Abstract
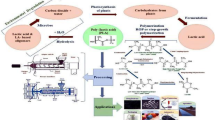
In this work, the effect of D‑Sorbitol (DS) on the crystallization and processibility of PLA was systematically explored by means of DSC, FTIR, POM, WAXD, and as well as dynamic rheological analysis. Our results show that, as expected, DS can act as an effective nucleating agent for PLA and thus strikingly improve its crystallization properties. With 0.25–0.75% DS in blends, the cold crystallization of PLA disappears accompanied by a concomitant elevation of crystallization temperature. Based on analyzing isothermal crystallization kinetics, it is clear that the incorporation of DS can significantly enhance the crystallization rate of all PLA samples. For instance, the semi-crystallization time of neat PLA is 14.2 min at 110 °C, while PLA/0.75% DS blend takes only 1.5 min. A rheological characterization demonstrated that, besides playing a role as a nucleating agent, DS also serves as a plasticizer which improves the melt processing performance as reducing the modulus and viscosity of PLA matrix. On the basis of FTIR data, we propose that hydrogen bonding interactions between PLA and DS are responsible for hampering a further improvement of both crystallization properties and rheological performance over adding a high content of DS.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Abi-Akl R, Ledieu E, Enke TN, Cordero OX, Cohen T (2019) Physics-based prediction of biopolymer degradation. Soft Matter 15:4098–4108
Ravikumar K, Kumaran V, Basu B (2019) Biophysical implications of Maxwell stress in electric field stimulated cellular microenvironment on biomaterial substrates. Biomaterials 209:54–66
Zumstein MT, Schintlmeister A, Nelson TF, Baumgartner R, Woebken D, Wagner M, Kohler H-PE, McNeill K, Sander M (2018) Biodegradation of synthetic polymers in soils: tracking carbon into CO2 and microbial biomass. Sci Adv 4:1–8
Jalali Dil E, Arjmand M, Otero Navas I, Sundararaj U, Favis BD (2020) Interface bridging of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in polylactic acid/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate): morphology, rheology, and electrical conductivity. Macromolecules 53:10267–10277
Ma M, Zheng H, Chen S, Wu B, He H, Chen L, Wang X (2016) Super-toughened poly(l-lactic acid) fabricated via reactive blending and interfacial compatibilization. Polym Int 65:1187–1194
Urquijo J, Aranburu N, Dagréou S, Guerrica-Echevarría G, Eguiazábal JI (2017) CNT-induced morphology and its effect on properties in PLA/PBAT-based nanocomposites. Eur Polymer J 93:545–555
Han J, Branford-White CJ, Zhu LM (2010) Preparation of poly(ε-caprolactone)/poly(trimethylene carbonate) blend nanofibers by electrospinning. Carbohydr Polym 79:214–218
Li Y, Han C, Zhang X, Bian J, Han L (2013) Rheology, mechanical properties, and biodegradation of poly(ε-caprolactone)/silica nanocomposites. Polym Compos 34:1620–1628
Wahit MU, Akos NI, Laftah WA (2012) Influence of natural fibers on the mechanical properties and biodegradation of poly(lactic acid) and poly(ε-caprolactone) composites: a review. Polym Compos 33:1045–1053
Anjum A, Zuber M, Zia KM, Noreen A, Anjum MN, Tabasum S (2016) Microbial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and its copolymers: a review of recent advancements. Int J Biol Macromol 89:161–174
Sabapathy PC, Devaraj S, Meixner K, Anburajan P, Kathirvel P, Ravikumar Y, Zabed HM, Qi X (2020) Recent developments in polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) production - A review. Bioresour Technol 306:123–132
Zuo H, Liu J, Huang D, Bai Y, Cui L, Pan L, Zhang K, Wang H (2021) Sustainable and high-performance ternary blends from polylactide,CO2‐based polyester and microbial polyesters with different chemical structure. J Polym Sci 59:1578–1595
Farah S, Anderson DG, Langer R (2016) Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications - a comprehensive review. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 107:367–392
