Abstract
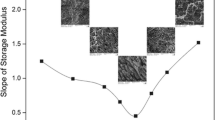
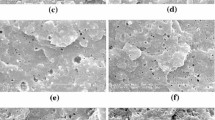
PHB/bio-PBS and PHBV/bio-PBS blends have been comparatively evaluated for their thermo-mechanical, morphological and rheological properties. Differential scanning calorimetry indicated crystallisation of PHB and PHBV to be largely restricted, whereas the thermal stability of PHB and PHBV blends marginally increased upon blending with bio-PBS. The immiscibility of the two components of two blends influenced the morphological changes from domain-dispersed to co-continuous type where the domain sizes of the dispersed phase bio-PBS increased in tune with compositions. Dynamic mechanical analysis showed distinct glass transition relaxation peaks of two components whereas WAXD studies confirmed a sharper decline in crystallisation of the PHB/bio-PBS based blends than in PHBV/bio-PBS systems, though the lamellar sizes estimated from Scherrer’s equation. At higher frequencies, the non-Newtonian melt flow dynamics of blends showed a sharp drop in their complex viscosity attributed to alignment of droplets along the flow direction (shear) due to phase separated morphology. Constitutive modelling of complex viscosity indicate the polymer melts to follow Carreau-Yasuda model, where the zero-shear viscosity decreased with bio-PBS content, irrespective of the nature of the matrix. Application of Cox-Merz rule has lead to estimations that PHB and PHBV matrices could give rise to co-continuous morphologies at a 35 wt. % and 41 wt. % of bio-PBS contents respectively.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gigli M, Fabbri M, Lotti N, Gamberini R, Rimini B, Munari A (2016) Poly(butylene succinate)-based polyesters for biomedical applications: A review. Eur Polymer J 75:431–460
Ha C-S, Cho W-J (2002) Miscibility, properties, and biodegradability of microbial polyester containing blends. Prog Polym Sci 27:759–809
Verlinden RAJ, Hill DJ, Kenward MA, Williams CD, Radecka I (2007) Bacterial synthesis of biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates. J Appl Microbiol 102:1437–1449
Winnacker M (2019) Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Recent Advances in Their Synthesis and Applications. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 121:1900101
Sudesh K, Abe H, Doi Y (2000) Synthesis, structure and properties of polyhydroxyalkanoates: biological polyesters. Prog Polym Sci 25:1503–1555
Di Lorenzo ML (2021) Poly(l-Lactic Acid)/Poly(Butylene Succinate) Biobased Biodegradable Blends. Polym Rev 61:457–492
Ma P, Cai X, Wang W, Duan F, Shi D, Lemstra PJ (2014) Crystallization behavior of partially crosslinked poly(β-hydroxyalkonates)/poly(butylene succinate) blends. J Appl Polym Sci 131:41020
Zhang K, Mohanty AK, Misra M (2012) Fully Biodegradable and Biorenewable Ternary Blends from Polylactide, Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) and Poly(butylene succinate) with Balanced Properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:3091–3101
Wu F, Misra M, Mohanty AK (2019) Super Toughened Poly(lactic acid)-Based Ternary Blends via Enhancing Interfacial Compatibility. ACS Omega 4:1955–1968
Zembouai I, Bruzaud S, Kaci M, Benhamida A, Corre Y-M, Grohens Y, Taguet A, Lopez-Cuesta J-M (2014) Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3-Hydroxyvalerate)/Polylactide Blends: Thermal Stability, Flammability and Thermo-Mechanical Behavior. J Polym Environ 22:131–139
Qiu Z, Ikehara T, Nishi T (2003) Poly(hydroxybutyrate)/poly(butylene succinate) blends: miscibility and nonisothermal crystallization. Polymer 44:2503–2508
Qiu Z, Ikehara T, Nishi T (2003) Miscibility and crystallization behaviour of biodegradable blends of two aliphatic polyesters. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) and poly(butylene succinate) blends. Polymer 44:7519–7527
Zytner P, Wu F, Misra M, Mohanty AK (2020) Toughening of Biodegradable Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/Poly(ε-caprolactone) Blends by In Situ Reactive Compatibilization. ACS Omega 5:14900–14910
Chun YS, Kim WN (2000) Thermal properties of poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) and poly(ϵ-caprolactone) blends. Polymer 41:2305–2308
Qiu Z, Komura M, Ikehara T, Nishi T (2003) Miscibility and crystallization behavior of biodegradable blends of two aliphatic polyesters. Poly(butylene succinate) and Poly(ε-caprolactone). Polymer 44:7749–7756
