Abstract
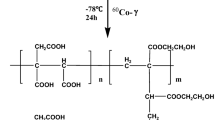
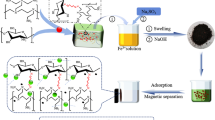
A series of novel polyethylenimine (PEI)-modified magnetic hydrogel nanocomposites (PEI-mHNs) for heavy metal ions removal were prepared by copolymerization of acrylamide, acrylic acid and PEI-modified magnetic nanoparticles using polyethylene glycol diacrylate as chemical crosslinker and PEI-modified magnetic nanoparticles as physical crosslinker. FTIR and XRD results preliminarily confirmed the target structure of PEI-mHNs without destroying the structure of magnetic nanoparticles during modification and radical copolymerization. PEI-mHNs have rough and uneven surface with many porous and gap structure, which makes the rapid adsorption rate and high adsorption capacity of heavy metal ions(Cu(II) (150 mg/g), Cd(II) (236.7 mg/g) and Pb(II) (371.4 mg/g). The adsorption capacity of PEI-mHNs could be improved by increasing the pH of the original solution and initial concentration of heavy metal ions. Heavy metal ions adsorption isotherms and kinetics conformed to the Langmuir model and pseudo-second-order kinetic model, respectively. Besides, PEI-mHNs had good magnetic responsiveness, desorption and reusability which made them potential materials to remove heavy metal ions from the aqueous solution.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Dahaghin Z, Mousavi HZ, Sajjadi SM (2017) A novel magnetic ion imprinted polymer as a selective magnetic solid phase for separation of trace lead (II) ions from agricultural products, and optimization using a Box-Behnken design. Food Chem 237:275–281
He Y, Liu Q, Hu J, Zhao C, Peng C, Yang Q, Wang H, Liu H (2017) Efficient removal of Pb (II) by amine functionalized porous organic polymer through post-synthetic modification. Sep Purif Technol 180:142–148
Liu J, Hu C, Huang Q (2019) Adsorption of Cu2+, Pb2+, and Cd2+ onto oil tea shell from water. Bioresour Technol 271:487–491
Jiang WY, Xing YH, Zhang LY, Guo XM, Lu YW, Yang M, Wang J, Wei GT (2021) Polyethylenimine-modified sugarcane bagasse cellulose as an effective adsorbent for removing Cu(II) from aqueous solution. J Appl Polym Sci 138:49830
Tang H, Zhou WJ, Lu A, Zhang LN (2014) Characterization of new sorbent constructed from Fe3O4/chitin magnetic beads for the dynamic adsorption of Cd2+ ions. J Mater Sci 49:123–133
Gurer-Orhan H, Sabir HU, Ozgunes H (2004) Correlation between clinical indicators of lead poisoning and oxidative stress parameters in controls and lead-exposed workers. Toxicology 195:147–154
Pourjavadi A, Abedin M, Hossein ASH (2016) Synthesis of poly(amidoamine)-graft-poly(methyl acrylate) magnetic nanocomposite for removal of lead contaminant from aqueous media. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:2437–2448
Anantha RK, Kota S (2016) Removal of lead by adsorption with the renewable biopolymer composite of feather (Dromaius novaehollandiae) and chitosan (Agaricus bisporus). Environ Technol Innov 6:11–26
Rajeshkumar S, Liu Y, Zhang X, Ravikumar B, Bai G, Li X (2018) Studies on seasonal pollution of heavy metals in water, sediment, fish and oyster from the Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake in China. Chemosphere 191:626–638
Mishra A, Nath A, Pande PP, Shankar R (2021) Treatment of gray wastewater and heavy metal removal from aqueous medium using hydrogels based on novel crosslinkers. J Appl Polym Sci 138:50242
Castro L, Blazquez LM, Gonzalez F, Munoz JA, Ballester A (2018) Heavy metal adsorption using biogenic iron compounds. Hydrometallurgy 179:44–51
Saravannan A, Kumar PS, Renita AA (2018) Hybrid synthesis of novel material through acid modification followed ultrasonication to improve adsorption capacity for zinc removal. J Clean Prod 172:92–105
Semerjian L (2018) Removal of heavy metals (Cu, Pb) from aqueous solutions using pine (Pinus halepensis) sawdust: equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Environ Technol Innov 12:91–103
Cegłowski M, Gierczyk B, Frankowski M, Popenda L (2018) A new low-cost polymeric adsorbents with polyamine chelating groups for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from water solutions. React Funct Polym 131:64–74
