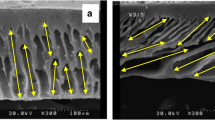
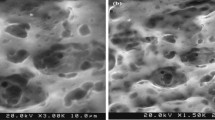
Abstract
This study aims to form a dynamic layer of the magnetic protective layer (f- Fe3O4/PDDA) on a surface of cellulose acetate (CA) membrane to prevent direct membrane-foulant interactions during an ultrafiltration process. To this end, Fe3O4 nanoparticles with an approximate size of 151.8 ± 8.2 nm were spin-coated on the surface of CA membrane to provide magneto-induced actuation motions of the magnetic nano-colloid in 3-dimensional space, with the help of an external magnetic field (magnetic rod). ATR-FTIR, QCM-D, and cross-flow filtration of this magnetic-responsive membrane were investigated to determine its influences on surface fouling by humic acid solutions. In fact, ATR-FTIR and QCM-D analyses have demonstrated a minimum membrane fouling for the magnetic-responsive membrane that operated under the influence of an oscillating magnetic field. Cross-flow filtration results showed a practically higher permeation (retaining 54% of the initial flux at its steady-flow) and humic acid rejection (more than 85%) in the presence of an oscillating magnetic field compared to its performance in the absence of an oscillating magnetic field. Findings from this magnetically responsive membranes could represent a new class of fouling-resistant membrane.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nazri NAM, Lau WJ, Padaki M, Ismail AF (2014) A facile modification approach for polyacrylonitrile-based UF hollow fiber membrane utilizing polyacrylonitrile-g-poly(vinyl alcohol) graft copolymer. J Polym Res 21:594
Mahdavi H, Norouzian S (2018) Preparation and characterization of modified ultrafiltration nylon 6 membrane modified by poly (acrylamide-co-maleic anhydride). J Polym Res 25
Ostrowska-Czubenko J, Gierszewska M, Pieróg M (2015) pH-responsive hydrogel membranes based on modified chitosan: water transport and kinetics of swelling. J Polym Res 22:153
Hernández S, Saad A, Ormsbee L, Bhattacharyya D (2016) Chapter 16 - nanocomposite and responsive membranes for water treatment. In: Hankins NP, Singh R (eds) Emerging membrane Technology for Sustainable Water Treatment. Elsevier Boston, pp 389–431
López-Roldán R, Rubalcaba A, Martin-Alonso J, González S, Martí V, Cortina JL (2016) Assessment of the water chemical quality improvement based on human health risk indexes: application to a drinking water treatment plant incorporating membrane technologies. Sci Total Environ 540:334–343
Dutta K, De S (2017) Smart responsive materials for water purification: an overview. J Mater Chem A 5:22095–22112
Zhao Y, Zhao H, Chen L, Feng X, Zhang Q, Wang J, Zhang R (2013) Thermo-responsive modification and properties study of PVDF flat membrane. J Polym Res 20:58
Zhao Y, Bai J, Feng X, Chen L, Shen X, Liu M, Li J (2013) Properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride)-graft-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) membranes prepared by alkali treatment. J Polym Res 20:32
Wandera D, Wickramasinghe SR, Husson SM (2010) Stimuli-responsive membranes. J Membr Sci 357:6–35
Chu L, Xie R, Ju X (2011) Stimuli-responsive membranes: smart tools for controllable mass-transfer and separation processes. Chin J Chem Eng 19:891–903
Yang Q, Himstedt HH, Ulbricht M, Qian X, Ranil Wickramasinghe S (2013) Designing magnetic field responsive nanofiltration membranes. J Membr Sci 430:70–78
Low SC, Ng QH (2019) Progress of stimuli responsive membrane in water treatment. In: Ismail AF, Al-Ahmed A (eds) Lau WJ, Arun M Isloor. Advanced Nanomaterials for Membrane Synthesis and Its Applications. Elsevier Inc. Amsterdam, Netherlands
Husson SM (2012) Synthesis Aspects in the Design of Responsive Membranes. In: Bhattacharyya D, Schafer T, Wickramasinghe SR, Daunert S (eds) Responsive Membranes and Materials. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd Chichester, West Sussex, England
Karppi J, Åkerman S, Åkerman K, Sundell A, Penttilä I (2010) Adsorption of metal cations from aqueous solutions onto the pH responsive poly(vinylidene fluoride grafted poly(acrylic acid) (PVDF-PAA) membrane. J Polym Res 17:71–76
Ng QH, Lim JK, Ahmad AL, Ooi BS, Low SC (2014) Efficacy evaluation of the antifouling magnetite-PES composite membrane through QCM-D and magnetophoretic filtration performances. Sep Purif Technol 132:138–148
Jian P, Yahui H, Yang W, Linlin L (2006) Preparation of polysulfone–Fe3O4 composite ultrafiltration membrane and its behavior in magnetic field. J Membr Sci 284:9–16
