Abstract
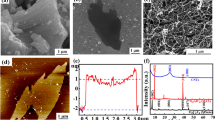
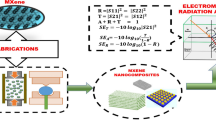
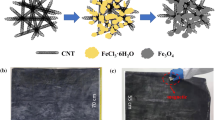
A large number of electronic devices could generate a lot of electromagnetic waves, which could interfere with other equipment and harm the human body. Therefore, an electromagnetic interference shielding (EMI) material is urgently needed to protect the human body and the electronic equipment. In this paper, the multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and the nano-Fe3O4 were added into the polylactic acid (PLA) matrix to form the composite film with electromagnetic interference shielding performance. And the structure and properties of MWCNTs/Fe3O4/PLA composite films, such as the morphology, chemical structure, crystallization, mechanical property, conductive property, magnetic property and electromagnetic interference shielding property, were researched. The result shows that too much Fe3O4 could lead to agglomeration, and the coupling agent KH570 had grafted and modified the surface of MWCNTs. The MWCNTs and nano-Fe3O4 could increase the crystallinity of PLA matrix. With the increase of MWCNTs, the maximum tensile stress of composite films gradually increased, and the maximum tensile strain decreased, and the resistance value showed a significant downward trend. The Fe3O4 could improve the magnetic properties of composite film. The MWCNTs and Fe3O4 could improve the electromagnetic interference shielding efficiency (EMI SE). The MWCNTs played a more significant role than the Fe3O4 in the process of EMI, and the EMI SE of the composite film with 3:1 ratios of MWCNTs/Fe3O4 could rise to 22 dB.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomassin JM, Jerome C, Pardoen T, Bailly C, Huynen I, Detrembleur C (2013) Polymer/carbon based composites as electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials. Mat Sci Eng R 74:211–232
Xiao S, Mei H, Han D, Dassios KG, Cheng L (2017) Ultralight lamellar amorphous carbon foam nanostructured by SiC nanowires for tunable electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 122:718–725
Zheng X, Feng J, Zong Y, Miao H, Hu X, Bai J, Li X (2015) Hydrophobic graphene nanosheets decorated by monodispersed superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanocrystals as synergistic electromagnetic wave absorbers. J Mater Chem C 3:4452–4463
Kausar A, Ahmad S, Salman SM (2017) Effectiveness of polystyrene/carbon nanotubes composites in electromagnetic interference shielding materials: a review. Polym Plast Technol 56:1027–1042
Rajesh K, Andrei VA, Rajesh KS, Ashwani KS, Jyoti S, Ravinder KK, Kedar S, Yoshiyuki S, Stanislav AM (2019) Self-assembled nanostructures of 3D hierarchical faceted-iron oxide containing vertical carbon nanotubes on reduced graphene oxide hybrids for enhanced electromagnetic interface shielding. Compos Part B 168:66–76
Zeng Z, Jin H, Chen M, Li W, Zhou L, Zhang Z (2016) Lightweight and anisotropic porous MWCNT/WPU composites for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Funct Mater 26:303–310
Yan Q, Yan Z, Na Q, Wang Q, Zhang X, Li Y (2019) Preparation of graphene aerogel with high mechanical stability and microwave absorption ability via combining surface support of metallic-CNTs and interfacial cross-linking by magnetic nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Inter 11:10409–10417
Wang G, Zhao G, Wang S, Zhang L, Park CB (2018) Injection-molded microcellular PLA/graphite nanocomposites with dramatically enhanced mechanical and electrical properties for ultra-efficient EMI shielding applications. J Mater Chem C 6:6847–6859
Hooman A, Marcelo A, Jose IV (2019) Recent advances in carbon-based polymer nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Prog Mater Sci 103:319–373
Liang Q, Lu Y (2013) Copper/bamboo fabric composite prepared via a silver catalytic electroless deposition process for electromagnetic interference shielding. Int J Mater Res 104:912–917
Park SH, Bae J (2017) Polymer composite containing carbon nanotubes and their applications. Recent Pat Nanotech 11:109–115
Ates M, Eker AA (2017) Carbon nanotube-based nanocomposites and their applications. J Adhes Sci Technol 31:1977–1997
Koysuren O, Yesil S, Bayram G (2007) Effect of surface treatment on electrical conductivity of carbon black filled conductive polymer composites. J Appl Polym Sci 104:3427–3433
Yu Z, He H, Wang C, Wang H, Chen Y (2018) Study on effect of ferroferric oxide and polypyrrole on antielectromagnetic radiation finishing and electromagnetic interference shielding property of cotton fabric. J silk in Chinese 55:19–24
Wang G, Wang L, Mark LH, Shaayegan V, Wang G, Li H, Zhao G, Park CB (2018) Ultralow-threshold and lightweight biodegradable porous PLA/ MWCNT with segregated conductive networks for high-performance thermal insulation and electromagnetic interference shielding applications. ACS Appl Mater Inter 10:1195–1203
