Abstract
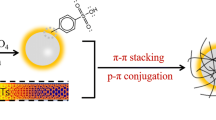
Polystyrene (PS) microspheres with special morphology of bowl-shaped were synthesized by simple dispersion polymerization. The SEM results showed that the diameter of bowl cavity is about 1.4 μm, and many small cavities appeared at the reverse side of the bowl cavity. The absorber hybrids of bowl-shaped PS@MWCNTs were constructed using bowl-shaped PS microspheres with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) via π-π stacking effect, and the absorbing performance were investigated. Compared with PS@MWCNTs hybrids, the bowl-shaped PS@MWCNTs hybrids demonstrate excellent absorbing performance, the reflection loss(RL) is -34.92 dB at 13.01 GHz in thickness of 2.0 mm, while the reflection loss(RL) of PS@MWCNTs is -22.42 dB. When the thickness of bowl-shaped PS@MWCNTs hybrids is 2.8 mm, the reflection loss(RL) can reach -38.57 dB, and the effective absorption bandwidth (RL ≤ -10 dB) is as high as 4.81 GHz (6.45–11.26 GHz). The results indicated that the existence of bowl cavity structure is vital to the energy attenuation of incident electromagnetic wave due to the enhancement of impedance matching, electromagnetic wave transmission path and multiple reflection in the interior of absorbing materials.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng Y, Li Z, Li Y, Dai S, Ji G, Zhao H, Cao J, Du Y (2018) Rationally Regulating Complex Dielectric Parameters of Mesoporous Carbon Hollow Spheres to Carry out Efficient Microwave Absorption. Carbon 127:643–652
Lv L, Liu J, Liu H, Liu C, Lu Y, Sun K, Fan R, Wang N, Lu N, Guo Z (2018) An Overview of Electrically Conductive Polymer Nanocomposites toward Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Eng Sci 2:26–42
Zhang H, Wang B, Feng A, Zhang N, Jia Z, Huang Z, Liu X, Wu G (2019) Mesoporous Carbon Hollow Microspheres with Tunable Pore Size and Shell Thickness as Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorbers. Compos Part B-Eng 167:690–699
Kuang J, Hou X, Xiao T, Li Y, Wang Q, Jiang P, Cao W (2019) Three- Dimensional Carbon Nanotube/SiC Nanowire Composite Network Structure for High-Efficiency Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Ceram Int 45(5):6263–6267
Xie P, Li H, He B, Dang F, Lin J, Fan R, Hou C, Liu H, Zhang J, Ma Y (2018) Bio-Gel Derived Nickel/Carbon Nanocomposites with Enhanced Microwave Absorption. J Mater Chem C 6(32):8812–8822
Luo C, Jiao T, Tang Y, Kong J (2018) Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Absorption of Iron-Containing SiBCN Ceramics at 1158 K High-Temperature. Adv Eng Mater 20(6):1701168
Shu R, Li W, Wu Y, Zhang J, Zhang G (2019) Nitrogen-Doped Co-C/MWCNTs Nanocomposites Derived from Bimetallic Metal-Organic Frameworks for Electromagnetic Wave Absorption in the X-Band. Chem Eng J 362:513–524
Wang C, Murugadoss V, Kong J, He Z, Mai X, Shao Q, Chen Y, Guo L, Liu C, Angaiah S (2018) Overview of Carbon Nanostructures and Nanocomposites for Electromagnetic Wave Shielding. Carbon 140:696–733
Kong L, Wang C, Yin X, Fan X, Wang W, Huang J (2017) Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties of CNTs Modified by a Tetrapyridinoporphyrazine Interface Layer. J Mater Chem C 5(30):7479–7488
El Moumen A, Tarfaoui M, Nachtane M, Lafdi K (2019) Carbon Nanotubes as a Player to Improve Mechanical Shock Wave Absorption. Compos Part B-Eng 164:67–71
Kong L, Yin X, Xu H, Yuan X, Wang T, Xu Z, Huang J, Yang R, Fan H (2019) Powerful Absorbing and Lightweight Electromagnetic Shielding CNTs/RGO Composite. Carbon 145:61–66
Ting T, Jau Y, Yu R (2012) Microwave Absorbing Properties of Polyaniline/MWCNTs Composites with Various Polyaniline Contents. Appl Surf Sci 258(7):3184–3190
Qing Y, Wang X, Zhou Y, Huang Z, Luo F, Zhou W (2014) Enhanced Microwave Absorption of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes/Epoxy Composites Incorporated with Ceramic Particles. Compos Sci Technol 102:161–168
Pande S, Chaudhary A, Patel D, Singh BP, Mathur RB (2014) Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Multiwall Carbon Nanotube/Polycarbonate Composites for Electrostatic Discharge and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Applications. RSC Adv 4(27):13839–13849
Cao M-S, Yang J, Song W-L, Zhang D-Q, Wen B, Jin H-B, Hou Z-L, Yuan J (2012) Ferroferric Oxide/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube vs Polyaniline/Ferroferric Oxide/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Multiheterostructures for Highly Effective Microwave Absorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(12):6949–6956
