a post-drafting melt blown process. J Polym Res 29 (8). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03184-2
Liu G, Guan J, Wang X, Yu J, Ding B (2023) Polylactic acid (pla) melt-blown nonwovens with superior mechanical properties. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 11(10):4279–4288. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.3c00159
Sun C, Chen X, Zheng D, Yao W, Tan H, Zhang Y, Liu S (2021) Exploring the synergetic effects of the major components of biomass additives in the pyrolysis of polylactic acid. Green Chem 23(22):9014–9023. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1gc03002g
Yang Y, Zhang M, Ju Z, Tam P, Hua T, Younas M, Kamrul H, Hu H (2020) Poly(lactic acid) fibers, yarns and fabrics: Manufacturing, properties and applications. Text Res J 91(13–14):1641–1669. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517520984101
Makowski T, Svyntkivska M, Piorkowska E, Kregiel D (2020) Multifunctional polylactide nonwovens with 3D network of multiwall carbon nanotubes. Appl Surf Sci 527:143898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146898
Zhu F, Su J, Zhao Y, Hussain M, Yasin S, Yu B, Han J (2019) Influence of halloysite nanotubes on poly(lactic acid) melt-blown nonwovens compatibilized by dual-monomer melt-grafted poly(lactic acid). Text Res J 89(19–20):4173–4185. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517519826926
Zeng Q, Ma P, Su X, Lai D, Lai X, Zeng X, Li H (2020) Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic and magnetic poly(lactic acid) nonwoven fabric for oil–water separation. Ind Eng Chem Res 59(19):9127–9135. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c01033
Srithep Y, Veang-in O, Pholharn D, Turng L, Morris J (2021) Improving polylactide toughness by plasticizing with low molecular weight polylactide-poly(butylene succinate) copolymer. J Renew Mater 9(7):1267–1281. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2021.015604
Zirak N, Shirinbayan M, Farzaneh S, Tcharkhtchi A (2022) Effect of molecular weight on crystallization behavior of poly (lactic acid) under isotherm and non-isotherm conditions. Polym Adv Tech 33(4):1307–1316. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5603
Kawahara Y, Takarada W, Yamamoto M, Kondo Y, Tashiro K, Kikutani T (2020) fiber structure, tensile behavior and antibacterial activity of polylactide/poly(butylene terephthalate) bicomponent fibers produced by high-speed melt-spinning. J Macromol Sci B 59(7):440–456. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2020.1741880
Maleki H, Barani H (2020) Stereocomplex electrospun fibers from high molecular weight of poly(L-lactic acid) and poly(D-lactic acid). J Polym Eng 40(2):136–142. https://doi.org/10.1515/polyeng-2019-0026
Jalali A, Romero-Diez S, Nofar M, Park C (2021) Entirely environment-friendly polylactide composites with outstanding heat resistance and superior mechanical performance fabricated by spunbond technology: Exploring the role of nanofibrillated stereocomplex polylactide crystals. Int J Biol Macromol 193:2210–2220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.11.052
Li X, Gong S, Yang L, Zhang F, Xie L, Luo Z, Xia X, Wang J (2020) Study on the degradation behavior and mechanism of Poly(lactic acid) modification by ferric chloride. Polymer 188:121911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2019.121991
Díaz M, Barbosa S, Capiati N (2009) Effect of styrene addition on polystyrene molecular degradation by Lewis acids. J App Polym Sci 114(5):3081–3086. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.30797
Frolova S, Demin V (2011) Degradation of wood cellulose with Lewis acids with the aim to prepare powder cellulose. Russ J App Chem 81(1):148–152. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1070427208010321
Jia S, Zhao L, Wang X, Chen Y, Pan H, Han L, Zhang H, Dong L, Zhang H (2022) Poly (lactic acid) blends with excellent low temperature toughness: A comparative study on poly (lactic acid) blends with different toughening agents. Int J Biol Macromol 201:662–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.126
Nijenhuis A, Colstee E, Grijpma D, Pennings A (1996) High molecular weight poly(l-lactide) and poly(ethylene oxide) blends: thermal characterization and physical properties. Polymer 37(26):5849–5857. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(96)00455-7
Bai D, Diao X, Ju Y, Liu H, Bai H, Zhang Q, Fu Q (2018) Low-temperature sintering of stereocomplex-type polylactide nascent powder: The role of optical purity in directing the chain interdiffusion and cocrystallization across the particle interfaces. Polymer 150:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2018.07.028
