Abstract
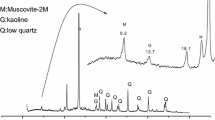
This research paper investigated the effects of the silica content and the sulfur vulcanization system on the mechanical properties of silica-filled natural rubber (NR) composite film and foam to be used in various applications. Three different sulfur vulcanization systems (conventional (CV), semi-efficient (Semi-EV), and efficient (EV)) were thoroughly studied to improve the quality of vulcanized NR and their composite with silica. The ground silica was treated with Silane 69. Scanning Electron Microscope demonstrated that the treated silica in NR was well dispersed. In addition, the treated silica resulted in better mechanical properties than for untreated silica. The optimum amount of silica in non-vulcanized rubber was 16 phr. Furthermore, the mechanical properties of vulcanized rubber from the CV system were better than those from the Semi-EV and EV systems due to the higher degree of crosslinking in the former. In addition, when the TSi/NR composite foam specimens at 8 phr had an applied load that was 4.41 times that of non-silica rubber foam.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tanaka Y (2001) Structural characterization of natural polyisoprenes: solve the mystery of natural rubber based on structural study. Rubber Chem Technol 74(3):355–375
Shah AA et al (2013) Biodegradation of natural and synthetic rubbers: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 83:145–157
Vudjung C et al (2014) Effect of natural rubber contents on biodegradation and water absorption of interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) hydrogel from natural rubber and cassava starch. Energy Procedia 56:255–263
Rattanasom N, Saowapark T, Deeprasertkul C (2007) Reinforcement of natural rubber with silica/carbon black hybrid filler. Polym testing 26(3):369–377
Al-Hartomy OA et al (2015) Influence of carbon black/silica ratio on the physical and mechanical properties of composites based on epoxidized natural rubber. J Compos Mater 50(3):377–386
Longseng R, Khaokong C (2020) Hexamethylene diamine-modified epoxidized natural rubber and its effect on cure characteristics and properties of natural rubber blends. Iran Polym J 29(12):1113–1121
Tang Y et al (2020) Application of carboxylated ethylene/vinyl acetate copolymer-modified nanosilica in tire tread rubber. Iran Polym J 29(10):853–864
Roshanaei H, Khodkar F, Alimardani M (2020) Contribution of filler–filler interaction and filler aspect ratio in rubber reinforcement by silica and mica. Iran Polym J 29(10):901–909
Shiva M, Akhtari SS, Shayesteh M (2020) Effect of mineral fillers on physico-mechanical properties and heat conductivity of carbon black-filled SBR/butadiene rubber composite. Iran Polym J 29(11):957–974
Thongpin C et al (2009) The effect of excess silane-69 used for surface modification on cure characteristic and mechanical properties of precipitated silica filled natural rubber (PSi/NR). In Adv Maters Res Trans Tech Publ
Thongsang S, Sombatsompop N (2005) Effect of NaOH and Si69 treatments on the properties of fly ash/natural rubber composites. Polym Compos 27(1):30–40
Sombatsompop N, Wimolmala E, Markpin T (2007) Fly‐ash particles and precipitated silica as fillers in rubbers. II. Effects of silica content and Si69‐treatment in natural rubber/styrene–butadiene rubber vulcanizates. J Appl Polym Sci 104(5):3396–3405
Yao H et al (2015) Effect of silane coupling agent on the fatigue crack propagation of silica‐filled natural rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 132(20)
Lee J-Y et al (2016) Influence of the silanes on the crosslink density and crosslink structure of silica-filled solution styrene butadiene rubber compounds. Compos Interfaces 24(7):711–727
Yan H et al (2005) Effect of nitrile rubber on properties of silica-filled natural rubber compounds. Polym Testing 24(1):32–38
Chen L et al (2016) From the volume-filling effect to the stress-bearing network: the reinforcement mechanisms of carbon black filler in natural rubber. Macromol Mater Eng 301(11):1390–1401