An GS, Han JS, Shin JR, Cha JH, Kim BG, Jung YG, Choi SC (2019) Size- tunable carboxylic functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticle and evaluation of its magnetic and dispersion properties. J Alloy Comp D 792:1008–1012
Liu S, Wu G, Chen X, Zhang X, Yu J, Liu M, Zhang Y, Wang P (2019) Degradation behavior in vitro of carbon nanotubes (CNTs)/poly(lactic acid) (PLA) composite suture. Polymers 11:1015
Ren F, Li Z, Xu L, Sun Z, Ren P, Yan D, Li Z (2018) Large-scale preparation of segregated PLA/carbon nanotube composite with high efficient electromagnetic interference shielding and favourable mechanical properties. Compos Part B 155:405–413
Li X, Qi C, Han L, Chu C, Bai J, Guo C, Xue F, Shen B, Chu PK (2017) Influnence of dynamic compressive loading on the in vitro degradation behavior of pure PLA and mg/PLA composite. Acta Biomater 64:269–278
Gorrasi G, Milone C, Piperopoulos E, Lanza M, Sorrentino A (2013) Hybrid clay mineral-carbon nanotube-PLA nanocomposite films. Preparation and photodegradation effect on their mechanical, thermal and electrical properties. Appl Clay Sci 71:49–54
Shen B, Zhai W, Tao M, Ling J, Zheng W (2013) Lightweight, multifunctional polyetherimide/ graphene@Fe3O4 composite foams for shielding of electromagnetic pollution. ACS Appl Mater Inter 5:11383–11391
Zeng X, Yu S, Sun R, Xu J (2015) Mechanical reinforcement while remaining electrical insulation of glass fibre/polymer composites using core-shell CNT@SiO2 hybrids as fillers. Compos Part A 73:260–268
Poduval RK, Noimark S, Colchester RJ, Macdonald TJ, Parkin IP, Desjardins AE, Papakonstantinou I (2017) Optical fiber ultrasound transmitter with electrospun carbon nanotube-polymer composite. Appl Phys Lett 110:223701
Maiti S, Shrivastava NK, Suin S, Khatua BB (2013) Polystyrene/ MWCNT/ graphite nanoplate nanocomposites:efficient electromagnetic interference shielding material through graphite nanoplate-MWCNT-graphite nanoplate networking. ACS Appl Mater Inter 5:4712–4724
Zhang HM, Zhang GC, Li JT, Fan X, Jing ZX, Li JW, Shi XT (2017) Lightweight, multi-functional microcellular PMMA/ Fe3O4@ MWCNTs nanocomposite foams with efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos Part A 100:128–138
Sang G, Dong J, He X, Jiang J, Li J, Xu P, Ding Y (2019) Electromagnetic interference shielding performance of polyurethane composites: a comparative study of GNs-IL/Fe3O4 and MWCNTs-IL/Fe3O4 hybrid fillers. Compos Part B 164:467–475
Liang C, Song P, Ma A, Shi X, Gu H, Wang L, Qiu H, Kong J, Gu J (2019) Highly oriented three-dimensional structures of Fe3O4 decorated CNTs/reduced graphene oxide foam/epoxy nanocomposites against electromagnetic pollution. Compos Sci Technol 181:107683
Munir A (2015) Microwave radar absorbing properties of multiwalled carbon nanotubes polymer composites: a review. Adv Polym Technol 36:21617
Yu J, Lu W, Pei S, Gong K, Wang L, Meng L, Huang Y, Smith JP, Booksh KS, Li Q, Byun JH, Oh Y, Yan Y, Chou TW (2016) Omnidirectionally stretchable highperformance supercapacitor based on isotropic buckled carbon nanotube films. ACS Nano 10(5):5204–5211
Zhang WM, Wu XL, Hu JS, Guo YG, Wan LJ (2008) Carbon coated Fe3O4 nanospindles as a superior anode material for lithiumion batteries. Adv Funct Mater 18(24):3941–3946
Bayat M, Yang H, Ko FK, Michelson D, Mei A (2014) Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of hybrid multifunctional Fe3O4/carbon nanofiber composite. Polymer 55:936–943
Wu G, Liu S, Wu X, Ding X (2017) Core-shell structure of carbon nanotube nanocapsules reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites. J Appl Polym Sci 134:44919
Li N, Huang Y, Du F, He X, Lin X, Gao H, Ma Y, Li F, Chen Y, Eklund PC (2006) Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding of single-walled carbon nanotube epoxy composites. Nano Lett 6:1141–1145
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Open Project of Provincial-level Scientific Research Platforms of Yancheng Polytechnic College (No. YGKF-201805), the Transformation of Scientific and Technological Achievements Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi (No. 2020CG014), the Postgraduate Education Innovation Project in Shanxi (No. 2020SY466), the Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project of Taiyuan University of Technology (No. 202085), the MOE (Ministry of Education in China) Project of Humanities and Social Sciences (No. 18YJC760051), 2017 Shanxi Philosophy and Social Science Project (No. 201702) and the Program for the Philosophy and Social Sciences Research of Higher Learning Institutions of Shanxi (PSSR) (No. 201803060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Wang, P., Yang, Y. et al. Influence of MWCNTs and nano-Fe3O4 on the properties and structure of MWCNTs/ Fe3O4/PLA composite film with electromagnetic interference shielding function. J Polym Res 27, 288 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02234-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02234-x