Abstract
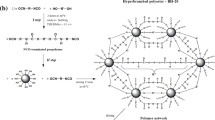
Polystyrene-based polyHIPEs were synthesized by RAFT polymerization and strengthened by introducing UPy groups (2-Ureido-4[1H] pyrimidinone) into polyHIPEs. Incorporation of UPy groups into polyHIPEs has created pores and controlled the porous morphology of resulting material. Meanwhile, the incorporation of quadruple hydrogen bond introduced some pins into polyHIPE. In comparison to the polyHIPE without reinforcement through quadruple hydrogen bond, the porosity of the reinforced sample was as high as 92 % and its Young’s modulus reached to 28.5 ± 3.9 MPa which was improved by 50 %.

ᅟ









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Ballard N, Gayet F, Bon SA (2012) High internal phase emulsion gels (HIPE-gels) from polymer dispersions reinforced with quadruple hydrogen bond functionality. Chem Commun 48(8):1117–1119. doi:10.1039/c2cc16670d
Cheng C, Gong S, Fu Q, Shen L, Liu Z, Qiao Y, Fu C (2010) Hexamethylenetetramine as both a ligand and a reducing agent in AGET atom transfer radical batch emulsion polymerization. Polym Bull 66(6):735–746. doi:10.1007/s00289-010-0305-y
Xu WF, Bai R, Zhang FA (2014) Effects of internal-phase contents on porous polymers prepared by a high-internal-phase emulsion method. J Polym Res 21(9). doi:10.1007/S10965-014-0524-2
Tsagalas L (2008) Production of porous electrodes for fuel cells supports. University of Notre Dame, Dissertation Abstracts International
Kovacic S, Kren H, Krajnc P, Koller S, Slugovc C (2013) The use of an emulsion templated microcellular poly(dicyclopentadiene-co-norbornene) membrane as a separator in lithium-ion batteries. Macromol Rapid Commun 34(7):581–587. doi:10.1002/marc.201200754
Yang Y, Wei Z, Wang C, Tong Z (2013) Lignin-based Pickering HIPEs for macroporous foams and their enhanced adsorption of copper(ii) ions. Chem Commun 49(64):7144–7146. doi:10.1039/c3cc42270d
Tunc Y, Golgelioglu C, Tuncel A, Ulubayram K (2012) Polystyrene-based high internal phase emulsion polymer monolithic stationary phase for capillary electrochromatography. Sep Sci Technol 47(16):2444–2449. doi:10.1080/01496395.2012.672846
Wang YC, Tao SY, An YL (2013) A reverse membrane emulsification process based on a hierarchically porous monolith for high efficiency water-oil separation. J Mater Chem A 1(5):1701–1708. doi:10.1039/c2ta00007e
Fernández-Trillo F, van Hest JCM, Thies JC, Michon T, Weberskirch R, Cameron NR (2009) Reversible immobilization onto PEG-based emulsion-templated porous polymers by co-assembly of stimuli responsive polymers. Adv Mater 21(1):55–59. doi:10.1002/adma.200801986
Pierre SJ, Thies JC, Dureault A, Cameron NR, van Hest JCM, Carette N, Michon T, Weberskirch R (2006) Covalent enzyme immobilization onto photopolymerized highly porous monoliths. Adv Mater 18(14):1822–1826. doi:10.1002/adma.200600293
Zhang H, Lv X, Li Y, Wang Y, Li J (2009) P25-graphene composite as a high performance photocatalyst. ACS Nano 4(1):380–386. doi:10.1021/nn901221k
Viswanathan P, Chirasatitsin S, Ngamkham K, Engler AJ, Battaglia G (2012) Cell instructive microporous scaffolds through interface engineering. J Am Chem Soc 134(49):20103–20109. doi:10.1021/ja308523f
Zhang QC, Tan K, Ye ZY, Zhang Y, Tan WS, Lang MD (2012) Preparation of open porous polycaprolactone microspheres and their applications as effective cell carriers in hydrogel system. Mater Sci Eng C 32(8):2589–2595. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2012.07.045
Caldwell S, Johnson DW, Didsbury MP, Murray BA, Wu JJ, Przyborski SA, Cameron NR (2012) Degradable emulsion-templated scaffolds for tissue engineering from thiol-ene photopolymerisation. Soft Matter 8(40):10344–10351. doi:10.1039/c2sm26250a
Li ZF, Xiao MD, Wang JF, Ngai T (2013) Pure protein scaffolds from Pickering high internal phase emulsion template. Macromol Rapid Commun 34(2):169–174. doi:10.1002/marc.201200553
Akay G, Birch MA, Bokhari MA (2004) Microcellular polyHIPE polymer supports osteoblast growth and bone formation in vitro. Biomaterials 25(18):3991–4000. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.10.086