Li X, Wang Y, Wang Z, Qi Y, Li L, Zhang P, Chen X, Huang Y (2018) Composite PLA/PEG/nHA/dexamethasone scaffold prepared by 3D printing for bone regeneration. Macromol Biosci 18:1800068
Avinc O, Khoddami A (2009) Overview of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) Fibre: part I: production, properties, performance, environmental impact, and end-use applications of poly(lactic acid) fibres. Fibre Chem 41(311):391–401
Galiano F, Briceño K, Marino T, Molino A, Christensen KV, Figoli A (2018) Advances in biopolymer-based membrane preparation and applications. J Membr Sci 564:562–586
Lim LT, Auras R, Rubino M (2008) Processing technologies for poly(lactic acid). Prog Polym Sci 33:820–852
Xie K, Shen J, Ye L, Liu Z, Li Y (2019) Increased gt conformer contents of PLLA molecular chains induced by Li-TFSI in melt: another route to promote PLLA crystallization. Macromolecules 52:7065–7072
Aliotta L, Canesi I, Lazzeri A (2021) Study on the preferential distribution of acetyl tributyl citrate in poly(lactic) acid-poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blends. Polym Test 98:107163
Ding Y, Lu B, Wang P, Wang G, Ji J (2018) PLA-PBAT-PLA tri-block copolymers: effective compatibilizers for promotion of the mechanical and rheological properties of PLA/PBAT blends. Polym Degrad Stab 147:41–48
Han Y, Shi J, Mao L, Wang Z, Zhang L (2020) Improvement of compatibility and mechanical performances of PLA/PBAT composites with epoxidized soybean oil as compatibilizer. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:21779–21790
Kilic NT, Can BN, Kodal M, Ozkoc G (2019) Compatibilization of PLA/PBAT blends by using Epoxy-POSS. J Appl Polym Sci 136:47217
Li P, Zhu X, Kong M, Lv Y, Huang Y, Yang Q, Li G (2021) Fully biodegradable polylactide foams with ultrahigh expansion ratio and heat resistance for green packaging. Int J Biol Macromol 183:222–234
Malayarom P, Somboonphong N, Pattamaprom C (2021) Simultaneous improvement of impact strength and thermal resistance of PLA/PDLA stereocomplex with core-shell rubber blends. Int J Polym Anal Charact 26:277–289
Shazleen SS, Yasim-Anuar TAT, Ibrahim NA, Hassan MA, Ariffin H (2021) Functionality of cellulose nanofiber as bio-based nucleating agent and nano-reinforcement material to enhance crystallization and mechanical properties of polylactic acid nanocomposite. Polymers 13:389–408
Buzarovska A, Bogoeva-Gaceva G, Fajgar R (2016) Effect of the talc filler on structural, water vapor barrier and mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid) composites. J Polym Eng 36:181–188
Shakoor A, Thomas NL (2014) Talc as a nucleating agent and reinforcing filler in poly(lactic acid) composites. Polym Eng Sci 54:64–70
Barrau S, Vanmansart C, Moreau M, Addad A, Stoclet G, Lefebvre JM, Seguela R (2011) Crystallization behavior of carbon nanotube – Polylactide nanocomposites. Macromolecules 44:6496–6502
Magiera A, Markowski J, Pilch J, Blazewicz S (2018) Degradation behavior of electrospun PLA and PLA/CNT nanofibres in aqueous environment. J Nanomater 2018:1–15
Tsuji H, Kawashima Y, Takikawa H, Tanaka S (2007) Poly(l-lactide)/nano-structured carbon composites: Conductivity, thermal properties, crystallization, and biodegradation. Polymer 48:4213–4225
Piekarska K, Piorkowska E, Bojda J (2017) The influence of matrix crystallinity, filler grain size and modification on properties of PLA/calcium carbonate composites. Polym Test 62:203–209
Picard E, Espuche E, Fulchiron R (2011) Effect of an organo-modified montmorillonite on PLA crystallization and gas barrier properties. Appl Clay Sci 53:58–65
Tsuji H, Takai H, Fukuda N, Takikawa H (2006) Non-isothermal crystallization behavior of poly(L-lactic acid) in the presence of various additives. Macromol Mater Eng 291:325–335
Bai H, Huang C, Xiu H, Zhang Q, Fu Q (2014) Enhancing mechanical performance of polylactide by tailoring crystal morphology and lamellae orientation with the aid of nucleating agent. Polymer 55:6924–6934
