Abstract
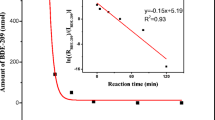
Hydrogenated bisphenol-A polycarbonate (PHBPA) was successfully synthesized from dimethyl carbonate (DMC) and hydrogenated bisphenol-A (HBPA) by the method of two-step polycondensation. The chemical structure and the molecular weight of PHBPA was identified by 1H-NMR spectra and gel permeation chromatography (GPC), respectively. In order to analyze the thermal degradation mechanism of PHBPA, a non-isothermal pyrolysis process was conducted and the violate products were detected using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS). There were some reactions occurred during the pyrolysis including decarboxylation, disproportionation of the C–H transfer and β–H transfer, and the Fries rearrangement. In addition, the well-known Flynne–Walle–Ozawa (FWO) and Coats–Redfern kinetic analysis methods were used to calculate the values of activation energy and pre-exponential factors. Furthermore, isothermal pyrolysis experiments were performed and revealed that the reaction of decarboxylation occurred at 225 °C. This decarboxylation suggests that the molecular chain of PHBPA does not easily grow to a high-molecular-weight polymer.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levchik SV, Weil ED (2005) Overview of recent developments in the flame retardancy of polycarbonates. Polym Int 54:981–998
Pang X, Ge X, Ji J, Liang W, Liu R, Chen X, Yin G, Ge J (2019) Improving oxygen permeability and thermostability of polycarbonate via copolymerization modification with bio-phenol polysiloxane. Polymers (Basel) 11:1302
Wen W, Guo J, Zhao X, Li X, Yang H, Chen JK (2018) Synthesis of an efficient S/N-based flame retardant and its application in polycarbonate. Polymers (Basel) 10:441
Poothanari MA, Xavier P, Bose S, Kalarikkal N, Komalan C, Thomas S (2019) Compatibilising action of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in polycarbonate/polypropylene (PC/PP) blends: phase morphology, viscoelastic phase separation, rheology and percolation. J Polym Res 26
Jiang L, Zhou M, Ding Y, Zhou Y, Dan Y (2018) Aging induced ductile-brittle-ductile transition in bisphenol A polycarbonate. J Polym Res 25
Feng J, Hao J, Du J, Yang R (2012) Using TGA/FTIR TGA/MS and cone calorimetry to understand thermal degradation and flame retardancy mechanism of polycarbonate filled with solid bisphenol A bis(diphenyl phosphate) and montmorillonite. Polym Degrad Stab 97:605–614
Feng Y, Li Z, Wang Y, Chen W, Wang B, Liu C, Shen C (2019) Thermal degradation behavior and kinetics of 3D porous polycarbonate monoliths. Macromol Mater Eng 304:1800667
Lee LH (1964) Mechanisms of thermal degradation of phenolic condensation polymers. I. Studies on the thermal stability of polycarbonate. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: General Papers 2:2859–2873
Puglisi C, Samperi F, Carroccio S, Montaudo G (1999) MALDI− TOF investigation of polymer degradation. Pyrolysis of poly (bisphenol A carbonate). Macromolecules 32:8821–8828
Montaudo G, Puglisi C, Samperi F (1989) Thermal decomposition processes in polycarbonates. Polym Degrad Stab 26:285–304
Davis A, Golden J (1968) Thermal degradation of polycarbonate. J Chem Soc B: Physical Organic 45–47
Puglisi C, Sturiale L, Montaudo G (1999) Thermal decomposition processes in aromatic polycarbonates investigated by mass spectrometry. Macromolecules 32:2194–2203
Jang BN, Wilkie CA (2004) A TGA/FTIR and mass spectral study on the thermal degradation of bisphenol A polycarbonate. Polym Degrad Stab 86:419–430
Bozi J, Czégény Z, Mészáros E, Blazsó M (2007) Thermal decomposition of flame retarded polycarbonates. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 79:337–345
Huang J, He C, Li X, Pan G, Tong H (2018) Theoretical studies on thermal degradation reaction mechanism of model compound of bisphenol A polycarbonate. Waste Manag 71:181–191
Jang BN, Wilkie CA (2005) The thermal degradation of bisphenol A polycarbonate in air. Thermochim Acta 426:73–84
Jiang J, Wang Y, Luo Z, Qi T, Qiao Y, Zou M, Wang B (2019) Design and application of highly efficient flame retardants for polycarbonate combining the advantages of Cyclotriphosphazene and silicone oil. Polymers (Basel) 11:1155
Feng Y, Wang B, Wang F, Zhao Y, Liu C, Chen J, Shen C (2014) Thermal degradation mechanism and kinetics of polycarbonate/silica nanocomposites. Polym Degrad Stab 107:129–138
Siddiqui MN, Redhwi HH, Antonakou EV, Achilias DS (2018) Pyrolysis mechanism and thermal degradation kinetics of poly(bisphenol A carbonate)-based polymers originating in waste electric and electronic equipment. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 132:123–133
Li G, Qin Y, Wang X, Zhao X, Wang F (2010) Study on the influence of metal residue on thermal degradation of poly(cyclohexene carbonate). J Polym Res 18:1177–1183
Janković B (2008) A kinetic study of the isothermal degradation process of Lexan® using the conventional and Weibull kinetic analysis. J Polym Res 16:213–230
Zhu W, Huang X, Li C, Xiao Y, Zhang D, Guan G (2011) High-molecular-weight aliphatic polycarbonates by melt polycondensation of dimethyl carbonate and aliphatic diols: synthesis and characterization. Polym Int 60:1060–1067
Hu Y, Qiao L, Qin Y, Zhao X, Chen X, Wang X, Wang F (2009) Synthesis and stabilization of novel aliphatic polycarbonate from renewable resource. Macromolecules 42:9251–9254