Toh-Ae P et al (2013) Comparison of properties of admicellar polymerization surface modified silica-and conventional fillers-reinforced tyre tread compounds. Asian J Chem 25(9):5226
Tohsan A et al (2011) Novel biphasic structured composite prepared by in situ silica filling in natural rubber latex. Polym Adv Technol 23(10):1335–1342
Bertora A et al (2011) A new modifier for silica in reinforcing SBR elastomers for the tyre industry. Macromol Mater Eng 296(5):455–464
Chang A et al (2016) Crack growth of natural rubber filled with functionalized silica particles. J Appl Polym Sci 133(6)
Xu T et al (2017) Self‐crosslinkable epoxidized natural rubber–silica hybrids. J Appl Polym Sci 134(14)
Cataldo F (2002) Preparation of silica-based rubber compounds without the use of a silane coupling agent through the use of epoxidized natural rubber. Macromol Mater Eng 287(5):348–352
Zafarmehrabian R et al (2012) The effects of silica/carbon black ratio on the dynamic properties of the tread compounds in truck tires. J Chem 9(3):1102–1112
Saengdee L et al (2021) Thermoplastic vulcanizates derived from modified natural rubbers and polypropylene. Iranian Polym J
Buitrago-Suescún O, Britto R (2020) Devulcanization of ground tire rubber: thermo-oxidation followed by microwave exposure in the presence of devulcanizing agent. Iran Polym J 29(7):553–567
Nakason C, Wannavilai P, Kaesaman A (2006) Effect of vulcanization system on properties of thermoplastic vulcanizates based on epoxidized natural rubber/polypropylene blends. Polym Testing 25(1):34–41
Habieb AB et al (2020) Rubber compounds made of reactivated EPDM for fiber-reinforced elastomeric isolators: an experimental study. Iran Polym J 29(11):1031–1043
Yamano M et al (2021) Preparation and characterization of vulcanized natural rubber with high stereoregularity. Polymer 124271
Heideman G et al (2005) Effect of zinc complexes as activator for sulfur vulcanization in various rubbers. Rubber Chem Technol 78(2):245–257
Ahsan Q, Mohamad N, Soh T (2015) Effects of accelerators on the cure characteristics and mechanical properties of natural rubber compounds. International Journal of Automotive and Mechanical Engineering 12:2954
Sahoo S, Bhowmick AK (2007) Influence of ZnO nanoparticles on the cure characteristics and mechanical properties of carboxylated nitrile rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 106(5):3077–3083
Boonkerd K, Deeprasertkul C, Boonsomwong K (2016) Effect of sulfur to accelerator ratio on crosslink structure, reversion, and strength in natural rubber. Rubber Chem Technol 89(3):450–464
de Lima DR et al (2021) Effect of vulcanization systems on the properties of natural rubber latex films. Polym Bull 78(7):3943–3957
Sadequl A et al (1998) The effect of accelerator/sulphur ratio on the scorch time of epoxidized natural rubber. Eur Polymer J 34(1):51–57
Wimolmala E, Khongnual K, Sombatsompop N (2009) Mechanical and morphological properties of cellular NR/SBR vulcanizates under thermal and weathering ageing. J Appl Polym Sci 114(5):2816–2827
Frisch KC (1981) History of science and technology of polymeric foams. J Macromol Sci—Chem 15(6):1089–1112
Calvert KO (1982) Polymer latices and their applications. Appl Sci
Ruiz-Herrero J, Rodriguez-Perez M, De Saja J (2005) Design and construction of an instrumented falling weight impact tester to characterise polymer-based foams. Polym Testing 24(5):641–647
Sims G, Bennett J (1998) Cushioning performance of flexible polyurethane foams. Polym Eng Sci 38(1):134–142
Wang B et al (2007) Compressive response and energy absorption of foam EPDM. J Appl Polym Sci 105(6):3462–3469
Luo L et al (2020) Synergistic flame retardancy of aqueous hybridization between iron phosphonate and ammonium polyphosphate towards polyethyleneimine-based foam. Iran Polym J 29(3):265–274
Bayat H et al (2020) An experimental study on one-step and two-step foaming of natural rubber/silica nanocomposites. Nanotechnol Rev 9:427–435