Bai H, Zhang W, Deng H, Zhang Q, Fu Q (2011) Control of crystal morphology in poly(l-lactide) by adding nucleating agent. Macromolecules 44:1233–1237
Harris AM, Lee EC (2008) Improving mechanical performance of injection molded PLA by controlling crystallinity. J Appl Polym Sci 107:2246–2255
Nakajima H, Takahashi M, Kimura Y (2010) Induced crystallization of PLLA in the Presence of 1,3,5-Benzenetricarboxylamide derivatives as nucleators: preparation of haze-free crystalline PLLA materials. Macromol Mater Eng 295:460–468
He D, Wang Y, Shao C, Zheng G, Li Q, Shen C (2013) Effect of phthalimide as an efficient nucleating agent on the crystallization kinetics of poly(lactic acid). Polym Test 32:1088–1093
Han Q, Wang Y, Shao C, Zheng G, Li Q, Shen C (2013) Nonisothermal crystallization kinetics of biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/zinc phenylphosphonate composites. J Compos Mater 48:2737–2746
Wang S, Han C, Bian J, Han L, Wang X, Dong L (2011) Morphology, crystallization and enzymatic hydrolysis of poly(L-lactide) nucleated using layered metal phosphonates. Polym Int 60:284–295
Yang T-C, Hung K-C, Wu T-L, Wu T-M, Wu J-H (2015) A comparison of annealing process and nucleating agent (zinc phenylphosphonate) on the crystallization, viscoelasticity, and creep behavior of compression-molded poly(lactic acid) blends. Polym Degrad Stab 121:230–237
Kawamoto N, Sakai A, Horikoshi T, Urushihara T, Tobita E (2007) Nucleating agent for poly(L-lactic acid)—An optimization of chemical structure of hydrazide compound for advanced nucleation ability. J Appl Polym Sci 103:198–203
Xu T, Zhang A, Zhao Y, Han Z, Xue L (2015) Crystallization kinetics and morphology of biodegradable poly(lactic acid) with a hydrazide nucleating agent. Polym Test 45:101–106
Dell’Erba R, Groeninckx G, Maglio G, Malinconico M, Migliozzi A (2001) Immiscible polymer blends of semicrystalline biocompatible components: thermal properties and phase morphology analysis of PLLA/PCL blends. Polymer 42:7831–7840
Kim JK, Park D-J, Lee M-S, Ihn KJ (2001) Synthesis and crystallization behavior of poly(l-lactide)-block-poly(e-caprolactone) copolymer. Polymer 42:7429–7441
Liu W, Chen P, Wang X, Wang F, Wu Y (2017) Effects of poly(butyleneadipatecoterephthalateas a macromolecular. Cell Polym 36:75–96
Feng L, Bian X, Li G, Chen X (2021) Thermal properties and structural evolution of poly(l-lactide)/poly(d-lactide) blends. Macromolecules 54:10163–10176
Shao J, Xiang S, Bian X, Sun J, Li G, Chen X (2015) Remarkable melting behavior of PLA stereocomplex in linear PLLA/PDLA blends. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:2246–2253
Narita J, Katagiri M, Tsuji H (2011) Highly enhanced nucleating effect of melt-recrystallized stereocomplex crystallites on poly(L-lactic acid) crystallization. Macromol Mater Eng 296:887–893
Yamane H, Sasai K (2003) Effect of the addition of poly(d-lactic acid) on the thermal property of poly(l-lactic acid). Polymer 44:2569–2575
Tsuji H, Sawada M, Bouapao L (2009) Biodegradable polyesters as crystallization-accelerating agents of poly(l-lactide). ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1:1719–1730
Ohkoshi I, Abe H, Doi Y (2000) Miscibility and solid-state structures for blends of poly[(S)-lactide] with atactic poly[(R,S)-3-hydroxybutyrate]. Polymer 41:5985–5992
Shi H, Chen X, Chen W, Pang S, Pan L, Xu N, Li T (2017) Crystallization behavior, heat resistance, and mechanical performances of PLLA/myo-inositol blends. J Appl Polym Sci 134:44732
Tachibana Y, Maeda T, Ito O, Maeda Y, Kunioka M (2010) Biobased myo-inositol as nucleator and stabilizer for poly(lactic acid). Polym Degrad Stab 95:1321–1329
Kang KS, Lee SI, Lee TJ, Narayan R, Shin BY (2008) Effect of biobased and biodegradable nucleating agent on the isothermal crystallization of poly(lactic acid). Korean J Chem Eng 25:599–608
Kulkarni A, Narayan R (2021) Effects of modified thermoplastic starch on crystallization kinetics and barrier properties of PLA. Polymers 13:4125