Busby W, Cameron NR, Jahoda ABC (2002) Tissue engineering matrixes by emulsion templating. Polym Int 51(10):871–881. doi:10.1002/pi.934
Busby W, Cameron NR, Jahoda CAB (2001) Emulsion-derived foams (PolyHIPEs) containing poly(ε-caprolactone) as matrixes for tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 2(1):154–164. doi:10.1021/bm0000889
Mert EH, Yildirim H, Uzumcu AT, Kavas H (2013) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic polyHIPEs with humic acid surface modified magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. React Funct Polym 73(1):175–181. doi:10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2012.09.005
Arrua RD, Basbus JF, Strumia MC, Alvarez Igarzabal CI, Nazareno MA (2012) Synthesis of macroporous polymers with radical scavenging properties by immobilization of polyphenolic compounds. React Funct Polym 72(11):807–813. doi:10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2012.07.017
Sergienko AY, Tai HW, Narkis M, Silverstein MS (2004) Polymerized high internal phase emulsions containing a porogen: specific surface area and sorption. J Appl Polym Sci 94(5):2233–2239. doi:10.1002/app.21170
Wakeman RJ, Bhumgara ZG, Akay G (1998) Ion exchange modules formed from polyHIPE foam precursors. Chem Eng J 70(2):133–141. doi:10.1016/S0923-0467(98)00088-8
He HK, Li WW, Zhong MJ, Konkolewicz D, Wu DC, Yaccato K, Rappold T, Sugar G, David NE, Matyjaszewski K (2013) Reversible CO2 capture with porous polymers using the humidity swing. Energy Environ Sci 6(2):488–493. doi:10.1039/c2ee24139k
Schofield WCE, Bain CD, Badyal JPS (2012) Cyclodextrin-functionalized hierarchical porous architectures for high-throughput capture and release of organic pollutants from wastewater. Chem Mater 24(9):1645–1653. doi:10.1021/cm300552k
Kovacic S, Krajnc P (2009) Macroporous monolithic poly(4-vinylbenzyl chloride) columns for organic synthesis facilitation by in situ polymerization of high internal phase emulsions. J Polym Sci, Polym Chem 47(23):6726–6734. doi:10.1002/pola.23732
Mert EH, Kaya MA, Yildirim H (2012) Preparation and characterization of polyester-glycidyl methacrylate polyHIPE monoliths to use in heavy metal removal. Des Monomers Polym 15(2):113–126. doi:10.1163/156855511x615001
Schwab MG, Senkovska I, Rose M, Klein N, Koch M, Pahnke J, Jonschker G, Schmitz B, Hirscher M, Kaskel S (2009) High surface area polyHIPEs with hierarchical pore system. Soft Matter 5(5):1055–1059. doi:10.1039/B815143a
Szczurek A, Fierro V, Pizzi A, Celzard A (2013) Mayonnaise, whipped cream and meringue, a new carbon cuisine. Carbon 58:245–248. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2013.02.056
Haibach K, Menner A, Powell R, Bismarck A (2006) Tailoring mechanical properties of highly porous polymer foams: silica particle reinforced polymer foams via emulsion templating. Polymer 47(13):4513–4519. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2006.03.114
Menner A, Haibach K, Powell R, Bismarck A (2006) Tough reinforced open porous polymer foams via concentrated emulsion templating. Polymer 47(22):7628–7635. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2006.09.022
Menner A, Ikem V, Salgueiro M, Shaffer MSP, Bismarck A (2007) High internal phase emulsion templates solely stabilised by functionalised titania nanoparticles. Chem Commun 41:4274–4276. doi:10.1039/b708935j
Wu R, Menner A, Bismarck A (2010) Tough interconnected polymerized medium and high internal phase emulsions reinforced by silica particles. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 48(9):1979–1989. doi:10.1002/pola.23965
Ikem VO, Menner A, Bismarck A (2011) Tailoring the mechanical performance of highly permeable macroporous polymers synthesized via Pickering emulsion templating. Soft Matter 7(14):6571–6577. doi:10.1039/c1sm05272a
Wong LLC, Villafranca PMB, Menner A, Bismarck A (2013) Hierarchical polymerized high Internal phase emulsions synthesized from surfactant-stabilized emulsion templates. Langmuir 29(20):5952–5961. doi:10.1021/la3047643
Liu W, He G, He Z (2011) Polystyrene/magnetite hybrid foams prepared via 60 Co γ-ray radiation of high internal phase emulsions. J Polym Res 19(1):9765. doi:10.1007/s10965-011-9765-5
