Abstract
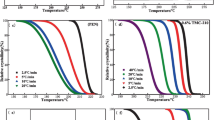
Low crystallization rate and inherent brittleness characteristics limit the wide application of PET. In this paper, it was found that a low molecular weight Phenyl phosphonic acid salts compound (TMC-210) is a very effective nucleator and can enhance the impact strength very much. So, the effect of TMC-210 on the crystallization behaviour and mechanical properties of poly(ethylene terephthalate) were systematically evaluated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), polarized optical microscopy (POM), wide angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and mechanical properties test. The results show that TMC-210 obviously improves the crystallization temperature and accelerates the crystallization rate of PET and reflects a significant heterogeneous nucleating effect with a nucleation efficiency of 99.8 % when introducing a low content of 0.6 wt% TMC-210. The spherulites size and number of blended PET are greater than pure PET. The crystal structure of PET does not change but the blends with high TMC-210 content appears new diffraction peaks in x-ray diffraction spectrogram and it may attribute to the agglomeration of TMC-210 particles, which is verified by SEM observation. The impact fracture surface of PET develops a brittle ductile transition and thus the impact strength of PET improves significantly. Additionally, Lauritzen–Hoffman equation was used to discuss the effect of TMC-210 on the fold surface free energy (σ e) of PET in the crystallization process and found that the σ e values of PET/TMC-210 blends is smaller than that of pure PET.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haubruge HG, Jonas AM, Legras R (2004) Morphological study of melt-crystallized poly(ethylene terephthalate). A. Comparison of transmission electron microscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering of bulk samples. Macromolecules 37(1):126–134
Durmus A, Ercan N, Soyubol G, Deligöz H, Kaşgöz A (2009) Nonisothermal crystallization kinetics of poly(ethylene terephthalate)/clay nanocomposites prepared by melt processing. Polym Compos:1056–1066
Tang S, Xin Z (2009) Structural effects of ionomers on the morphology, isothermal crystallization kinetics and melting behaviors of PET/ionomers. Polymer 50(4):1054–1061
Wang Q, Keffer DJ, Petrovan S, Thomas JB (2010) Molecular dynamics simulation of poly(ethylene terephthalate) oligomers. J Phys Chem B 114(2):786–795
Tao Y, Mai K (2007) Non-isothermal crystallization and melting behavior of compatibilized polypropylene/recycled poly(ethylene terephthalate) blends. Eur Polym J 43(8):3538–3549
Chen H, Pyda M, Cebe P (2009) Non-isothermal crystallization of PET/PLA blends. Thermochim Acta 492(1–2):61–66
Antoniadis G, Paraskevopoulos KM, Vassiliou AA, Papageorgiou GZ, Bikiaris D, Chrissafis K (2011) Nonisothermal melt-crystallization kinetics for in situ prepared poly(ethylene terephthalate)/monmorilonite (PET/OMMT). Thermochim Acta 521(1–2):161–169
Calcagno CIW, Mariani CM, Teixeira SR, Mauler RS (2007) The effect of organic modifier of the clay on morphology and crystallization properties of PET nanocomposites. Polymer 48(4):966–974
Pan P, Liang Z, Cao A, Inoue Y (2009) Layered metal phosphonate reinforced poly (L-lactide) Composites with a highly enhanced crystallization rate. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1(2):402–411
Shen Z, Luo F, Xing Q, Si P, Lei X, Ji L, Ding S, Wang K (2016) Effect of an aryl amide derivative on the crystallization behaviour and impact toughness of poly(ethylene terephthalate). CrystEngComm 18:2135–2143
Cui Z, Qiu Z (2015) Thermal properties and crystallization kinetics of poly(butylene suberate). Polymer 67:12–19
Lim JY, Kim J, Kim S, Kwak S, Lee Y, Seo Y (2015) Nonisothermal crystallization behaviors of nanocomposites of poly(vinylidene fluoride) and multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Polymer 62:11–18
Xu T, Zhang A, Zhao Y, Han Z, Xue L (2015) Crystallization kinetics and morphology of biodegradable poly(lactic acid) with a hydrazide nucleating agent. Polym Test 45:101–106
Cruz-Delgado VJ, Ávila-Orta CA, Espinoza-Martínez AB, Mata-Padilla JM, Solis-Rosales SG, Jalbout AF, Medellín-Rodríguez FJ, Hsiao BS (2014) Carbon nanotube surface-induced crystallization of polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polymer 55:642–650
Hao W, Wang X, Yang W, Zheng K (2012) Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of recycled PET-Si3N4 nanocomposites. Polym Test 31(1):110–116
Fillon B, Lotz B, Thierry A, Wittmann JC (1993) Self-nucleation and enhanced nucleation of polymers. Definition of a convenient calorimetric “efficiency scale” and evaluation of nucleating additives in isotactic polypropylene (α phase). J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 31(10):1395–1405
Hong P-D, Chung W-T, Hsu C-F (2002) Crystallization kinetics and morphology of poly(trimethylene terephthalate). Polymer 43(11):3335–3343
Dou J, Liu Z (2013) Crystallization behavior of poly(ethylene terephthalate)/pyrrolidinium ionic liquid. Polym Int 62(12):1698–1710
Medellin-Rodriguez FJ, Phillips PJ, Lin JS (1995) Application of secondary nucleation theory to Semirigid macromolecules: PEEK, PET, and PEN. Macromolecules 28(23):7744–7755
XF L, Hay JN (2001) Isothermal crystallization kinetics and melting behaviour of poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polymer 42(23):9423–9431
Hu G, Feng X, Zhang S, Yang M (2008) Crystallization behavior of poly(ethylene terephthalate)/multiwalled carbon nanotubes composites. J Appl Polym Sci 108(6):4080–4089
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21264012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We are sure that this work is original research and is not submitted to any other journal and there is no conflict of interest both for financial support or relationships.
Additional information
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21264012).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Z., Luo, F., Lei, X. et al. Enhanced crystallization behaviour and impact toughness of poly(ethylene terephthalate) with a phenyl phosphonic acid salts compound. J Polym Res 23, 212 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-016-1108-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-016-1108-0