Abstract
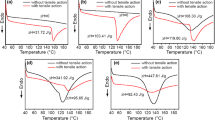
Thermoplastic cassava starch (TPS) /nanosilica (nano-SiO2) composites were prepared by adding different surface properties of nanosilica. The effect of different surface properties of nano-SiO2 on the retrogradation kinetics, morphology, spherulites size, molecular interactions, short-range molecular structure and crystal type of TPS was investigated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), polarized light microscopy (PLM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and 13C NMR. The results indicated that the retrogradation degree and rate of TPS containing hydrophobic nano-SiO2 were higher than that of hydrophilic nano-SiO2, and the spherulites were clearer. Hydrophobic nano-SiO2 could uniformly disperse in starch matrix. V-type crystal formed after adding hydrophilic nano-SiO2, and A + V types after adding hydrophobic nano-SiO2. The crystallinity of TPS adding hydrophobic nano-SiO2 was higher than that of hydrophilic nano-SiO2, but the crystal size and interplanar spacing were smaller. Hydrophobic nano-SiO2 could promote the formations of double helix structure and the ordered molecular structure.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hsieh C, Liu W, Whaley J, Shi Y (2019) Structure, properties, and potential applications of waxy tapioca starches – A review. Trends Food Sci Technol 83:225–234
Chen Q, Shi Y, Chen G, Cai M (2020) Enhanced mechanical and hydrophobic properties of composite cassava starch films with stearic acid modified MCC (microcrystalline cellulose)/NCC (nanocellulose) as strength agent. Int J Biol Macromol 142:846–854
Liu H, Xie F, Yu L, Chen L, Li L (2009) Thermal processing of starch-based polymers. Prog Polym Sci 34(12):1348–1368
Zhang MQ, Rong MZ, Zhang HB, Friedrich K (2003) Mechanical properties of low nano-silica filled high density polyethylene composites. Polym Eng Sci 43(2):490–500
Zhou SX, Wu LM, Sun J, Shen WD (2003) Effect of nanosilica on the properties of polyester-based polyurethane. J Appl Polym Sci 88(1):189–193
Tang S, Zou P, Xiong H, Tang H (2008) Effect of nano-SiO2 on the performance of starch/polyvinyl alcohol blend films. Carbohyd Polym 72(3):521–526
Wang Z, Gu Z, Hong Y, Cheng L, Li Z (2011) Bonding strength and water resistance of starch-based wood adhesive improved by silica nanoparticles. Carbohyd Polym 86(1):72–76
Frost K, Barthes J, Kaminski D, Lascaris E, Niere J, Shanks R (2011) Thermoplastic starch–silica–polyvinyl alcohol composites by reactive extrusion. Carbohyd Polym 84(1):343–350
Tang M, Hong Y, Gu Z, Zhang Y, Cai X (2013) The effect of xanthan on short and long-term retrogradation of rice starch. Starch - Stärke 65(7–8):702–708
Sikora M, Krystyjan M, Dobosz A, Tomasik P, Walkowiak K, Masewicz Ł, Kowalczewski PŁ, Baranowska HM (2019) Molecular analysis of retrogradation of corn starches. Polymers 11(11):1764
Li W, Li C, Gu Z, Qiu Y, Cheng L, Hong Y, Li Z (2016) Relationship between structure and retrogradation properties of corn starch treated with 1,4-α-glucan branching enzyme. Food Hydrocoll 52:868–875
Fredrisson H, Silverio J, Andersson R (1998) The influence of amylose and amylopectin characteristics on gelatinization and retrogradation properties of different starches. Carbohyd Polym 35:119–134
Bertoft E, Annor GA, Shen X, Rumpagaporn P, Seetharaman K, Hamaker BR (2016) Small differences in amylopectin fine structure may explain large functional differences of starch. Carbohyd Polym 140:113–121
Zheng M, Su H, You Q, Zeng S, Zheng B, Zhang Y, Zeng H (2019) An insight into the retrogradation behaviors and molecular structures of lotus seed starch-hydrocolloid blends. Food Chem 295:548–555
Liu R, Xu C, Cong X, Wu T, Song Y, Zhang M (2017) Effects of oligomeric procyanidins on the retrogradation properties of maize starch with different amylose/amylopectin ratios. Food Chem 221:2010–2017
Fu Z, BeMiller JN (2017) Effect of hydrocolloids and salts on retrogradation of native and modified maize starch. Food Hydrocolloids 69:36–48
Wang L, Xu J, Fan X, Wang Q, Wang P, Yuan J, Yu Y, Zhang Y, Cui L (2018) The effect of branched limit dextrin on corn and waxy corn gelatinization and retrogradation. Int J Biol Macromol 106:116–122
Ji N, Liu C, Zhang S, Yu J, Xiong L, Sun Q (2017) Effects of chitin nano-whiskers on the gelatinization and retrogradation of maize and potato starches. Food Chem 214 (Supplement C):543–549