Mespouille L, Coulembier O, Kawalec M, Dove AP, Dubois P (2014) Implementation of metal-free ring-opening polymerization in the preparation of aliphatic polycarbonate materials. Prog Polym Sci 39:1144–1164
Sun J, Birnbaum W, Anderski J, Picker MT, Mulac D, Langer K, Kuckling D (2018) Use of light-degradable aliphatic polycarbonate nanoparticles as drug carrier for photosensitizer. Biomacromolecules 19:4677–4690
Durand P-L, Brège A, Chollet G, Grau E, Cramail H (2018) Simple and efficient approach toward photosensitive biobased aliphatic polycarbonate materials. ACS Macro Lett 7:250–254
Suyama T, Tokiwa Y (1997) Enzymatic degradation of an aliphatic polycarbonate, poly (tetramethylene carbonate). Enzym Microb Technol 20:122–126
Delbreilh L, Dargent E, Grenet J, Saiter JM, Bernès A, Lacabanne C (2007) Study of poly(bisphenol A carbonate) relaxation kinetics at the glass transition temperature. Eur Polym J 43:249–254
Liu C, Yu J, Sun X, Zhang J, He J (2003) Thermal degradation studies of cyclic olefin copolymers. Polym Degrad Stab 81:197–205
Tsai Y, Jheng L-C, Hung C-Y (2010) Synthesis, properties and enzymatic hydrolysis of biodegradable alicyclic/aliphatic copolyesters based on 1,3/1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol. Polym Degrad Stab 95:72–78
Zhu W, Zhou W, Li C, Xiao Y, Zhang D, Guan G, Wang D (2011) Synthesis, characterization and degradation of novel biodegradable poly(butylene-co-hexamethylene carbonate) Copolycarbonates. J Macromol Sci A 48:583–594
Zhu W, Li C, Zhang D, Guan G, Xiao Y, Zheng L (2012) Thermal degradation mechanism of poly(butylene carbonate). Polym Degrad Stab 97:1589–1595
Liu W, Zhu W, Li C, Guan G, Zhang D, Xiao Y, Zheng L (2015) Thermal degradation mechanism of poly(hexamethylene carbonate). Polym Degrad Stab 112:70–77
Yang TC-K, Lin SS-Y, Chuang T-H (2002) Kinetic analysis of the thermal oxidation of metallocene cyclic olefin copolymer (mCOC)/TiO2 composites by FTIR microscopy and thermogravimetry (TG). Polym Degrad Stab 78:525–532
Liu F, Qiu J, Wang J, Zhang J, Na H, Zhu J (2016) Role of cis-1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid in the regulation of the structure and properties of a poly(butylene adipate-co-butylene 1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylate) copolymer. RSC Adv 6:65889–65897
Brunelle DJ, Jang T (2006) Optimization of poly(1,4-cyclohexylidene cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylate) (PCCD) preparation for increased crystallinity. Polymer 47:4094–4104
Tsai Y, Jheng L-C, Hung C-Y (2010) Synthesis, properties and enzymatic hydrolysis of biodegradable alicyclic/aliphatic copolyesters based on 1,3/1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol. Polym Degrad Stab 95:72–78
Vyazovkin S, Sbirrazzuoli N (2006) Isoconversional kinetic analysis of thermally stimulated processes in polymers. Macromol Rapid Commun 27:1515–1532
Doyle C (1962) Estimating isothermal life from thermogravimetric data. J Appl Polym Sci 6:639–642
Flynn JH, Wall LA (1966) A quick, direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Lett 4:323–328
Ozawa T (1965) A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 38:1881–1886
Apaydin-Varol E, Polat S, Putun A (2014) Pyrolysis kinetics and thermal decomposition behavior of polycarbonate – a TGA-FTIR study. Therm Sci 18:833–842
Coats AW, Redfern J (1964) Kinetic parameters from thermogravimetric data. Nature 201:68–69
Abe H (2006) Thermal degradation of environmentally degradable poly(hydroxyalkanoic acid)s. Macromol Biosci 6:469–486
Abe H, Takahashi N, Kim KJ, Mochizuki M, Doi Y (2004) Effects of residual zinc compounds and chain-end structure on thermal degradation of poly(epsilon-caprolactone). Biomacromolecules 5:1480–1488
Persenaire O, Alexandre M, Degée P, Dubois P (2001) Mechanisms and kinetics of thermal degradation of poly (ε-caprolactone). Biomacromolecules 2:288–294
Abate R, Ballistreri A, Montaudo G, Impallomeni G (1994) Thermal degradation of microbial poly (4-hydroxybutyrate). Macromolecules 27:332–336
Haba O, Itakura I, Ueda M, Kuze S (1999) Synthesis of polycarbonate from dimethyl carbonate and bisphenol-A through a non-phosgene process. J Polym Sci Part A: Polym Chem 37:2087–2093
Li Q, Zhu W, Li C, Guan G, Zhang D, Xiao Y, Zheng L (2013) A non-phosgene process to homopolycarbonate and copolycarbonates of isosorbide using dimethyl carbonate: synthesis, characterization, and properties. J Polym Sci Part A: Polym Chem 51:1387–1397
Acknowledgements
The financial support from the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China (MOST 109-3116-F-006-015-CC1 and MOST 108-2221-E-006-001-) is gratefully acknowledged. The authors also gratefully acknowledge the use of Bruker Avance 600NMR Spectrometer equipment belonging to the Instrument Center of National Cheng Kung University, and the use of TGA-GC/MS equipment belonging to the Instrument Center of National Tsing Hua University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, YH., Wang, CC. & Chen, CY. The thermal degradation mechanism and kinetic analysis of hydrogenated bisphenol-A polycarbonate. J Polym Res 27, 246 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02204-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02204-3