Abstract
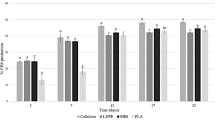
Polymer waste was subjected to biodegradation evaluation after compounding specimens with an oxo-prodegradant chemical (PDQ-M) and thermoplastic starch, to determine its susceptibility to degrade with time in contact with soil simulating an arid environment. The ASTM D 5988–18 test method was followed to evaluate the biodegradation extent of the materials under investigation, whilst using linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE), polycaprolactone (PCL) and TPS alongside the starch (positive control) as reference materials. The samples were also subjected to thermal characterisation using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), in addition to studying their infrared spectra (IR). It was noted that the LLPDE and the oxo-prodegradant induced polymer waste had a similar degradation extent evaluated after rigorous testing and monitoring, which was 23% after 180 days of experimental time. Furthermore, a plateau was reached for the biodegradation (%) as a function of time after some 50 days, which indicate that the additives in the samples act as a source of nutrient to sustain the biodegradation by enriching the microorganisms in the soil to produce carbon. The work in this study points towards a new method for treating polymer waste using physical blending with additives to biodegrade it with time as promising alternative for plastic waste accumulation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaza SL, Yao P, Bhada-Tata F, Van Woerden (2018) What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050. Urban Development Series. Washington, DC: World Bank. https://doi.org/10.1596/978-1-4648-1329-0
Al-Salem S, Al-Hazza’a A, Karam H, Al-Wadi M, Al-Dhafeeri A, Al-Rowaih A (2019) Insights into the evaluation of the abiotic and biotic degradation rate of commercial pro-oxidant filled polyethylene (PE) thin films. J Environ Mange 250:109475
Al-Salem, S.M, Al-Nasser AY, Behbehani MH, Sultan HH, Karam HJ, Al-Wadi MH, Al-Dhafeeri AT, Rasheed Z, Al-Foudaree M (2019) Thermal Response and Degressive Reaction Study of Oxo-Biodegradable Plastic Products Exposed to Various Degradation Media. Int J Polym Sci, 9612813
Al-Salem SM (2019) Influential Parameters on Natural Weathering Under Harsh Climatic Conditions of Mechanically Recycled Plastic Film Specimens. J Environ Mange 230:355–365
Viera JSC, Marques MRC, Nazareth MC, Jimenez PC, Castro IB (2020) On replacing single-use plastic with so-called biodegradable ones: The case with straws. Environ Sci Policy 106:177–181
Nazareth M, Marques MRC, Leite MCA, Castro IB (2019) Commercial plastics claiming biodegradable status: Is this also accurate for marine environments? J Hazard Mater 366:714–722
Jang YC, Lee G, Kwon Y, Lim YH, Jeong JH (2020) Recycling and management practices of plastic packaging waste towards a circular economy in South Korea. Resour Conserv Recycl 158:104798
Al-Salem SM, Uddin S, Lyons B (2020) Evidence of microplastics (MP) in gut content of major consumed marine fish species in the State of Kuwait (of the Arabian/Persian Gulf). Marine Poll Bullet 154:111052
Rajmohan KVS, Ramya C, Viswanathan MR, Varjani S (2019) Plastic pollutants: effective waste management for pollution control and abatement. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health 12:72–84
Qi R, Jones DL, Li Z, Liu Q, Yan C (2020) Behavior of microplastics and plastic film residues in the soil environment: A critical review. Sci Tot Environ 703:134722
Vroman I, Tighzert L (2009) Biodegradable Polymers Materials 2:307–344
EN 17033 2018 Plastics-Biodegradable mulch films for use in agriculture and horticulture Requirements and test methods European Standard, European Committee for Standardization, Brussels, Belgium