Liu L, Yang M, Xu J, Fan X, Gao W, Wang Q, Wang P, Xu B, Yuan J, Yu Y (2020) Exploring the mechanism of pullulan delay potato starch long-term retrogradation from the viewpoint of amylopectin chain motion. Int J Biol Macromol 145:84–91
Chaudhary DS (2008) Understanding amylose crystallinity in starch–clay nanocomposites. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys 46(10):979–987
Muller CMO, Laurindo JB, Yamashita F (2011) Effect of nanoclay incorporation method on mechanical and water vapor barrier properties of starch-based films. Ind Crops Prod 33(3):605–610
Liu Y, Fan L, Mo X, Yang F, Pang J (2018) Effects of nanosilica on retrogradation properties and structures of thermoplastic cassava starch. J Appl Polym Sci 135(2):45687
Liu S, Li X, Chen L, Li L, Li B, Zhu J, Liang X (2017) Investigating the H2O/O2 selective permeability from a view of multi-scale structure of starch/SiO2 nanocomposites. Carbohyd Polym 173:143–149
Liu S, Li X, Chen L, Li L, Li B, Zhu J (2017) Understanding physicochemical properties changes from multi-scale structures of starch/CNT nanocomposite films. Int J Biol Macromol 104:1330–1337
Maiti P, Nam PH, Okamoto M, Hasegawa N, Usuki A (2002) Influence of crystallization on intercalation, morphology, and mechanical properties of polypropylene/clay nanocomposites. Macromolecules 35(6):2042–2049
Hakim RH, Cailloux J, Santana OO, Bou J, Sánchez-Soto M, Odent J, Raquez JM, Dubois P, Carrasco F, Maspoch ML (2017) PLA/SiO2 composites: Influence of the filler modifications on the morphology, crystallization behavior, and mechanical properties. J Appl Polym Sci 134(40):45367
Strawhecker KE, Manias E (2003) Crystallization Behavior of Poly(ethylene oxide) in the Presence of Na+ Montmorillonite Fillers. Chem Mater 15(4):844–849
Liu S, Li X, Chen L, Li L, Li B, Zhu J (2018) Tunable d-limonene permeability in starch-based nanocomposite films reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals. J Agric Food Chem 66(4):979–987
Imberty A, Chanzy H, Perez S, Buleon A, Tran V (1988) The double-helical nature of the crystalline part of A-starch. J Mol Biol 201(2):365–378
Jiping P, Shujun W, Jinglin Y, Hongyan L, Jiugao Y, Wenyuan G (2007) Comparative studies on morphological and crystalline properties of B-type and C-type starches by acid hydrolysis. Food Chem 105(3):989–995
Schmitt H, Guidez A, Prashantha K, Soulestin J, Lacrampe MF, Krawczak P (2015) Studies on the effect of storage time and plasticizers on the structural variations in thermoplastic starch. Carbohyd Polym 115:364–372
van Soest JJG, Hulleman SHD, de Wit D, Vliegenthart JFG (1996) Crystallinity in starch bioplastics. Ind Crops Prod 5(1):11–22
Zhang QX, Yu ZZ, Xie XL, Naito K, Kagawa Y (2007) Preparation and crystalline morphology of biodegradable starch/clay nanocomposites. Polymer 48(24):7193–7200
Seligra PG, Medina Jaramillo C, Famá L, Goyanes S (2016) Biodegradable and non-retrogradable eco-films based on starch–glycerol with citric acid as crosslinking agent. Carbohyd Polym 138:66–74
Wang N, Zhang X, Han N, Bai S (2009) Effect of citric acid and processing on the performance of thermoplastic starch/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Carbohyd Polym 76(1):68–73
Baik MY, Dickinson LC, Chinachoti P (2003) Solid-State 13C CP/MAS NMR studies on aging of starch in white bread. J Agric Food Chem 51(5):1242–1248
Garbow JR, Schaefer J (1991) Magic-angle carbon-13 NMR study of wheat flours and doughs. J Agric Food Chem 39(5):877–880
Magalhaes NF, Andrade CT (2009) Thermoplastic corn starch/clay hybrids: Effect of clay type and content on physical properties. Carbohyd Polym 75(4):712–718
Singh V, Ali SZ, Divakar S (1993) 13C CP/MAS NMR spectroscopy of native and acid modified starches. Starch-Starke 45(2):59–62
Zhang B, Chen L, Li X, Li L, Zhang H (2015) Understanding the multi-scale structure and functional properties of starch modulated by glow-plasma: A structure-functionality relationship. Food Hydrocolloids 50(50):228–236
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51663002) and the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2017GXNSFAA198083 and 2020GXNSFAA159113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, YX., Liang, ZS., Liang, JN. et al. Effect of different surface properties of nanosilica on retrogradation behavior and structures of thermoplastic cassava starch. J Polym Res 28, 147 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02507-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02507-z