Blümm E, Owen AJ (1995) Miscibility, crystallization and melting of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/ poly(l-lactide) blends. Polymer 36:4077–4081
Wang X, Chen Z, Chen X, Pan J, Xu K (2010) Miscibility, crystallization kinetics, and mechanical properties of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)(PHBV)/poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate)(P3/4HB) blends. J Appl Polym Sci 117:838–848
Zhu W, Wang X, Chen X, Xu K (2009) Miscibility, crystallization, and mechanical properties of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate)/ poly(butylene succinate) blends. J Appl Polym Sci 114:3923–3931
Zembouai I, Kaci M, Bruzaud S, Benhamida A, Corre Y-M, Grohens Y (2013) A study of morphological, thermal, rheological and barrier properties of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-Co-3-Hydroxyvalerate)/polylactide blends prepared by melt mixing. Polym Test 32:842–851
Liu Q, Wu C, Zhang H, Deng B (2015) Blends of polylactide and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) with low content of hydroxyvalerate unit: Morphology, structure, and property. J Appl Polym Sci 132:42689
Gerard T, Budtova T (2012) Morphology and molten-state rheology of polylactide and polyhydroxyalkanoate blends. Eur Polymer J 48:1110–1117
Phua YJ, Pegoretti A, Araujo TM, Ishak ZAM (2015) Mechanical and thermal properties of poly(butylene succinate)/poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) biodegradable blends. J Appl Polym Sci 132:42815
Qiu TY, Song M, Zhao LG (2016) Testing, characterization and modelling of mechanical behaviour of poly (lactic-acid) and poly (butylene succinate) blends. Mech Adv Mater Mod Process 2:7
Kassos N, Kelly AL, Gough T, Gill AA (2018) Synergistic toughening and compatibilisation effect of poly(butylene succinate) in PLA/poly-caprolactone blends. Mater Res Express 6:035313
Garcia-Garcia D, Ferri JM, Boronat T, Lopez-Martinez J, Balart R (2016) Processing and characterization of binary poly(hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) and poly(caprolactone) (PCL) blends with improved impact properties. Polym Bull 73:3333–3350
Kumar V, Sehgal R, Gupta R (2021) Blends and composites of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and their applications. Eur Polymer J 161:110824
Hazer DB, Kılıçay E, Hazer B (2012) Poly(3-hydroxyalkanoate)s: Diversification and biomedical applications: A state of the art review. Mater Sci Eng C 32:637–647
Raza ZA, Khalil S, Abid S (2020) Recent progress in development and chemical modification of poly(hydroxybutyrate)-based blends for potential medical applications. Int J Biol Macromol 160:77–100
Rivera-Briso AL, Serrano-Aroca Á (2018) Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3-Hydroxyvalerate): Enhancement Strategies for Advanced Applications. Polymers 10:732
Mehrpouya M, Vahabi H, Barletta M, Laheurte P, Langlois V (2021) Additive manufacturing of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) biopolymers: Materials, printing techniques, and applications. Mater Sci Eng C 127:112216
Lim J, You M, Li J, Li Z (2017) Emerging bone tissue engineering via Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)-based scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C 79:917–929
Ma P, Hristova-Bogaerds DG, Zhang Y, Lemstra PJ (2014) Enhancement in crystallization kinetics of the bacterially synthesized poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) by poly(butylene succinate). Polym Bull 71:907–923
Ma P, Hristova-Bogaerds DG, Lemstra PJ, Zhang Y, Wang S (2012) Toughening of PHBV/PBS and PHB/PBS Blends via In situ Compatibilization Using Dicumyl Peroxide as a Free-Radical Grafting Initiator. Macromol Mater Eng 297:402–410
Barham PJ, Keller A, Otun EL, Holmes PA (1984) Crystallization and morphology of a bacterial thermoplastic: poly-3-hydroxybutyrate. J Mater Sci 19:2781–2794
Jost V, Schwarz M, Langowski H-C (2017) Investigation of the 3-hydroxyvalerate content and degree of crystallinity of P3HB-co-3HV cast films using Raman spectroscopy. Polymer 133:160–170
Miyata T, Masuko T (1998) Crystallization behaviour of poly(tetramethylene succinate). Polymer 39:1399–1404