Tangpasuthadol V et al (2008) Silica-reinforced natural rubber prepared by the sol-gel process of ethoxysilanes in rubber latex. J Appl Polym Sci 109(1):424–433
Prapruddivongs C, Thomyasirigul S (2019) Correlative roles of silica as a blowing aid and a Pb(II) adsorbent for natural rubber composite foams. Polym Testing 77
Bayat H, Fasihi M (2019) Effect of coupling agent on the morphological characteristics of natural rubber/silica composites foams. e-Polymers 19:430–436
Panploo K, Chalermsinsuwan B, Poompradub S (2019) Natural rubber latex foam with particulate fillers for carbon dioxide adsorption and regeneration. RSC Adv 9(50):28916–28923
Sadequl A (2000) The effect of accelerator/sulphur ratio on the cure time and torque maximum of epoxidized natural rubber. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 46(3–4):597–615
Liang T, Isayev AI (2019) Effect of ultrasonic extrusion of star styrene-butadiene rubber on properties of carbon black-and silica-filled compounds and vulcanizates. J Appl Polym Sci 136(18):47451
Rahaman MS et al (2021) Radiation crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol/polyvinyl pyrrolidone/acrylic acid hydrogels: swelling, crosslinking and dye adsorption study. Iranian Polym J 1–16
Gelling I, Tinker A, bin Abdul Rahman H (1991) Solubility parameters of epoxidised natural rubber
Tangboriboonrat P, Suchiva K, Kuhakarn S (1994) Characterization of non-crosslinked natural rubber latex by phase transfer technique. Polymer 35(23):5144–5145
Bashir AS et al (2015) Mechanical, thermal, and morphological properties of (eggshell powder)-filled natural rubber latex foam. J Vinyl Add Tech 23(1):3–12
Pornprasit P, Aiemrum A (2018) Natural rubber latex foam for seedling. Proceedings of the 10th Int Conf Sci Technol Innov Sustainable Well-Being (STISWB 2018) 515–519
Ansarifar A et al (2005) The use of a silanised silica filler to reinforce and crosslink natural rubber. Int J Adhes Adhes 25(1):77–86
Cao L et al (2019) Synergistic reinforcement of silanized silica-graphene oxide hybrid in natural rubber for tire-tread fabrication: A latex based facile approach. Compos B Eng 161:667–676
Reowdecha M et al (2021) Film and latex forms of silica-reinforced natural rubber composite vulcanized using electron beam irradiation. Heliyon 7(6):e07176
Ngeow Y et al (2019) TEM observation of silane coupling agent in silica-filled rubber tyre compound. Journal of Rubber Research 22(1):1–12
Li S-D et al (2006) Thermal degradation kinetics and morphology of natural rubber/silica nanocomposites. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 6(2):541–546
Ghorai S et al (2019) Devulcanization of waste rubber and generation of active sites for silica reinforcement. ACS Omega 4(18):17623–17633
Wang Q et al (2012) Reinforcement of natural rubber with core-shell structure silica-poly(methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles. J Nanomater 2012:1–9
Wang Q et al (2012) Reinforcement of natural rubber with core-shell structure silica-poly (methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles. J Nanomater 2012
Saville BA, Watson A (1967) Structural characterization of sulfur-vulcanized rubber networks. Rubber chem technol 40(1):100–148
Morrison N, Porter M (1984) Temperature effects on the stability of intermediates and crosslinks in sulfur vulcanization. Rubber Chem Technol 57(1):63–85
Menon A, Pillai C, Nando G (1994) Chemical crosslink density and network structure of natural rubber vulcanizates modified with phosphorylated cardnol prepolymer. J Appl Polym Sci 51(13):2157–2164
Quang NT et al (2019) Study on the effect of modified and unmodified silica on the properties of natural rubber vulcanizates. Vietnam Journal of Chemistry 57(3):357–362
Larpkasemsek A et al (2019) Effects of sulfur vulcanization system on cure characteristics, physical properties and thermal aging of epoxidized natural rubber. J Metals, Mater Minerals 29(1)
