Abstract
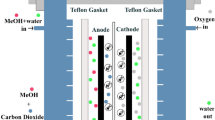
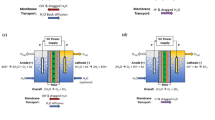
Novel sulfonated diamine (NSDA) having pendant sulfonic acid group was synthesized. Polycondensation reaction of this NSDA, dianhydride, and graphene oxide (GO) yielded sulfonated imidized graphene oxide (SIGO). Sulfonated imidized graphene oxide(SIGO) along with NSDA, 4,4′-oxydianiline (ODA) and 1,4,5,8-naphthalene tetracarboxylic dianhydride dianhydride(NTDA) were used for the preparation of polymer electrolyte membranes (PEMs). High temperature proton conduction due to the hydrophobic- hydrophilic phase separation resulted from the incorporation of SIGO. 2.28 meq/g of ion exchange capacity (IEC), 11.18 × 10−2 S/cm of proton conductivity at room temperature and bound water of worth 5.1% between temperature ranges of 100 °C to 150 °C were exhibited by NSPI/3 wt%SIGO composite membrane. Maximum power density of 74.9 mWcm−2 was achieved at 70 °C by NSPI/ 3% SIGO in single cell direct methanol fuel cell test. All these results make these composite membranes suitable candidate to be used as PEM.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hou J, Shao Y, Ellis MW, Moore RB, Yi B (2011) Graphene based electrochemical energy conversion and storage: fuel cells,supercapacitors and lithium ion batteries. J Phys Chem Chem Phys 13(34):15384–15402
Geim AK, Novoselov KS (2007) The rise of graphene. Nat Mater 6:183–191
Zhu Y, Murali S, Cai W, Li X, Suk JW, Potts JR, Ruoff RS (2010) Graphene and graphene oxide: synthesis, properties and applications. Adv Mater 22:3906–3924
Compton OC, Nguyen ST (2010) Graphene oxide,highly reduced graphene oxide and graphene : versatile building blocks for carbon based materials. Small 6(6):711–723
Nair RR, Blake P, Grigorenko AN, Novoselov KS, Booth TJ, Stauber T, Peres NMR, Geim AK (2008) Fine structure constant defines visual transparency of graphene. Science. 320(5881):1308
Neto AHC, Guinea F, Peres NMR, Novoselov KS, Geim AK (2009) The electronic properties of graphene. Rev Mod Phys 81(1):109–162
Geim AK (2009) Graphene status and prospects. Science. 324(5934):1530–1534
Yu S, Liu Q, Yang W, Han K, Wang Z, Zhu H (2013) Graphene-CeO2 hybrid support for Pt nanoparticles as potential electrocatalyst for direct methanol fuel cells. Electrochim Acta 94:245–251
Saito M, Arimura N, Hayamizu K, Okada T (2004) Mechanism of ion exchange and water transport in Perfluorosulfonated ionomer membranes for fuel cells. J Phys Chem B 108:16064–16070
Miyake N, Wainright JS, Savinell RF (2001) Evaluation of a sol-gel derived nafion-silica hybrid membrane for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell applications: II. Methanol uptake and methanol permeability. J Electrochem 148(8):A905–A909
Pineri M, Gebel G, Davies RJ, Diat O (2007) Water sorption and desorption in nafion membrane at low temperature probed by micro x-ray diffraction. J Power Sources 172(2):587–596
Hou J, Yu H, Wang L, Xing D, Hou Z, Ming P, Shao Z, Yi B (2008) Conductivity of aromatic based proton exchange membranes at sub zero temperatures. J Power Sources 180(1):232–237
Zhang H, Shen PK (2012) Recent development of polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cell. Chem Rev 112(5):2780–2832
Pandey RP, Shahi VK (2013) Aliphatic-aromatic sulphonated polyimide and acid functionalized polysilsesquioxane composite membranes for fuel cell applications. J Mater Chem A 1(45):14375–14383
Chen BK, Wu TY, Kuo CW, Peng YC, Shih IC, Hao L, Sun IW (2013) 4,4-Oxydianiline (ODA) containing sulfonated polyimide/protic ionic liquid composite membranes for anhydrous proton conduction. Int J Hydrog Energy 38(26):11321–11330
Feizi LA, Ataei SM, Yeganeh H (2010) Survey of sulfonated polyimide membrane as a good candidate for nafion substitution in fuel cell. Int J Hydrog Energy 35(17):9385–9397
Chen BK, Wrong JM, Wu TY, Chen LC, Shih IC (2014) Improving the conductivity of sulfonated polyimides as proton exchange membranes by doping of a protic ionic liquid. Polymer 6(11):2720–2736
Lee SY, Yasuda T, Watanabe M (2010) Fabrication of protic ionic liquid/sulfonated polyimide composite membranes for non humidified fuel cells. J Power Sources 195:5909–5914
Tseng CY, Ye YS, Cheng MY, Kao KY, Shen WC, Rick J (2011) Sulfonated polyimide proton exchange membranes with graphene oxide show improved proton conductivity,methanol crossover impedance and mechanical properties. Adv Energy Mater 1(6):1220–1224
Shukla G, Pandey RP, Shahi VK (2016) Temperature resistant phosphorylated graphene oxide sulphonated polyimide composite caation exchange membrane for water desalination with improved performance. J Membr Sci 520:972–982
He Y, Tong C, Geng I, Liu I, Lu C (2014) Enhanced performance of the sulfonated polyimide proton exchange membranes by graphene oxide: size effect of graphene oxide. J Membr Sci 458:36–46
Kowsari E, Zare A, Anasri V (2015) Phosphoric acid doped ionic liquid functionalized graphene oxide/sulfonated polyimide composites as proton exchange membrane. Int J Hydrog Energy 40(40):13964–13978
Pandey RP, Shahi VK (2015) Sulfonated imidized graphene oxide based polymer electrolyte membrane for improved water retention,stability and proton conductivity. J Power Sources 299:104–113
Ma W, Wu L, Zhang D, Wang S (2013) Preparation and properties of 3- aminopropyl-triethoxysilane functionalized graphene/polyurethane nanocomposite coating. Colloid Polym Sci 291(12):2765–2773
Ma WS, Li J, Zhao XS (2013) Improving the thermal and mechanical properties of silicone polymer by incorporating functionalized graphene oxide. J Mater Sci 48(15):5287–5294
Wootthikanokkhan J, Seeponkai N (2006) Methanol permeability and properties of DMFC membranes based on sulfonated PEEK/PVDF blends. J Appl Polym Sci 102(6):5941–5947
Heo Y, Im H, Kim J (2013) The effect of sulfonated graphene oxide on sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) membrane for direct methanol fuel cells. J Membr Sci 425-426:11–22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rehman, W., Liaqat, K., Fazil, S. et al. Chemically tethered functionalized graphene oxide based novel sulfonated polyimide composite for polymer electrolyte membrane. J Polym Res 26, 82 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1744-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1744-2