Afkhami A, Removal N-A (2009) preconcentration and determination of Mo (VI) from water and wastewater samples using maghemite nanoparticles. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 346:52–57
Luzardo FHM, Velasco FG, Correia IKS, Silva PMS, Salay LC (2017) Removal of lead ions from water using a resin of mimosa tannin and carbon nanotubes. Environ Technol Innov 7:219–228
Yin N, Wang K, Ya X, Li Z (2018) Novel melamine modified metalorganic frameworks for remarkably high removal of heavy metal Pb (II). Desalination 430:120–127
Tang SCN, Lo IMC (2013) Magnetic nanoparticles: essential factors for sustainable environmental applications. Water Res 47:2613–2632
Berglund LA, Ikkala O, Nogues J, Gedde UW (2010) Making flexible magnetic aerogels and stiff magnetic nanopaper using cellulose nanofibrils as templates. Nat Nanotechnol 5:584–588
Lee H, Lee E, Kim DK, Jang NK, Jeong YY, Jon S (2006) Antibiofouling Polymer-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Potential Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agents for in Vivo Cancer Imaging. J Am Chem Soc 128:7383–7389
Liu X, Hu Q, Fang Z, Zhang X, Zhang B (2009) Magnetic chitosan nanocomposites: a useful recyclable tool for heavy metal ion removal. Langmuir 25:3–8
Xiong R, Wang YR, Zhang XX, Lu CH (2014) Facile synthesis of magnetic nanocomposites of cellulose@ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles for water treatment. RSC Adv 4:22632
Shan C, Ma Z, Tong M, Ni J (2015) Removal of Hg(II) by poly(1-vinylimidazole)-grafted Fe3O4@SiO2 magnetic nanoparticles. Water Res 69:252–260
Ge F, Li MM, Ye H, Zhao BX (2012) Effective removal of heavy metal ions Cd2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Cu2+ from aqueous solution by polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 211–212:366–372
Jiang LP, Liu P (2014) Design of Magnetic Attapulgite/Fly Ash/Poly(acrylic acid) Ternary Nanocomposite Hydrogels and Performance Evaluation as Selective Adsorbent for Pb2+ Ion. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:1785–1794
Horák D, Trchová M, Beneš MJ, Veverka M, Pollert E (2010) Monodisperse magnetic composite poly(glycidyl methacrylate)/La0.75Sr0.25MnO3 microspheres by the dispersion polymerization. Polymer 51:3116–3122
Tran HV, Tran LD, Nguyen TN (2010) Preparation of chitosan/magnetite composite beads and their application for removal of Pb(II) and Ni(II) from aqueous solution. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 30(2):304–310
Wang H, Han YJ, Liu Y, Bai T, Gao H, Zhang P, Wang W, Liu WG (2012) High-strength hydrogel as a reusable adsorbent of copper ions. J Hazard Mater 213:258–264
Ramirez E, Burillo SG, Barrera-Diaz C, Roa G, Bilyeu B (2011) Use of pH-sensitive polymer hydrogels in lead removal from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 192:432–439
Milosavljevic NB, Ristic MD, Peric-Grujic AA, Fillipovic JM, Strbac SB, Rakocevic ZL, Krusic MTK (2011) Sorption of zinc by novel pH-sensitive hydrogels based on chitosan, itaconic acid and methacrylic acid. J Hazard Mater 192:846–854
Saber-Samandari S, Gazi M (2013) Cellulose graft-polyacrylamide/ hydroxyapatite composite hydrogel with possible application in removal of Cu (II) ions. React Funct Polym 73:1523–1530
Natkanski P, Kustrowski P, Bialas A, Piwowarska Z, Michalik M (2013) Thermal stability of montmorillonite polyacrylamide and polyacrylate nanocomposites and adsorption of Fe(III) ions. Appl Clay Sci 75–76:153–157
Yu ZH, Zhang XD, Huang YM (2013) Magnetic chitosaniron(III) hydrogel as a fast and reusable adsorbent for chromium(VI) removal. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:11956–11966
Yan H, Yang LY, Yang Z, Yang H, Li AM (2012) Cheng RS. Preparation of chitosan/poly(acrylic acid) magnetic composite microspheres and applications in the removal of copper(II) ions from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 229:371–380
Gong X, Ngai T (2013) Interactions between Solid Surfaces with Preadsorbed Poly(ethylenimine) (PEI) Layers: Effect of Unadsorbed Free PEI Chains. Langmuir 29:5974–5981