Urayama H, Moon S, Kimura Y (2003) Microstructure and Thermal Properties of Polylactides with Different L- and D-Unit Sequences: Importance of the Helical Nature of the L-Sequenced Segments. Macromol Mater Eng 288(2):137–143. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.200390006
Shao J, Liu Y, Sheng X, Bian X, Sun J, Li G, Chen X, Huo H (2015) The stereocomplex formation and phase separation of PLLA/PDLA blends with different optical purities and molecular weights. Chinese J Polymer Sci 33(12):1713–1720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-015-1715-y
Molinaro S, Cruz Romero M, Boaro M, Sensidoni A, Lagazio C, Morris M, Kerry J (2013) Effect of nanoclay-type and PLA optical purity on the characteristics of PLA-based nanocomposite films. J Food Eng 117(1):113–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.01.021
Sema S, Arslan D, Vatansever E, Kahraman Y, Durmus A, Salehiyan R, Nofar M (2022) Effect of mixing strategy on the structure-properties of the PLA/PBAT blends Incorporated with CNC. J Renew Mater 10(1):149–164. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.017003
Tsuji H (2005) Poly(lactide) stereocomplexes: formation, structure, properties, degradation, and applications. Macromol Biosci 5(7):569–597. https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.200500062
Tsuji H (2016) Poly(lactic acid) stereocomplexes: A decade of progress. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 107:97–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2016.04.017
Jalali A, Shahbikian S, Huneault M (2017) Elkoun S (2017) Effect of molecular weight on the shear-induced crystallization of poly(lactic acid). Polymer 112:393–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2017.02.017
Ai X, Wang D, Li X, Pan H, Kong J, Yang H, Zhang H, Dong L (2018) The properties of chemical cross-linked poly(lactic acid) by bis(tert-butyl dioxy isopropyl) benzene. Polym Bull 76(2):575–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2351-9
Ai X, Li X, Yu Y, Pan H, Yang J, Wang D, Yang H, Zhang H, Dong L (2019) the mechanical, thermal, rheological and morphological properties of PLA/PBAT blown films by using bis(tert-butyl dioxy isopropyl) benzene as crosslinking agent. Polym Eng Sci 59(S1):E227–E236. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.24927
Al-Itry R, Lamnawar K, Maazouz A (2012) Improvement of thermal stability, rheological and mechanical properties of PLA, PBAT and their blends by reactive extrusion with functionalized epoxy. Polym Degrad Stabil 97(10):1898–1914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.06.028
Tan D, Zhou C, Ellison C, Kumar S, Macosko C, Bates F (2010) Meltblown fibers: Influence of viscosity and elasticity on diameter distribution. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 165(15–16):892–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2010.04.012
Sun H, Peng S, Wang M, Zhu F, Bhat G, Yu B (2020) Preparation and Characterization of magnetic PLA/Fe3O4-g-PLLA composite melt blown nonwoven fabric for air filtration. J Eng Fibers Fabr 15. https://doi.org/10.1177/1558925020968222
Li H, Zhang H, Hu J, Wang G, Cui J, Zhang Y, Zhen Q (2022) Facile preparation of hydrophobic PLA/PBE micro-anofiber fabrics via the melt-blown process for high-efficacy oil/water separation. Polymers (Basel) 14 (9). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091667
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the fund of the Chinese Science Academy (Changchun Branch) (No. 2022SYHZ0033, 2023SYHZ0035), Science and Technology Bureau of Jilin Province of China (No. 20220203019SF), and Development and Reform Commission of Jilin Province of China (No. 2022C039-3).
Funding
Science and Technology Bureau of Jilin Province of China, No. 20220203019SF, Junjia Bian, Development and Reform Commission of Jilin Province of China, No. 2022C039-3, Junjia Bian, Chinese Science Academy (Changchun Branch), No. 2022SYHZ0033, Junjia Bian, No.2023SYHZ0035, Hongwei Pan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
He authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Tian, H., Wang, Z. et al. Effect of molecular weight on the properties and structure of biodegradable poly-lactic acid melt-blown nonwovens. J Polym Res 31, 77 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-024-03927-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-024-03927-3