dos Santos FA, Iulianelli GCV, Tavares MIB (2017) Effect of microcrystalline and nanocrystals cellulose fillers in materials based on PLA matrix. Polym Test 61:280–288
Kamal MR, Khoshkava V (2015) Effect of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) on rheological and mechanical properties and crystallization behavior of PLA/CNC nanocomposites. Carbohydr Polym 123:105–114
Ozdemir B, Nofar M (2021) Effect of solvent type on the dispersion quality of spray-and freeze-dried CNCs in PLA through rheological analysis. Carbohydr Polym 268:118243
Zhang X, Yang B, Fan B, Sun H, Zhang H (2021) Enhanced nonisothermal crystallization and heat resistance of poly(l-lactic acid) by d-Sorbitol as a homogeneous nucleating agent. ACS Macro Lett 10:154–160
Fischer EW, Sterzel HJ, Wegner G (1973) Investigation of the structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemical reactions. Kolloid Z Z Polym 251:980–990
Lu X, Tang L, Wang L, Zhao J, Li D, Wu Z, Xiao P (2016) Morphology and properties of bio-based poly (lactic acid)/high-density polyethylene blends and their glass fiber reinforced composites. Polym Test 54:90–97
Lin Y, Zhang K, Dong Z, Dong L, Li Y (2007) Study of hydrogen-bonded blend of polylactide with biodegradable hyperbranched poly(ester amide). Macromolecules 40:6257–6267
Sun J, Huang Y, Jin Y, Tian H, Men S (2022) Improvement of mechanical properties and heat distortion temperature of polylactic acid by highly aromatic hyperbranched polyamide. J Appl Polym Sci 139:e52738
Zhang J, Duan Y, Sato H, Tsuji H, Noda I, Yan S, Ozaki Y (2005) Crystal modifications and thermal behavior of poly(L-lactic acid) revealed by infrared spectroscopy. Macromolecules 38:8012–8021
Avrami M (1940) Kinetics of phase change. II transformation-time relations for random distribution of nuclei. J Chem Phys 8:212–224
Hoffman JD (1982) Regime III crystallization in melt-crystallized polymers: the variable cluster model of chain folding. Polymer 24:3–26
Lauritzen JI, Hoffman JD (1973) Extension of theory of growth of chain-folded polymer crystals to large undercoolings. J Appl Phys 44:4340–4352
Miyata T, Masuko T (1998) Crystallization behaviour of poly(tetramethylene succinate). Polymer 39:1399–1404
Hoffman JD, Weeks JJ (1962) Melting process and the equilibrium melting temperature of polychlorotrifluoroethylene. J Res Natl Bureau Stand Sect Phys Chem 66A 1:13–28
Wu D, Wu L, Wu L, Xu B, Zhang Y, Zhang M (2007) Nonisothermal cold crystallization behavior and kinetics of polylactide/clay nanocomposites. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys 45:1100–1113
Vasanthakumari R, Pennings AJ (1983) Crystallization kinetics of poly(L-lactic acid). Polymer 24:175–178
Tábi T, Hajba S, Kovács JG (2016) Effect of crystalline forms (α′ and α) of poly(lactic acid) on its mechanical, thermo-mechanical, heat deflection temperature and creep properties. Eur Polymer J 82:232–243
Kawai T, Rahman N, Matsuba G (2007) Crystallization and melting behavior of poly (L-lactic acid). Macromolecules 40:9463–9469
Tábi T (2019) The application of the synergistic effect between the crystal structure of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and the presence of ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA) to produce highly ductile PLA/EVA blends. J Therm Anal Calorim 138:1287–1297
Acknowledgements
The work is funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 21674055). The authors X. Wang and J. Zhao also acknowledge the financial support provided by Open Research Fund (Nos. K2022-39 and K2022-25) of State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers (Fudan University).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Hu, J., Zhang, Y. et al. A dual role of D-Sorbitol in crystallizing and processing poly (lactic acid). J Polym Res 30, 102 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-023-03480-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-023-03480-5