Abstract
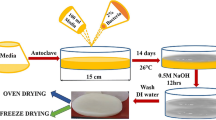
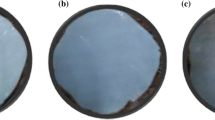
Bacterial cellulose membranes have attracted a great deal of attention as novel biomedical materials. In this paper, bacterial cellulose was treated with acidic, alkaline, and redox solutions to investigate the subsequent changes in the characteristics of the cellulose. The chemical structure, crystalline state, water-holding capacity, and micromorphology of each modified BC were characterized by FTIR, SEM, and XRD. After these treatments, the intermolecular or intramolecular hydrogen bonds of the BC were broken and the water bound to the BC was released from the BC hydrogel. During these processes, the crystallinity and surface morphology of the BC were also modified. Meanwhile, the crystalline form of the BC changed from cellulose I to II in alkaline medium. In particular, the BC nanofiber hydrogel broke into floccules when treated with highly concentrated NaOH solution at a temperature of −5 °C, but these floccules congregated into a bulk state again after removing the NaOH.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dubey V, Saxena C, Singh L, Ramana KV, Chauhan RS (2002) Sep Purif Technol 27:163–171
Fumihiro Y, Naoto T, Watanabe K (1997) Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:219–224
Kacurakova M, Smith AC, Gidley MJ, Wilson RH (2002) Carbohydr Res 337:1145–1153
Wan YZ, Huang Y, Yuan CD, Raman S, Zhu Y, Jiang HJ (2007) Mater Sci Eng C 27:855–864
Hu W, Chen S, Li X, Shi S, Shen W, Zhang X (2009) Mater Sci Eng C 29:1216–1219
Rambo CR, Recouvreux DOS, Carminatti CA, Pitlovanciv AK, Antnio RV, Porto LM (2002) Mater Sci Eng C 28:549–554
Czaja W, Krystynowicz A, Bielecki S, Brown JRM (2006) Biomaterials 27:145–151
Klemm DO, Udhardt URE, Schumann DA, Marsch SE (2004) Abstr Pap Am Chem Soc 227:U303–U306
Sokolnicki AM, Fisher RJ, Harrah TP, Kaplan DL (2006) J Membrane Sci 272:15–27
Svensson A, Nicklasson E, Harrah T, Panilaitis B, Kaplan DL, Brittberg M (2005) Biomaterials 26:419–431
Chen YM, Xi TF, Zheng YD, Guo TT, Hou JQ, Wan YZ (2009) J Bioact Compat Polym 24:137–145
Kim J, Cai ZJ, Lee HS, Choi GS, Lee DH, Jo C (2011) J Polym Res 18(4):1022–9760
Czaja WK, Young DJ, Kawecki M, Brown RM Jr (2007) Biomacromolecules 8:11–12
Datta S, Grant DJW (2004) Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:42–57
George J, Ramana KV, Sabapathy SN, Jagannath JH, Bawa AS (2002) Int J Biol Macromol 37:189–194
Liu Sixin, Li Congfa (2007) Bacterial cellulose. China Agricultural University Press, Beijing
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE Jr, Conrad CM (1959) Text Res J 29(10):786–794
Wei Z, HongZhang C, RunYu M (2007) J Beijing University Chem Tech 34:138–141
Bragg WL (1913) Proc Camb Philos Soc 17:43–57
Wang Y, Zhao Y, Deng Y (2008) Carbohydr Polym 72:178–184
Wang Y (2008) Cellulose fiber dissolution in sodium hydroxide solution at low temperature: dissolution kinetics and solubility improvement (Ph.D. thesis). Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta
Cheng YM (2009) Study of the degradation and biosafety evaluation of nHA/BC used for tissue engineering scaffold materials (Ph.D. thesis). University of Science and Technology, Beijing, pp 51–52
Rogovin ZA, Shorygin НН (1956) In: Cellulose and concomitant chemistry (transl. by Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry Chinese Academy of Sciences). Science Press, Beijing, pp 115–116
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China projects (grant nos. 50773004 and 51073024), the Science and Technology Plan Project of Beijing (no. Z111103066611005) and the Royal Society–NSFC International Joint Project (grant no. 5111130207).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Zheng, Y., Yang, Z. et al. Chemical modifications and characteristic changes in bacterial cellulose treated with different media. J Polym Res 19, 9945 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-012-9945-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-012-9945-y