Zhong B, Cheng Y, Wang M, Bai Y, Huang X, Yu Y, Wang H, Wen G (2018) Three Dimensional Hexagonal Boron Nitride Nanosheet/Carbon Nanotube Composites with Light Weight and Enhanced Microwave Absorption Performance. Compos Part A-Appl Sci Manuf 112:515–524
Yun S, Kirakosyan A, Surabhi S, Jeong J-R, Choi J (2017) Controlled Morphology of MWCNTs Driven by Polymer-Grafted nanoparticles for Enhanced Microwave Absorption. J Mater Chem C 5(33):8436–8443
Shen H, Du X, Ren X, Xie Y, Sheng X, Zhang X (2017) Morphology Control of Anisotropic Nonspherical Functional Polymeric Particles by One-Pot Dispersion Polymerization. React Funct Polym 112:53–59
Liu X, Nie X, Yu R, Feng H (2018) Design of Dual-Frequency Electromagnetic Wave Absorption by Interface Modulation Strategy. Chem Eng J 334:153–161
Kuang J, Xiao T, Hou X, Zheng Q, Wang Q, Jiang P, Cao W (2019) Microwave Synthesis of Worm-Like SiC Nanowires for Thin Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Materials. Ceram Int 45(9):11660–11667
Pak SY, Kim HM, Kim SY, Youn JR (2012) Synergistic Improvement of Thermal Conductivity of Thermoplastic Composites with Mixed Boron Nitride and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Fillers. Carbon 50(13):4830–4838
Bokobza L, Zhang J (2012) Raman Spectroscopic Characterization of Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes and of Composites. Express Polym Lett 6(7):601–608
Tuinstra F, Koenig J (1970) Characterization of Graphite Fiber Surfaces with Raman Spectroscopy. J Compos Mater 4(4):492–499
Qing Y, Zhou W, Luo F, Zhu D (2016) Titanium Carbide (MXene) Nanosheets as Promising Microwave Absorbers. Ceram Int 42(14):16412–16416
You W, She W, Liu Z, Bi H, Che R (2017) High-Temperature Annealing of an Iron Microplate with Excellent Microwave Absorption Performance and Its Direct Micromagnetic Analysis by Electron Holography and Lorentz Microscopy. J Mater Chem C 5(24):6047–6053
Zlotorzynski A (1995) The Application of Microwave Radiation to Analytical and Environmental Chemistry. Crit Rev Anal Chem 25(1):43–76
Bagheri M, Phung B, Blackburn T (2014) Influence of Temperature and Moisture Content on Frequency Response Analysis of Transformer Winding. IEEE T Dielect El In 21(3):1393–1404
Tian C, Du Y, Xu P, Qiang R, Wang Y, Ding D, Xue J, Ma J, Zhao H, Han X (2015) Constructing Uniform Core-Shell PPy@ PANI Composites with Tunable Shell Thickness toward Enhancement in Microwave Absorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(36):20090–20099
Quan B, Liang X, Ji G, Ma J, Ouyang P, Gong H, Xu G, Du Y (2017) Strong Electromagnetic Wave Response Derived from the Construction of Dielectric/Magnetic Media Heterostructure and Multiple Interfaces. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(11):9964–9974
Chuai D, Liu X, Yu R, Ye J, Shi Y (2016) Enhanced Microwave Absorption Properties of Flake-Shaped FePCB Metallic Glass/Graphene Composites. Compos Part A-Appl Sci Manuf 89:33–39
Zhang X, Ji G, Liu W, Zhang X, Gao Q, Li Y, Du Y (2016) A Novel Co/TiO2 Nnocomposite Derived from A Metal-Organic Framework: Synthesis and Efficient Microwave Absorption. J Mater Chem C 4:1860–1870
Shu R, Li W, Zhou X, Tian D, Zhang G, Gan Y, Shi J, He J (2018) Facile Preparation and Microwave Absorption Properties of RGO/MWCNTs/ZnFe2O4 Hybrid Nanocomposites. J Alloys Compd 743:163–174
Zhang N, Huang Y, Wang M, Liu X, Zong M (2019) Design and Microwave Absorption Properties of Thistle-like CoNi Enveloped in Dielectric Ag Decorated Graphene Composites. J colloid Interf Sci 534:110–121
Qing Y, Min D, Zhou Y, Luo F, Zhou W (2015) Graphene Nanosheet-and Flake Carbonyl Iron Particle-Filled Epoxy-Silicone Composites as Thin-hickness and Wide-Bandwidth Microwave Absorber. Carbon 86:98–107
Yu L, Zhu Y, Fu Y (2018) Waxberry-Like Carbon@ Polyaniline Microspheres with High-Performance Microwave Absorption. Appl Surf Sci 427:451–457
Acknowledgements
Thanks for the financial support of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51373136) and the Innovation Foundation for Doctor Dissertation of NPU (CX201964). Thanks for the help of analytical & testing center of NPU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, A., Wang, D., Li, Y. et al. The effect of microspheres surface morphology on the enhanced microwave absorbing properties of MWCNTs. J Polym Res 28, 91 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02303-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02303-1