Gelling I, Morrison N (1985) Sulfur vulcanization and oxidative aging of epoxidized natural rubber. Rubber Chem Technol 58(2):243–257
South JT, Case SW, Reifsnider KL (2003) Effects of thermal aging on the mechanical properties of natural rubber. Rubber Chem Technol 76(4):785–802
Skinner T, Watson A (1969) EV systems for NR. I. The purpose of efficient vulcanization and development of curing system. Rubber Chem Technol 42(2):404–417
Rao V, Johns J (2008) Thermal behavior of chitosan/natural rubber latex blends TG and DSC analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim 92(3):801–806
Kurian T, George K, Francis D (1988) Effect of vulcanization temperature on the cure characteristics and vulcanizate properties of natural rubber and styrene-butadiene rubber. Die Angewandte Makromolekulare Chemie: Applied Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics 162(1):123–134
Siriyong T, Keawwattana W (2012) Utilization of different curing systems and natural zeolite as filler and absorbent for natural rubber/nitrile rubber blend. Kasetsart Journal Natural Science 46:918–930
Gayathri R, Vasanthakumari R, Padmanabhan C (2013) Sound absorption, thermal and mechanical behavior of polyurethane foam modified with nano silica, nano clay and crumb rubber fillers. Int J Sci Eng Res 4(5):301–308
Lee E-K, Choi S-Y (2007) Preparation and characterization of natural rubber foams: Effects of foaming temperature and carbon black content. Korean J Chem Eng 24(6):1070–1075
Członka S et al (2019) Composites of rigid polyurethane foams and silica powder filler enhanced with ionic liquid. Polym Testing 75:12–25
Greenwood NN, Earnshaw A (1997) Chemistry of the Elements. Elsevier Sci
Bayat H, Fasihi M (2019) Curing characteristics and cellular morphology of natural rubber/silica composite foams. Polym Bulletin1–14
Bayat H, Fasihi M (2019) Effect of coupling agent on the morphological characteristics of natural rubber/silica composites foams. e-Polymers 19(1):430–436
Shojaei Dindarloo A et al (2019) Various nano-particles influences on structure, viscoelastic, Vulcanization and mechanical behaviour of EPDM nano-composite rubber foam. Plast, Rubber Compos 48(5):218–225
Park KW, Kim GH, Chowdhury SR (2008) Improvement of compression set property of ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer/ethylene-1-butene copolymer/organoclay nanocomposite foams. Polym Eng Sci 48(6):1183–1190
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Nanotechnology Center (Nanotech), NSTDA, Ministry of Science and Technology, Thailand, through its program of Research Network NANOTEC (RNN) Kasetsart University. The authors would also like to acknowledge the Faculty of Engineering, Kasetsart University Research Development Institute (KURDI), Bangkok, Thailand. This work was partially supported by a grant from the Thailand Research Fund (Grant No. MRG5980252). The Center of Excellence on Petrochemical and Materials Technology (PETROMAT) provided financial support. Special thanks was to Mr. Numporn Thungphotrakul for his kind help in some data correction for this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
Manuscript title: Properties of silica/natural rubber composite film and foam: Effects of silica content and sulfur vulcanization system.
☒ The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
☒ The authors whose names are listed immediately below certify that they have NO affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest, or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. Napaporn Kumkrong Peerapan Dittanet Pongdhorn Saeoui Surapitch Loykulnun Paweena Prapainainar.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumkrong, N., Dittanet, P., Saeoui, P. et al. Properties of silica/natural rubber composite film and foam: Effects of silica content and sulfur vulcanization system. J Polym Res 29, 302 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03129-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03129-9