Abstract
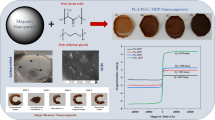
Magnetically-sensitive shape memory materials have attracted significant attention during recent decades, especially in biomedical applications, due to the noncontact triggering nature of their process. In the current study, Fe3O4 ceramic nanoparticles were deposited on the carbon nanotubes surface by an in situ chemical co-precipitation method in an alkaline solution. Then, the effect of incorporating these ceramic nanoparticles on the magnetic shape memory behavior of polyurethane-carbon nanotube nanocomposites has been studied up to 10wt% CNTs/Fe3O4. Other mechanical, thermal, and morphological tests were also performed on the fabricated nanocomposites, such as tensile, TGA, DTGA, DMTA, SEM, and TEM. A new model was finally obtained on the shape memory behavior of this composite. The obtained results showed that the magnetic hysteresis loops of PU-5%(CNTs/Fe3O4) and PU-10%(CNTs/Fe3O4) samples exhibited ferrimagnetism with the saturation magnetization of 2.9 and 4.6 emu.g−1 with respect to nonmagnetic polyurethane property and the best magnetic shape recovery result was obtained for PU-10%(CNTs/Fe3O4) nanocomposite. Finally, recovery stress was measured to be increased by 111% with the incorporation of CNTs/Fe3O4, and a modified Halpin–Tsai equation was derived with the correction factor of K = exp(-2.079–89.5Vf) to predict recovery stress of PU-CNTs/Fe3O4 nanocomposites.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meng H, Li G (2013) A review of stimuli-responsive shape memory polymer composites. Polymer 54:2199–2221
Arnebold A, Hartwig A (2016) Fast switchable, epoxy based shape-memory polymers with high strength and toughness. Polymer 83:40–49
Ratna D, Karger-Kocsis J (2008) Recent advances in shape memory polymers and composites: a review. J Mater Sci 43:254–269
Luo H, Zhou X, Ma Y, Yi G, Cheng X, Zhu Y, Zu X, Zhang N, Huang B, Yu L (2016) Shape memory-based tunable resistivity of polymer composites. Appl Surf Sci 363:59–65
Sujithra R, Srinivasan S, Arockiarajan A (2015) Shape recovery studies for coupled deformations in an epoxy based amorphous shape memory polymers. Polym Test 48:1–6
Baker RM, Tseng L-F, Iannolo MT, Oest ME, Henderson JH (2016) Self-deploying shape memory polymer scaffolds for grafting and stabilizing complex bone defects: A mouse femoral segmental defect study. Biomaterials 76:388–398
Guo J, Wang Z, Tong L, Lv H, Liang W (2015) Shape memory and thermo-mechanical properties of shape memory polymer/carbon fiber composites. Compos Part A: Appl Sci Manufact 76:162–171
Guo J, Wang Z, Tong L, Liang W (2016) Effects of short carbon fibres and nanoparticles on mechanical, thermal and shape memory properties of SMP hybrid nanocomposites. Compos Part B: Eng 90:152–159
Du H, Liu L, Leng J, Peng H, Scarpa F, Liu Y (2015) Shape memory polymer S-shaped mandrel for composite air duct manufacturing. Compos Struct 133:930–938
Delaey J, Dubruel P, Van Vlierberghe S (2020) Shape-Memory Polymers for Biomedical Applications. Adv Funct Mater 30:1909047
Gu S, Yan B, Liu L, Ren J (2013) Carbon nanotube–polyurethane shape memory nanocomposites with low trigger temperature. Eur Polym J 49:3867–3877
Hu J, Zhu Y, Huang H, Lu J (2012) Recent advances in shape–memory polymers: Structure, mechanism, functionality, modeling and applications. Prog Polym Sci 37:1720–1763
Xu Y, Chen D (2018) Shape memory-assisted self-healing polyurethane inspired by a suture technique. J Mater Sci 53:10582–10592
Cai Y, Jiang J-S, Liu Z-W, Zeng Y, Zhang W-G (2013) Magnetically-sensitive shape memory polyurethane composites cross-linked with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Compos Part A: Appl Sci Manufact 53:16–23
Cho JW, Kim JW, Jung YC, Goo NS (2005) Electroactive shape-memory polyurethane composites incorporating carbon nanotubes. Macromol Rapid Commun 26:412–416
Lee H-F, Yu HH (2011) Study of electroactive shape memory polyurethane–carbon nanotube hybrids. Soft Matter 7:3801–3807
Luo X, Mather PT (2010) Conductive shape memory nanocomposites for high speed electrical actuation. Soft Matter 6:2146–2149
Lu H, Liu Y, Gou J, Leng J, Du S (2010) Synergistic effect of carbon nanofiber and carbon nanopaper on shape memory polymer composite. Appl Phys Lett 96:084102