ASTM D6954 18 2018 Standard Guide for Exposing and Testing Plastics that Degrade in the Environment by a Combination of Oxidation and Biodegradation ASTM International PA
Agamuthu P, Faizura PN (2005) Biodegradability of degradable plastic waste. Waste Mange Res 23:95–100
Green Light Products Ltd. 2020. Fact sheet: Standards for biodegradable plastics. Available at: http://www.greenlightpackaging.com/downloads/Biodegradability_Fact_Sheet.pdf (accessed on: 29 April 2020)
Reddy MM, Vivekanandhan S, Misra M, Bhatia SK, Mohanty AK (2013) Biobased plastics and bionanocomposites: Current status and future opportunities. Prog Polym Sci 38:1653–1689
Castro-Aguirre E, Auras R, Selke S, Rubino M, Marsh T (2017) Insights on the aerobic biodegradation of polymers by analysis of evolved carbon dioxide in simulated composting conditions. Polym Degrad Stab 137:251–271
Portillo F, Yashchuk O, Hermida E (2016) Evaluation of the rate of abiotic and biotic degradation of oxo-degradable polyethylene. Polym Testing 53:58–69
Contat-Rodrigo L (2013) Thermal characterization of the oxo-degradation of polypropylene containing a pro-oxidant/pro-degradant additive. Polym Degrad Stab 98:2117–2124
Al-Salem SM, Sultan HH, Karam HJ, Al-Dhafeeri AT (2019) Determination of biodegradation rate of commercial oxo-biodegradable polyethylene film products using ASTM D 5988. J Polym Res 26(7):157
Gomes LB, Klein JM, Brandalise RN, Zeni M, Zoppas BC, Grisa AMC (2014) Study of Oxo-biodegradable Polyethylene Degradation in Simulated Soil. Mater Res 17:121–126
Pradhan R, Reddy M, Diebel W et al (2010) Comparative compostability and biodegradation studies of various components of green composites and their blends in simulated aerobic composting bioreactor. Int J Plast Technol 14:45–50
Du YL, Cao Y, Lu F, Li F, Cao Y, Wang XL, Wang YZ (2008) Biodegradation behaviors of thermoplastic starch (TPS) and thermoplastic dialdehyde starch (TPDAS) under controlled composting conditions. Polym Testing 27(8):924–930
Chinaglia S, Tosin M, Degli-Innocenti F (2018) Biodegradation rate of biodegradable plastics at molecular level. Polym Degrad Stab 147:237–244
Günkaya Z, Banar M (2016) An environmental comparison of biocomposite film based on orange peel-derived pectin jelly-corn starch and LDPE film: LCA and biodegradability. Int J Life Cycle Assess 21:465–475
Jandas PJ, Prabakaran K, Mohanty S, Nayak SK (2019) Evaluation of biodegradability of disposable product prepared from poly (lactic acid) under accelerated conditions. Polym Degrad Stab 164:46–54
Li L, Frey M, Browning KJ (2010) Biodegradability Study on Cotton and Polyester Fabrics. J Eng Fibers Fabr 5(4):42–53
Mariani PDSC, Neto APV, da Silva Jr. J.P., Cardoso E.J.B.N., Esposito E., Innocentini-Mei L.H., (2007) Mineralization of Poly(e-caprolactone)/Adipate Modified Starch Blend in Agricultural Soil. J Polym Environ 15:19–24
Mazibuko M, Ndumo J, Low M, Ming D, Harding K (2019) Investigating the natural degradation of textiles under controllable and uncontrollable environmental conditions. Procedia Manufacturing 35:719–724
Milošević M, Krkobabić A, Radoičić M, Šaponjić Z, Radetić T, Radetić M (2017) Biodegradation of cotton and cotton/polyester fabrics impregnated with Ag/TiO2 nanoparticles in soil. Carbohyd Polym 158:77–84
Modelli A, Calcagno B, Scandola M (1999) Kinetics of Aerobic Polymer Degradation in Soil by Means of the ASTM D 5988–96 Standard Method. J Environ Polym Degrad 7(2):109–116
Pischedda A, Tosin M, Degli-Innocenti F (2019) Biodegradation of plastics in soil: The effect of temperature. Polym Degrad Stab 170:109017
ASTM D 5988–18 (2018) Standard Test Method for Determining Aerobic Biodegradation of Plastic Materials in Soil ASTM International PA