Wong LLC, Ikem VO, Menner A, Bismarck A (2011) Macroporous polymers with hierarchical pore structure from emulsion templates stabilised by both particles and surfactants. Macromol Rapid Commun 32(19):1563–1568. doi:10.1002/marc.201100382
Claire Hermant M, Klumperman B, Koning CE (2009) Conductive Pickering-poly(high internal phase emulsion) composite foams prepared with low loadings of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem Commun 19:2738–2740. doi:10.1039/b820638d
Lepine O, Birot M, Deleuze H (2007) Elaboration of open-cell microcellular nanocomposites. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 45(18):4193–4203. doi:10.1002/pola.22160
Luo YW, Wang AN, Gao X (2012) Pushing the mechanical strength of PolyHIPEs up to the theoretical limit through living radical polymerization. Soft Matter 8(6):1824–1830. doi:10.1039/C1sm06756g
Lamson M, Epshtein-Assor Y, Silverstein MS, Matyjaszewski K (2013) Synthesis of degradable polyHIPEs by AGET ATRP. Polymer 54(17):4480–4485. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2013.06.048
Mao D, Li T, Liu H, Li Z, Shao H, Li M (2013) Preparation of macroporous polyHIPE foams via radiation-induced polymerization at room temperature. Colloid Polym Sci 291(7):1649–1656. doi:10.1007/s00396-013-2899-8
Chen Y, Ballard N, Bon SA (2013) Moldable high internal phase emulsion hydrogel objects from non-covalently crosslinked poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanogel dispersions. Chem Commun 49(15):1524–1526. doi:10.1039/c2cc38200h
Berda EB, Foster EJ, Meijer EW (2010) Toward controlling folding in synthetic polymers: fabricating and characterizing supramolecular single-chain nanoparticles. Macromolecules 43(3):1430–1437. doi:10.1021/ma902393h
Ferguson CJ, Hughes RJ, Nguyen D, Pham BTT, Gilbert RG, Serelis AK, Such CH, Hawkett BS (2005) Ab initio emulsion polymerization by RAFT-controlled self-assembly. Macromolecules 38(6):2191–2204. doi:10.1021/ma048787r
Chiefari J, Chong YK, Ercole F, Krstina J, Jeffery J, Le TPT, Mayadunne RTA, Meijs GF, Moad CL, Moad G, Rizzardo E, Thang SH (1998) Living free-radical polymerization by reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer: the RAFT process. Macromolecules 31(16):5559–5562. doi:10.1021/Ma9804951
Wang CX, Xu J, Gao Y, Yang DG, Li HM (2012) RAFT synthesis of acrylic polymers containing diol or dioxane groups. J Polym Res 19(6). doi:10.1007/S10965-012-9895-4
Yu Y, Hong D, Liu Z, Jia F, Zhou Y, Leng C (2013) Controllable preparation and characterization of the thermosensitive block polymers. J Polym Res 20(9). doi:10.1007/s10965-013-0235-0
Ji J, Jia L, Yan LF, Bangal PR (2010) Efficient synthesis of poly(acrylic acid) in aqueous solution via a RAFT process. J Macromol Sci Part A: Pure Appl Chem 47(5):445–451. doi:10.1080/10601321003659705
Dusek K, Galina H, Mikes J (1980) Features of network formation in the chain crosslinking (Co)polymerization. Polym Bull 3(1-2):19–25. doi:10.1007/Bf00263201
Barbetta A, Cameron NR (2004) Morphology and surface area of emulsion-derived (PolyHIPE) solid foams prepared with oil-phase soluble porogenic solvents: span 80 as surfactant. Macromolecules 37(9):3188–3201. doi:10.1021/ma0359436
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Highlight
The addition of the monomer containing quadruple hydrogen bond group improved the stability of high internal phase emulsion.
In comparison to the polyHIPE without reinforcement through quadruple hydrogen bond, the porosity of the reinforced sample was as high as 92 % and its Young’s modulus reached to 28.5 ± 3.9 MPa which was improved by 50 %.
The hypothetical mechanism for the mechanical enhancement effect by quadruple hydrogen bond has been proposed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, G., Yu, H., Wang, L. et al. Synthesis and properties of polystyrene-based polyHIPEs reinforced with quadruple hydrogen bond functionality. J Polym Res 22, 147 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-015-0791-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-015-0791-6