Wang R, Chen Y, Xie H, Kai G, Wang Z, Pan J (2011) Polysaccharide separation mechanism in polysulfone-Fe3O4 magnetic composite membranes. Chin Sci Bull 56:1951–1956
Ng QH, Lim JK, Ahmad AL, Ooi BS, Low SC (2015) Magnetic nanoparticles augmented composite membranes in removal of organic foulant through magnetic actuation. J Membr Sci 493:134–146
Ng QH, Lim JK, Ahmad AL, Low SC (2016) Stability and fouling mechanism of magnetophoretic-actuated PES composite membrane in pH-dependent aqueous medium. J Membr Sci 508:40–50
Feng M, Meng F, Pu Z, Jia K, Liu X (2015) Introducing magnetic-responsive CNT/Fe3O4composites to enhance the mechanical properties of sulfonated poly(arylene ether nitrile) proton-exchange membranes. J Polym Res 22:37
Lin X, Nguyen Quoc B, Ulbricht M (2016) Magnetoresponsive poly(ether sulfone)-based Iron oxide cum hydrogel mixed matrix composite membranes for switchable molecular sieving. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:29001–29014
Himstedt HH, Yang Q, Dasi LP, Qian X, Wickramasinghe SR, Ulbricht M (2011) Magnetically activated micromixers for separation membranes. Langmuir 27:5574–5581
Lin H, Sun W, Zhao C, Na H (2013) Self-assembly of multiwall carbon nanotubes on sulfonated poly (arylene ether ketone) as a proton exchange membrane. J Polym Res 20:306
Yu D-G, Jou C-H, Lin W-C, Yang M-C (2007) Surface modification of poly(tetramethylene adipate-co-terephthalate) membrane via layer-by-layer assembly of chitosan and dextran sulfate polyelectrolyte multiplayer. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 54:222–229
Ng QH, Lim JK, Ahmad AL, Ooi BS, Low SC (2014) Enhance the colloidal stability of magnetite nanoparticles using poly(sodium 4-styrene sulfonate) stabilizers. Appl Mech Mater 625:168–171
Lim JK, Majetich SA, Tilton RD (2009) Stabilization of superparamagnetic iron oxide core-gold shell nanoparticles in high ionic strength media. Langmuir 25:13384–13393
Lim JK, Yeap SP, Che HX, Low SC (2013) Characterization of magnetic nanoparticle by dynamic light scattering. Nanoscale Res Lett 8:381
Wandrey C, Hernandez-Barajas J, Hunkeler D (1999) Diallyldimethylammonium chloride and its polymers. In: Capek I (ed) Radical polymerization - polyelectrolytes. Springer Verlag, pp 123–183
Zhang S, Shao Y, Yin G, Lin Y (2009) Stabilization of platinum nanoparticle electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction using poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride). J Mater Chem 19:7995–8001
Lim JK, Chieh DCJ, Jalak SA, Toh PY, Yasin NHM, Ng BW, Ahmad AL (2012) Rapid Magnetophoretic separation of microalgae. Small 8:1683–1692
Fischer D, Dautzenberg H, Kunath K, Kissel T (2004) Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chlorides) and their N-methyl-N-vinylacetamide copolymer-based DNA-polyplexes: role of molecular weight and charge density in complex formation, stability, and in vitro activity. Int J Pharm 280:253–269
Meissl K, Smidt E, Schwanninger M (2007) Prediction of humic acid content and respiration activity of biogenic waste by means of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra and partial least squares regression (PLS-R) models. Talanta 72:791–799
Ma L, Su WY, Gan MY, Li XF, Luo LZ (2011) Effects of FeCl3/ammonium persulfate composite oxidant and magnetic field on film growth rate of polyaniline doped with dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid. J Polym Res 18:595–599
Mettai B, Mekki A, Merdj F, Sayah ZBD, Soumia KM, Safiddine Z, Mahmoud R, Chehimi MM (2018) In situ chemical deposition of PPy/NDSA and PPy/DBSA layers on QCM electrodes: synthesis, structural, morphological and ammonia sensing performances study. J Polym Res 25:95
Sauerbrey G (1959) Verwendung von Schwingquarzen zur Wägung dünner Schichten und zur Mikrowägung. Z Phys 155:206–222
Li N, Lee HK (2001) Solid-phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water: negative effect of humic acid. J Chromatogr A 921:255–263
Rodrigues A, Brito A, Janknecht P, Proenca MF, Nogueira R (2009) Quantification of humic acids in surface water: effects of divalent cations, pH, and filtration. J Environ Monit 11:377–382
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the financial support granted by Universiti Sains Malaysia RUI grant (814230).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Low, S.C., Ng, Q.H. & Tan, L.S. Study of magnetic-responsive nanoparticle on the membrane surface as a membrane antifouling surface coating. J Polym Res 26, 70 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1734-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1734-4