Yashchuk O, Portillo FS, Hermida EB (2012) Degradation of polyethylene film samples containing oxodegradable additives. Procedia Materials Science 1:439–445
Davis G (2006) The Characterisation of Two Different Degradable Polyethylene (PE) Sacks. Materials 57:314
Šerá J, Serbruyns L, De Wilde B, Koutný M (2020) Accelerated biodegradation testing of slowly degradable polyesters in soil. Polym Degrad Stab 171:109031
Rosa DS, Guedes CGF, Carvalho CL (2007) Processing and thermal, mechanical and morphological characterization of post-consumer polyolefins/thermoplastic starch blends. J Mater Sci 42:551–557
Mariani PDSC, Neto APV, da Silva Jr. J.P., Cardoso E.J.B.N., Esposito E., Innocentini-Mei L.H (2007) Mineralization of Poly(e-caprolactone) Adipate Modified Starch Blend in Agricultural Soil. J Polym Environ 15:19–24
Al-Salem SM, Abraham G, Al-Qabandi OA, Dashti AM (2015) Investigating the effect of accelerated weathering on the mechanical and physical properties of high content plastic solid waste (PSW) blends with virgin linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE). Polym Test 46:116–121
ISO 11358–1 (2014) International Standards Organisation, Plastics: thermogravimetry (TG) of polymers. Part 1: General principles
ISO 11357–1 (2009) International Standards Organisation British Standards (BS), Implementation of the International Standards Organization, Plastics: differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Part 1: General principles
ISO 11357–3 (2011) International Standards Organisation British Standards (BS), Implementation of the International Standards Organization, Plastics: differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Part 3: Determination of temperature and enthalpy of melting and crystallization
ISO 10640 (2011) International Standards Organisation, Plastics: Methodology for assessing polymer photoageing by FTIR and UV/visible spectroscopy
Al-Salem, S.M (2018) The first chemical identification of polyolefin (PO) waste blends using infrared spectroscopy. In: Proc. 9th International Conference on Waste Management and the Environment, Transactions of the Waste Management and the Environment IX, Seville, Spain, 17–19 September
ISO 17556 (2019) International Standards Organisation, Plastics: Determination of the ultimate aerobic biodegradability of plastic materials in soil by measuring the oxygen demand in a respirometer or the amount of carbon dioxide evolved
ASTM D4972–19 (2019) Standard Test Methods for pH of Soils ASTM International PA
ASTM D 2974–14 (2014) Standard Test Methods for Moisture, Ash, and Organic Matter of Peat and Other Organic Soils ASTM International PA
Bremner, JM (1996) Nitrogen‐total. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3 Chemical Methods, 1(5): 1085–121
BS 7755 (1995) British Standards (BS) Implementation of the International Standards Organization, Soil quality. Chemical methods: Determination of organic and total carbon after dry combustion (elementary analysis)
ISO 846, (2019) British Standards (BS) Implementation of the International Standards Organization, Plastics - Evaluation of the action of microorganisms
Krotz L, Giazzi G (2016) Elemental Analysis: CHNS/O characterization of polymers and plastics, Application Note 42230, Themro Fisher
Yang J, Miranda R, Roy C (2001) Using the DTG curve fitting method to determine the apparent kinetic parameters of thermal decomposition of polymers. Polym Degrad Stab 73:455–461
Park JW, Oh SC, Lee HP, Kim HT, Yoo KO (2000) A kinetic analysis of thermal degradation of polymers using a dynamic method. Polym Degrad Stab 67:535–540
Al-Salem SM, Bumajdad A, Khan AR, Sharma BK, Chandrasekaran SR, Al-Turki FA, Jassem FH, Al-Dhafeeri AT (2018) Non-isothermal degradation kinetics of virgin linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) and biodegradable polymer blends. J Polym Res 25:111
