Abstract
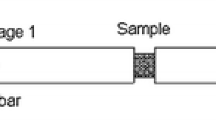
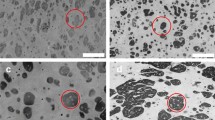
To benefit from nano-rubber copolymers, the properties and dynamic behavior of nano-rubbers reinforced Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA) were investigated. Dynamic tests were conducted on these materials at high strain rates and different temperatures using split Hopkinson pressure bars. The impact resistance of these materials was studied by performing low velocity impact tests with a drop weight tower at different impact energies and temperatures. The results showed decreased Young’s moduli and yield stresses. The mechanical behavior of the materials exhibited strain rate and temperature dependencies. Moreover, the nano-rubber-reinforced PMMA showed outstanding impact resistance compared with neat PMMA. The modified PMMA also exhibited impact properties similar to those of polycarbonate for certain ranges of impact energies and temperatures. No perforations were observed for all those energies and temperatures.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schirrer R (2001) Section 6.12 - damage mechanisms in amorphous glassy polymers: crazing. In: Lemaitre J (ed) Handbook of materials behavior models. Academic, Burlington, pp 488–499
Satapathy S, Bless S (2000) Deep punching PMMA. Exp Mech 40:31–37
(2005) Arkema launches Nanostrength for advanced composite materials. Addit Polym 2005(6):3. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-3747(05)70387-0
van der Sanden MCM, de Kok JMM, Meijer HEH (1994) Deformation and toughness of polymeric systems: 7. Influence of dispersed rubbery phase. Polymer 35:2995–3004
Bagheri R, Pearson RA (1996) Role of particle cavitation in rubber-toughened epoxies: 1. Microvoid toughening. Polymer 37:4529–4538
Hourston DJ, Lane JM (1992) The toughening of epoxy resins with thermoplastics: 1. Trifunctional epoxy resin-polyetherimide blends. Polymer 33:1379–1383
Baniassadi M, Laachachi A, Hassouna F, Addiego F, Muller R, Garmestani H, Ahzi S, Toniazzo V, Ruch D (2011) Mechanical and thermal behavior of nanoclay based polymer nanocomposites using statistical homogenization approach. Compos Sci Technol 71:1930–1935
Goyat MS, Ray S, Ghosh PK (2011) Innovative application of ultrasonic mixing to produce homogeneously mixed nanoparticulate-epoxy composite of improved physical properties. Compos A: Appl Sci Manuf 42:1421–1431
Matadi Boumbimba R, Bouquey M, Muller R, Jourdainne L, Triki B, Hébraud P, Pfeiffer P (2012) Dispersion and morphology of polypropylene nanocomposites: characterization based on a compact and flexible optical sensor. Polym Test 31:800–809
Basara C, Yilmazer U, Bayram G (2005) Synthesis and characterization of epoxy based nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 98:1081–1086
Matadi Boumbimba R, Froustey C, Viot P, Olive JM, Léonardi F, Gerard P, Inoubli R (2014) Preparation and mechanical characterisation of laminate composites made of glass fibre/epoxy resin filled with tri bloc copolymers. Compos Struct 116:414–422
Liu L, Wagner HD (2005) Rubbery and glassy epoxy resins reinforced with carbon nanotubes. Compos Sci Technol 65:1861–1868
Hwang GL, Hwang KC (2001) Breakage, fusion, and healing of carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett 1:435–438
Varela-Rizo H, Weisenberger M, Bortz DR, Martin-Gullon I (2010) Fracture toughness and creep performance of PMMA composites containing micro and nanosized carbon filaments. Compos Sci Technol 70:1189–1195
Liu J, Rasheed A, Minus ML, Kumar S (2009) Processing and properties of carbon nanotube/poly(methyl methacrylate) composite films. J Appl Polym Sci 112:142–156
Bakshi SR, Singh V, Graham D, McCartney SS, Agarwal A (2008) Deformation and damage mechanisms of multiwalled carbon nanotubes under high-velocity impact. Scr Mater 59:499–502
Feng J, Hao J, Du J, Yang R (2012) Using TGA/FTIR TGA/MS and cone calorimetry to understand thermal degradation and flame retardancy mechanism of polycarbonate filled with solid bisphenol a bis(diphenyl phosphate) and montmorillonite. Polym Degrad Stab 97:605–614
Chehata N, Ltaief A, Bkakri R, Bouazizi A (2014) Optical and electrical properties of conducting polymer-functionalized carbon nanotubes nanocomposites. Mater Sci Semicond Process 22:7–15
Tran TA, Leonardi F, Bourrigaud S, Gerard P, Derail C (2008) All acrylic block copolymers based on poly (methyl methacrylate) and poly (butyl acrylate). A link between the physico-chemical properties and the mechanical behaviour on impact tests. Polym Test 27:945–950
Lalande L, Plummer CJG, Månson J-AE, Gérard P (2006) Microdeformation mechanisms in rubber toughened PMMA and PMMA-based copolymers. Eng Fract Mech 73:2413–2426
Rubin A, Rébutin N, Gérard P, Gauthier C (2014) Mechanical properties of a rubber-reinforced block copolymer PMMA: effect of the nanostructuration on tribological performances. Mater Lett 135:184–187
Gerard P, Couvreur L, Magnet S, Ness J, Schmidt S (2009) Controlled architecture polymers at Arkema: synthesis, morphology and properties of all-acrylic block copolymers. In: Controlled/living radical polymerization: progress in RAFT, DT, NMP & OMRP American Chemical Society, pp 361–373