Schmidt AM (2006) Electromagnetic activation of shape memory polymer networks containing magnetic nanoparticles. Macromol Rapid Commun 27:1168–1172
Kumar UN, Kratz K, Heuchel M, Behl M, Lendlein A (2011) Shape-Memory Nanocomposites with Magnetically Adjustable Apparent Switching Temperatures. Adv Mater 23:4157–4162
Mohr R, Kratz K, Weigel T, Lucka-Gabor M, Moneke M, Lendlein A (2006) Initiation of shape-memory effect by inductive heating of magnetic nanoparticles in thermoplastic polymers. Proceed National Academy Sci 103:3540–3545
Hiergeist R, Andrä W, Buske N, Hergt R, Hilger I, Richter U, Kaiser W (1999) Application of magnetite ferrofluids for hyperthermia. J Magn Magn Mater 201:420–422
Rosensweig RE (2002) Heating magnetic fluid with alternating magnetic field. Journal Magn Magnc Mater 252:370–374
Razzaq MY, Anhalt M, Frormann L, Weidenfeller B (2007) Thermal, electrical and magnetic studies of magnetite filled polyurethane shape memory polymers. Mater Sci Eng A 444:227–235
Leng J, Lan X, Liu Y, Du S (2011) Shape-memory polymers and their composites: stimulus methods and applications. Prog Mater Sci 56:1077–1135
Weidenfeller B, Höfer M, Schilling F (2002) Thermal and electrical properties of magnetite filled polymers. Compos Part A: Appl Sci Manufact 33:1041–1053
Melly SK, Liu L, Liu Y, Leng J (2020) Active composites based on shape memory polymers: overview, fabrication methods, applications, and future prospects. J Mater Sci 55:10975–11051
Naito Y, Nishikawa M, Hojo M (2015) Effect of reinforcing layer on shape fixity and time-dependent deployment in shape-memory polymer textile composites. Compos Part A: Appl Sci Manufact 76:316–325
Chen J, Zhang Z-X, Huang W-B, Yang J-H, Wang Y, Zhou Z-W, Zhang J-H (2015) Carbon nanotube network structure induced strain sensitivity and shape memory behavior changes of thermoplastic polyurethane. Mater Des 69:105–113
Zhuo S, Liu Y, Zhou L, Feng X (2018) Enhanced dual-responsive shape memory nanocomposites with rapid and efficient self-healing capability. J Mater Sci 53:13936–13948
Fonseca M, Abreu B, Gonçalves F, Ferreira A, Moreira R, Oliveira M (2013) Shape memory polyurethanes reinforced with carbon nanotubes. Compos Struct 99:105–111
Moghim MH, Zebarjad SM (2016) Effect of strain rate on tensile properties of polyurethane/(multi-walled carbon nanotube) nanocomposite. J Vinyl Add Technol 22:356–361
Moghim MH, Zebarjad SM (2017) Tensile properties and deformation mechanisms of PU/MWCNTs nanocomposites. Polym Bull 74:4267–4277
Keshavarz M, Zebarjad SM, Daneshmanesh H, Moghim M (2017) On the role of TiO2 nanoparticles on thermal behavior of flexible polyurethane foam sandwich panels. J Therm Anal Calorim 127:2037–2048
Moghim MH, Keshavarz M, Zebarjad SM (2018) Effect of SiO2 nanoparticles on compression behavior of flexible polyurethane foam. Polym Bull 76:227–239
Zhang C-S, Ni Q-Q (2007) Bending behavior of shape memory polymer based laminates. Compos Struct 78:153–161
Deka H, Karak N, Kalita RD, Buragohain AK (2010) Biocompatible hyperbranched polyurethane/multi-walled carbon nanotube composites as shape memory materials. Carbon 48:2013–2022
Moghim MH, Zebarjad SM (2015) Fabrication and structural characterization of multi-walled carbon nanotube/Fe 3 O 4 nanocomposite. J Inorgan Organometall Polym Mater 25:1260–1266
Moghim MH, Zebarjad SM, Eqra R (2018) Experimental and modeling investigation of shape memory behavior of polyurethane/carbon nanotube nanocomposite. Polym Adv Technol 29:2496–2504
Xiao X, Hu J (2016) Animal hairs as water-stimulated shape memory materials: mechanism and structural networks in molecular assemblies. Sci rep 6:1–12
Xiao X, Hu J, Gui X, Lu J, Luo H (2017) Is biopolymer hair a multi-responsive smart material? Polym Chem 8:283–294
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moghim, M.H., Zebarjad, S.M. & Eqra, R. Effect of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on magneto-responsive shape memory behavior of polyurethane-carbon nanotube nanocomposites. J Polym Res 29, 28 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02880-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02880-9