Won SW, Park J, Mao J, Yun YS (2011) Utilization of PEI-modified Corynebacterium glutamicum biomass for the recovery of Pd(II) in hydrochloric solution. Bioresour Technol 102:3888–3893
Chen B, Zhao XS, Liu Y, Xu BG, Pan XJ (2015) Highly stable and covalently functionalized magnetic nanoparticles by polyethyleneimine for Cr(VI) adsorption in aqueous solution. RSC Adv 5:1398
Kumar PS, Senthamarai C, Durgadevi A (2014) Adsorption kinetics, mechanism, isotherm, and thermodynamic analysis of copper ions onto the surface modified agricultural waste. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 33:28–37
Kumar VV, Sivanesan S, Cabana H (2014) Magnetic cross-linked laccase aggregates—bioremediation tool for decolorization of distinct classes of recalcitrant dyes. Sci Total Environ 487:830–839
Paripoorani KS, Ashwin G, Vengatpriya P, Ranjitha V, Rupasree S, Kumar VV (2015) Insolubilisation of inulinase on magnetite chitosan micro-particles, an easily recoverable and reusable support. J Mol Catal B Enzym 113:47–55
Ding Y, Liu F, Jiang Q, Du B, Sun H (2013) Hydrothermal Synthesis and Characterization of Fe3O4 Nanorods. J Inorg Organomet Polym 23:379–384
Chandra S, Bhattacharya J (2019) Influence of temperature and duration of pyrolysis on the property heterogeneity of rice straw biochar and optimization of pyrolysis conditions for its application in soils. J Clean Prod 215:1123–1139
Sun Y, Yu IKM, Tsang DCW, Cao X, Lin D, Wang L, Graham NJD, Alessi DS, Komárek M, Sik Y, Feng Y (2019) Multifunctional iron-biochar composites for the removal of potentially toxic elements, inherent cations, and hetero-chloride from hydraulic fracturing wastewater. Environ Int 124:521–532
Shi S, Yang J, Liang S, Li M, Gan Q, Xiao K, Hu J (2018) Enhanced Cr (VI) removal from acidic solutions using biochar modified by Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 particles. Sci Total Environ 628–629:499–508
Amara M, Kerdjoudj H (2003) Modification of the Cation Exchange Resin Properties by Impregnation in Polyethyleneimine Solutions -Application to the Separation of Metallic Ions. Talanta 60:991–1001
Gao B, An F, Liu K (2006) Studies on Chelating Adsorption Properties of Novel Composite Material Polyethyleneimine/Silica Gel for Heavy-Metal Ions. Appl Surf Sci 253:1946–1952
Lagergren S (1898) About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kung Sven Veten Hand 24:1–39
McKay G, Ho YS (1998) The sorption of lead(II) on peat. Water Res 33:578–584
Nieboer E, Richardson DHS (1980) The replacement of the nodescript term ‘heavy metals’ by a biologically and chemically significant classification of metal ions. Environ Pollut B 1:3–26
Lin Z, Yang Y, Liang Z, Zeng L, Zhang A (2021) Preparation of Chitosan/Calcium Alginate/Bentonite Composite Hydrogel and Its Heavy Metal Ions Adsorption Properties. Polymers 13(11):1891
Yang JH, Chu YY, Li ZK, Zhang YP (2018) Effective removal of heavy metals by nanosized hydrous zirconia composite hydrogel and adsorption behavior study. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25(33):33464–33477
Yang J, Li M, Wang Y, Wu H, Sun Q (2019) High-Strength Physically Multi-Cross-Linked Chitosan Hydrogels and Aerogels for Removing Heavy-Metal Ions. J Agric Food Chem 67(49):13648–13657
Pekel N, Güven O (2008) Spectroscopic and thermal studies of poly[(N-vinylimidazole)-co-(maleic acid)]hydrogel and its quaternized form. Polym Int 57:637–643
Zheng SD, Shin JY, Song SY, Yu SJ, Suh H, Kim I (2014) Hexafunctional poly(propylene glycol) based hydrogels for the removal of heavy metal ions. J Appl Polym Sci 131(16):40610
Rodríguez E, Katime I (2003) Behavior of acrylic acid–itaconic acid hydrogels in swelling, shrinking, and uptakes of some metal ions from aqueous solution. J Appl Polym Sci 90:530–536
Elgueta E, Sánchez J, Dax D, Xu CL, Willför S, Rivas BL, González M (2016) Functionalized galactoglucomannan-based hydrogels for the removal of metal cations from aqueous solutions. J Appl Polym Sci 133(41):44093
Wu XH, Wang DZ, Zhang SY, Cai WJ, Yin YX (2015) Investigation of adsorption behaviors of Cu(II), Pb(II), and Cd(II) from water onto the high molecular weight poly (arylene ether sulfone) with pendant carboxyl groups. J Appl Polym Sci 132(20):41984
