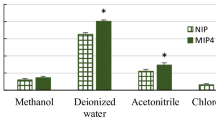
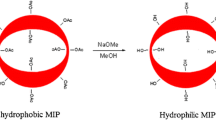
Abstract
Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP) are known as high selective sorbent, however, its application in aqueous medium is very limiting. In this way, a new hybrid MIP was successfully synthesized for saccharin (SAC) extraction in aqueous medium. SAC determination in surface waters becomes a challenge due to high dissipation that results in low concentration and susceptibility to potential interferences. Two polymer materials synthesized through bulk (HMIP-B) and suspension (HMIP-S) polymerizations were studied, and its performance has been compared according to morphological, adsorption isotherms, thermodynamics, and selectivity properties. The adsorption process was thermodynamically favorable and adsorption capacities (qe) were 1.24 and 4.32 mg g-1 for HMIP-B and HMIP-S, respectively. The material was characterized as heterogeneous with two binding sites fitted by Langmuir–Freundlich model and pseudo-second-order model. The imprinting factor (IF) was 4.8 for both materials and the HMIP-S presented superior results in selectivity, with a distribution constant (Kd) value of 12.1 times higher than HMIP-B for saccharin and a selectivity coefficient (k) of 7.73, 9.25 and 2.54 for acesulfame, caffeine and cyclamate, respectively. The selecitivity of HMIP in aqueous medium was tested in surface water samples, resulting in 89% of SAC recovery.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarley T, De OFM, Segatelli MG (2016) Evaluation of a new water-compatible hybrid molecularly imprinted polymer combined with restricted access for the selective recognition of folic acid in binding assays. J Appl Polym Sci 43463:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43463
Zhao S, Yang X, Zhao H et al (2015) Water-compatible surface imprinting of ‘Saccharin sodium’ on silica surface for selective recognition and detection in aqueous solution. Talanta 144:717–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.05.086
Benito-Peña E, Martins S, Orellana G, Moreno-Bondi MC (2009) Water-compatible molecularly imprinted polymer for the selective recognition of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in biological samples. Anal Bioanal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2405-1
Singh M, Kumar A, Tarannum N (2013) Water-compatible ’aspartame’-imprinted polymer grafted on silica surface for selective recognition in aqueous solution. Anal Bioanal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-6812-6
Ye J, He L, Guo L et al (2018) The synthesis of molecular recognition polymer particles via miniemulsion polymerization. React Funct Polym 126:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2018.02.013
Yu K, Li L, Wang Y et al (2018) Rapid extraction of trace bisphenol A in real water samples using hollow mesoporous silica surface dummy molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal Methods 10:3926–3932. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ay01530a
Yan H, Wang M, Han Y et al (2014) Hybrid molecularly imprinted polymers synthesized with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane-methacrylic acid monomer for miniaturized solid-phase extraction : A new and economical sample preparation strategy for determination of acyclovir in urine. J Chromatogr A 1346:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.04.045
Koler A, Gornik T, Kosjek T et al (2018) Preparation of molecularly imprinted copoly(acrylic acid-divinylbenzene) for extraction of environmentally relevant sertraline residues. React Funct Polym 131:378–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2018.08.016
Mansour MSM, Abdel-Shafy HI, Mehaya FMS (2018) Valorization of food solid waste by recovery of polyphenols using hybrid molecular imprinted membrane. J Environ Chem Eng 6:4160–4170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.06.019
Sun H-W, Guo Z-Y, Lv Y-K et al (2013) Determination of Tetracyclines Residues in Egg, Milk, and Milk Powder by Online Coupling of A Precolumn Packed with Molecular Imprinted Hybrid Composite Materials to RP-HPLC-UV. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 38:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826076.2013.873873
Huang Y, Wang R (2018) Review on Fundamentals, Preparations and Applications of Imprinted Polymers. Curr Org Chem 22:1600–1618. https://doi.org/10.2174/1385272822666180711120045