Wang K, Boumbimba RM, Bahlouli N, Ahzi S, Muller R, Bouquey M (2012) Dynamic behaviour of a melt mixing polypropylene organoclay nanocomposites. J Eng Mater Technol 134:010905
Wang K, Addiego F, Bahlouli N, Ahzi S, Rémond Y, Toniazzo V (2014) Impact response of recycled polypropylene-based composites under a wide range of temperature: effect of filler content and recycling. Compos Sci Technol 95:89–99
Richeton J, Ahzi S, Daridon L, Rémond Y (2005) A formulation of the cooperative model for the yield stress of amorphous polymers for a wide range of strain rates and temperatures. Polymer 46:6035–6043
Fotheringham D, Cherry BW, Bauwens-Crowet C (1976) Comment on "the compression yield behaviour of polymethyl methacrylate over a wide range of temperatures and strain-rates". J Mater Sci 11:1368–1371
Bauwens-Crowet C, Bauwens JC (1983) Effect of thermal history on the tensile yield stress of polycarbonate in the β transition range. Polymer 24:921–924
Z. El-Qoubaa, R. Othman, Characterization and modeling of the strain rate sensitivity of polyetheretherketone’s compressive yield stress, Materials & Design, 66, Part A (2015) 336–345
Ree T, Eyring H (1958) CHAPTER 3 - THE RELAXATION THEORY OF TRANSPORT PHENOMENA. In: Eirich FR (ed) Rheology. Academic Press, New York, pp 83–144
Matadi R, Gueguen O, Ahzi S, Gracio J, Muller R, Ruch D (2010) Investigation of the stiffness and yield behaviour of melt-intercalated poly(methyl methacrylate)/organoclay nanocomposites: characterisation and modelling. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 10:2956–2961
Vecchio KS, Jiang F (2007) Improved pulse shaping to achieve constant strain rate and stress equilibrium in split-Hopkinson pressure bar testing. Metall Mater Trans A 38:2655–2665
Brostow W (2009) Reliability and prediction of long-term performance of polymer-based materials. Pure Appl Chem 81:417
Rusinek A, Bernier R, Boumbimba RM, Klosak M, Jankowiak T, Voyiadjis GZ (2018) New devices to capture the temperature effect under dynamic compression and impact perforation of polymers, application to PMMA. Polym Test 65:1–9
Pawlak A, Galeski A, Rozanski A (2014) Cavitation during deformation of semicrystalline polymers. Prog Polym Sci 39:921–958
Lalande L, Plummer CJG, Månson J-AE, Gérard P (2006) The influence of matrix modification on fracture mechanisms in rubber toughened polymethylmethacrylate. Polymer 47:2389–2401
Matadi Boumbimba R, Froustey C, Viot P, Gerard P (2015) Low velocity impact response and damage of laminate composite glass fibre/epoxy based tri-block copolymer. Compos Part B 76:332–342
Bashar MT, Sundararaj U, Mertiny P (2013) Mode-I interlaminar fracture behaviour of nanoparticle modified epoxy/basalt fibre-reinforced laminates. Polym Test 32:402–412
Wu J, Thio YS, Bates FS (2005) Structure and properties of PBO–PEO diblock copolymer modified epoxy. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 43:1950–1965
Yang X, Yi F, Xin Z, Zheng S (2009) Morphology and mechanical properties of nanostructured blends of epoxy resin with poly(ɛ-caprolactone)-block-poly(butadiene-co-acrylonitrile)-block-poly(ɛ-caprolactone) triblock copolymer. Polymer 50:4089–4100
Bashar M, Sundararaj U, Mertiny P (2011) Study of matrix micro-cracking in nano clay and acrylic tri-block-copolymer modified epoxy/basalt fiber-reinforced pressure-retaining structures. Express Polym Lett 5:882–896
Inberg JPF, Gaymans RJ (2002) Polycarbonate and co-continuous polycarbonate/ABS blends: influence of notch radius. Polymer 43:4197–4205
Shah QH (2009) Impact resistance of a rectangular polycarbonate armor plate subjected to single and multiple impacts. Int J Impact Eng 36:1128–1135
Xu Y, Lu H, Gao T, Zhang W (2015) Predicting the low-velocity impact behavior of polycarbonate: influence of thermal history during injection molding. Int J Impact Eng 86:265–273
Cheng S-K, Chen C-Y (2004) Mechanical properties and strain-rate effect of EVA/PMMA in situ polymerization blends. Eur Polym J 40:1239–1248
Wu S (1985) Phase structure and adhesion in polymer blends: a criterion for rubber toughening. Polymer 26:1855–1863
Park JH, Jana SC (2003) The relationship between nano- and micro-structures and mechanical properties in PMMA–epoxy–nanoclay composites. Polymer 44:2091–2100
Tiwari RR, Natarajan U (2008) Thermal and mechanical properties of melt processed intercalated poly(methyl methacrylate)–organoclay nanocomposites over a wide range of filler loading. Polym Int 57:738–743
Fischer B, Ziadeh M, Pfaff A, Breu J, Altstädt V (2012) Impact of large aspect ratio, shear-stiff, mica-like clay on mechanical behaviour of PMMA/clay nanocomposites. Polymer 53:3230–3237
Acknowledgements
This study has been carried out in collaboration with ARKEMA research team of Lacq (France). We also thank Mr. Adoté Situ BLIVI for his help and his availability.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matadi Boumbimba, R., Coulibaly, M., Peng, Y. et al. Investigation of the impact response of PMMA-based nano-rubbers under various temperatures. J Polym Res 25, 76 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-018-1479-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-018-1479-5