Kumar S, Satapathy BK, Maiti SN (2013) Correlation of morphological parameters and mechanical performance of polyamide-612/poly (ethylene–octene) elastomer blends. Polym Adv Technol 24:511–519
Jost V, Miesbauer O (2018) Effect of different biopolymers and polymers on the mechanical and permeation properties of extruded PHBV cast films. J Appl Polym Sci 135:46153
Gan Z, Abe H, Kurokawa H, Doi Y (2001) Solid-State Microstructures, Thermal Properties, and Crystallization of Biodegradable Poly(butylene succinate) (PBS) and Its Copolyesters. Biomacromol 2:605–613
Yoo ES, Im SS (1999) Melting behavior of poly(butylene succinate) during heating scan by DSC. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 37:1357–1366
Ahn BD, Kim SH, Kim YH, Yang JS (2001) Synthesis and characterization of the biodegradable copolymers from succinic acid and adipic acid with 1,4-butanediol. J Appl Polym Sci 82:2808–2826
S̆krbić Z, Divjaković V (1996) Temperature influence on changes of parameters of the unit cell of biopolymer PHB. Polymer 37:505–507
Bluhm TL, Hamer GK, Marchessault RH, Fyfe CA, Veregin RP (1986) Isodimorphism in bacterial poly(β-hydroxybutyrate-co-β-hydroxyvalerate). Macromolecules 19:2871–2876
Galego N, Rozsa C, Sánchez R, Fung J, Analı́a V, Santo Tomás J (2000) Characterization and application of poly(β-hydroxyalkanoates) family as composite biomaterials. Polym Test 19:485–492
Konwar DB, Jacob J, Satapathy BK (2016) A comparative study of poly(l-lactide)-block-poly(ϵ-caprolactone) six-armed star diblock copolymers and polylactide/poly(ϵ-caprolactone) blends. Polym Int 65:1107–1117
Bayarı S, Severcan F (2005) FTIR study of biodegradable biopolymers: P(3HB), P(3HB-co-4HB) and P(3HB-co-3HV). J Mol Struct 744–747:529–534
Cai Y, Lv J, Feng J (2013) Spectral Characterization of Four Kinds of Biodegradable Plastics: Poly (Lactic Acid), Poly (Butylenes Adipate-Co-Terephthalate), Poly (Hydroxybutyrate-Co-Hydroxyvalerate) and Poly (Butylenes Succinate) with FTIR and Raman Spectroscopy. J Polym Environ 21:108–114
Furukawa T, Sato H, Murakami R, Zhang J, Duan Y-X, Noda I, Ochiai S, Ozaki Y (2005) Structure, Dispersibility, and Crystallinity of Poly(hydroxybutyrate)/Poly(l-lactic acid) Blends Studied by FT-IR Microspectroscopy and Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Macromolecules 38:6445
Kennouche S, Le Moigne N, Kaci M, Quantin J-C, Caro-Bretelle A-S, Delaite C, Lopez-Cuesta J-M (2016) Morphological characterization and thermal properties of compatibilized poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV)/poly(butylene succinate) (PBS)/halloysite ternary nanocomposites. Eur Polymer J 75:142–162
Han Y-K, Kim S-R, Kim J (2002) Macromol Res 10:108
Das D, Sethy S, Satapathy BK (2018) Matrix tacticity controlled tuning of microstructure, constitutive behavior and rheological percolation effect of melt-mixed amino-functionalized MWCNT/PP nanocomposites. Polym Eng Sci 58:1115–1126
Sethy S, Samantara L, Satapathy BK (2020) Phase-selective micro-structural effects on rheological-networks, segmental relaxation, and electrical conductivity behavior of melt-mixed polyamide-12/polypropylene-multi walled carbon nanotubes ternary nanocomposites. Polym Eng Sci 60:1301–1315
Wongwiwattana P, Thomas NL (2021) Co-continuous phase prediction in poly(lactic acid) /poly(caprolactone) blends from melt viscosity measurements. Polym Plast Technol Mater 60:1393–1410
Acknowledgements
Authors gratefully acknowledge PTT MCC Biochem Company (Bangkok, Thailand) for their help in providing BioPBS at nominal cost.
Funding
The financial assistance offered by the Ministry of Education, India, through the MHRD fellowship programme and the funding support by ICMR grant no: 5/3/8/45/2020-ITR are highly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Harshal Peshne: Writing – original draft, conceptualization, investigation, methodology, data collection and analysis. Bhabani K. Satapathy: Supervision, funding acquisition, writing – review & editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Peshne, H., Satapathy, B.K. Comparative studies of structural, thermal, mechanical, rheological and dynamic mechanical response of melt mixed PHB/bio-PBS and PHBV/bio-PBS blends. J Polym Res 29, 496 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03323-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03323-9