Zygler A, Wasik A, Namieśnik J (2010) Retention behaviour of some high-intensity sweeteners on different SPE sorbents. Talanta 82:1742–1748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2010.07.070
Richardson SD, Kimura SY (2016) Water Analysis: Emerging Contaminants and Current Issues. Anal Chem 88:546–582. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04493
Richardson SD, Ternes TA (2018) Water Analysis: Emerging Contaminants and Current Issues. Anal Chem 90:398–428. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04577
Praveena SM, Cheema MS, Guo HR (2019) Non-nutritive artificial sweeteners as an emerging contaminant in environment: A global review and risks perspectives. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 170:699–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.048
Tran NH, Reinhard M, Khan E et al (2019) Emerging contaminants in wastewater, stormwater runoff, and surface water: Application as chemical markers for diffuse sources. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.160
Gilart N, Borrull F, Fontanals N, Marcé RM (2014) Selective materials for solid-phase extraction in environmental analysis. Trends Environ Anal Chem 1:e8–e17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teac.2013.11.002
Arbelaez P, Borrull F, Pocurull E, Maria Marce R (2015) Determination of high-intensity sweeteners in river water and wastewater by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1393:106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.03.035
Ordonez E, Y; Benito Quintana, Jose; Rodil, Rosario; Cela R, (2012) Determination of artificial sweeteners in water samples by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1256:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.07.073
Hashemi M, Zohrabi P, Abdolhosseini S (2015) Spectrophotometric determination of cyclamate in artificial sweeteners and beverages after ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction. Anal Methods 7:2594–2602. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ay02903h
Zanetti M, Midori F, Oliveira D et al (2014) Synthesis and characterization of cross-linked molecularly imprinted polyacrylamide for the extraction / preconcentration of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid from water samples. React Funct Polym 83:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2014.07.004
Casarin J, Gonçalves C, Gava M et al (2017) Poly(methacrylic acid )/ SiO 2 / Al 2 O 3 based organic-inorganic hybrid adsorbent for adsorption of imazethapyr herbicide from aqueous medium. React Funct Polym 121:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2017.10.023
Ambrus A, Hamilton DJ, Kuiper HA, Racke KD (2003) CHEMISTRY AND THE ENVIRONMENT DIVISION * SIGNIFICANCE OF IMPURITIES IN THE SAFETY EVALUATION OF CROP PROTECTION PRODUCTS ( IUPAC Technical Report ). Pure Appl Chem 75:937–973. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200375070937
Moreira K, Gava M, Ricardo C, Tarley T (2013) Polymers Synthesis and adsorption studies of novel hybrid mesoporous copolymer functionalized with protoporphyrin for batch and on-line solid-phase extraction of Cd 2 + ions. React Funct Polym 73:838–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2013.03.017
Williams PA, Groundwater PW, Overgaard J et al (2016) An analysis of the experimental and theoretical charge density distributions of the piroxicam – saccharin co-crystal and its constituents. RSC Adv 6(85):81578–81590. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra10411h
Saavedra LNM, Baeta BEL, Pereira MC et al (2017) Thermodinamic study of a magnetic molecular imprinted polymer for removal of nitrogenous pollutant from gasoline. Fuel 210:380–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.08.087
Zygler A, Wasik A, Namieśnik J (2009) Analytical methodologies for determination of artificial sweeteners in foodstuffs. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 28:1082–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2009.06.008
Acknowledgments
The authors thank CAPES (Finance code 001) for doctoral fellowship, FAPDF (Process nº 0193.001046/2015 and process nº 193.000.566/2009), CNPq (process nº 308748/2015-8), INCTAA, Institute of Chemistry, University of Brasilia, for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dourado, C.S., Casarin, F., Braga, J.W.B. et al. Synthesis and evaluation of hybrid molecularly imprinted polymers for selective extraction of saccharin in aqueous medium. J Polym Res 28, 40 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02402-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02402-z