Panja S, Hanson S, Wang C (2020) EDTA-Inspired Polydentate Hydrogels with Exceptionally High Heavy Metal Adsorption Capacity as Reusable Adsorbents for Wastewater Purification. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:25276–25285
Ma J, Zhou G, Chu L, Liu Y, Liu C, Luo S, Wei Y (2016) Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions with An EDTA Functionalized Chitosan/Polyacrylamide Double Network Hydrogel. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:843–851
Cavus S, Gurdag G (2009) Noncompetitive Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Poly[2-(acrylamido)-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid-co-itaconic acid] Hydrogel. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:2652–2658
Qin LL, Yan LG, Chen J, Liu TT, Yu HQ, Du B (2016) Enhanced Removal of Pb2+, Cu2+, and Cd2+ by Amino-Functionalized Magnetite/Kaolin Clay. Ind Eng Chem Res 55:7344–7354
Hua R, Li Z (2014) Sulfhydryl functionalized hydrogel with magnetism: Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption behavior study for heavy metal removal. Chem Eng J 249:189–200
Zhang JB, Wang Y, Liang DX, Xiao ZF, Xie YJ, Li J (2020) Sulfhydryl-Modified Chitosan Aerogel for the Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions and Organic Dyes. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:14531–14536
Li X, Wang SF, Liu YG, Jiang LH, Song B, Li MF, Zeng GM, Tan XF, Cai XX, Ding Y (2017) Adsorption of Cu(II), Pb(II), and Cd(II) Ions from Acidic Aqueous Solutions by Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic Acid-Modified Magnetic Graphene Oxide. J Chem Eng Data 62:407–416
Hassan M, Liu YJ, Naidu R, Du JH, Qi FJ, Donne SW, Islam MM (2021) Mesoporous Biopolymer Architecture Enhanced the Adsorption and Selectivity of Aqueous Heavy-Metal Ions. ACS Omega 6:15316–15331
Paulino AT, Belfiore LA, Kubota LT, Muniz EC, Almeida VC, Tambourgi EB (2011) Effect of magnetite on the adsorption behavior of Pb(II), Cd(II), and Cu(II) in chitosan-based hydrogels. Desalination 275:187–196
Sun JH, Chen Y, Yu HQ, Yan LG, Du B, Pei ZG (2018) Removal of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ from aqueous solutions by magnetic alginate microsphere based on Fe3O4/MgAl-layered double hydroxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 532:474–484
Huang QQ, Chen Y, Yu HQ, Yan LG, Zhang JH, Wang B, Du B, Xing LT (2018) Magnetic graphene oxide/MgAl-layered double hydroxide nanocomposite:One-pot solvothermal synthesis, adsorption performance and mechanisms for Pb2+, Cd2+, and Cu2+. Chem Eng J 341:1–9
Ge F, Li MM, Ye H, Zhao BX (2012) Effective removal of heavy metal ions Cd2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Cu2+from aqueous solution by polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 211–212:366–372
Zhu Q, Li ZK (2015) Hydrogel-supported nanosized hydrous manganese dioxide: Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption behavior study for Pb2+, Cu2+, Cd2+and Ni2+ removal from water. Chem Eng J 281:69–80
Lia J, Huang QQ, Yu HQ, Yan LG (2022) Enhanced removal performance and mechanistic study of Cu2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ by magnetic layered double hydroxide nanosheets assembled on graphene oxide. J Water Process Eng 48:102893
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Sichuan province (Grant No. 2019YFG0264); Technology Foundation for Selected Overseas Chinese Scholar, Department of Personnel of Sichuan province (Grant No. 19BZ08-009); State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection (Grant No. SKLGP2018Z005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
All authors declare that no conflict of interest exists.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, T., Tang, Q., Wang, T. et al. Adsorption behaviours of copper(II), lead(II), and cadmium(II) ions from aqueous solution by polyethylenimine -modified magnetic hydrogel nanocomposites. J Polym Res 29, 520 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03377-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03377-9