Shujun W, Jiugao Y, Jinglin Y (2005) Preparation and characterization of compatible thermoplastic starch/polyethylene blends. Polym Degrad Stab 87:395–401
Ibrahim H, Farag M, Megahed H, Mehanny S (2014) Characteristics of starch-based biodegradable composites reinforced with date palm and flax fibers. Carbohyd Polym 10:11–19
Rodriguez-Gonzalez FJ, Ramsay BA, Favis BD (2003) High performance LDPE/thermoplastic starch blends: a sustainable alternative to pure polyethylene. Polymer 44:1517–1526
Xiang S, Feng L, Bian X, Chena GLX (2020) Evaluation of PLA content in PLA/PBAT blends using TGA. Polym Testing 81:106211
Ghenoa G, Ganzerla R, Bortoluzzia M, Paganica R (2015) Determination of degradation kinetics of two polyester thermosetting powder coatings using TGA and colorimetric analysis. Prog Org Coat 78:239–243
Finzi-Quintão CM, Novack KM, Silva ACB (2016) Identification of Biodegradable and Oxo-biodegradable Plastic Bags Samples Composition. Macromolecular Symposia (September 30th) https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.201500156.
Amin RM, Sreekumar PA, Harthi MA Al, De K, Abu-Sharkh BF (2013) Natural Weather Ageing of the Low-Density Polyethylene: Effect of Polystarch N J Appl Polym Sci https://doi.org/10.1002/APP.3778
Guarás MP, Alvarez VA, Ludueña LN, (2015) Processing and characterization of thermoplastic starch/polycaprolactone/compatibilizer ternary blends for packaging applications. J Polym Res 22: 165
Jia S, Yu D, Zhu Y, Wang Z, Chen L, Fu L (2017) Morphology, Crystallization and Thermal Behaviors of PLA-Based Composites: Wonderful Effects of Hybrid GO/PEG via Dynamic Impregnating. Polymers 9:528
Palai B, Biswal M, Mohanty S, Nayak SK (2019) In situ reactive compatibilization of polylactic acid (PLA) and thermoplastic starch (TPS) blends; synthesis and evaluation of extrusion blown films thereof. Ind Crops Prod 14:111748
Fairbrother A, Hsueh H-C, Kim JH, Jacobs D, Sung L-P (2019) Temperature and light intensity effects on photodegradation of high-density polyethylene. Polym Degrad Stab 16:153–160
Tai NL, Adhikari R, Shanks R, Adhikari B (2019) Aerobic biodegradation of starch–polyurethane flexible films under soil burial condition: Changes in physical structure and chemical composition. Polym Degrad Stab 170:109017
Sable S, Mandal DK, Ahuja S, Bhunia H (2019) Biodegradation kinetic modeling of oxo-biodegradable polypropylene/polylactide/nanoclay blends and composites under controlled composting conditions. J Environ Manage 249:109186
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research (KISR) for supporting research project EM065K.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.M. Al-Salem: Conceptualization, funds acquisition, data analysis, initial and final draft preparation, M.W. Kishk: Experimental, initial draft preparation and data analysis, H.J. Karam: Experimental and data analysis, M.M. Al-Qassimi: Experimental and data analysis, M.H. Al-Wadi; Experimental; A.J. Al-Shemmari: Experimental and data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Data availability statement
The data used in this work is provided as a Supplementary Material File.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this article declare that no conflict of interest (partial or in full) exists in this work, including any towards materials, equipment or tradenames.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Salem, S.M., Kishk, M.W., Karam, H.J. et al. Inducing polymer waste biodegradation using oxo-prodegradant and thermoplastic starch based additives. J Polym Res 28, 100 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02457-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02457-6