Abstract
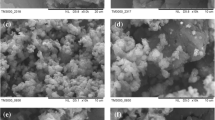
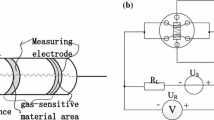
This work is an attempt to improve the selectivity and sensitivity response of zeolite Y towards 3 different types of ketone vapors (acetone, MEK and MIBK) which are known to be toxic and flammable substances. The effects of cation type, cation concentration, ketone vapor type, and cyclic interval were investigated. Three different cations were exchanged in zeolite Y at 50 % mole: NaY, 50KNaY, 50MgNaY and 50CaNaY for the zeolite Y at a fixed Si/Al ratio of 5.1. 50KNaY sample exhibits the highest electrical conductivity sensitivity. This arises from the electrostatic interaction between the cation and the zeolite framework, which affects the adsorption properties of zeolite. The dPPV was mixed with 80KNaY matrix at 10 % v/v and was exposed to 3 different ketone vapors. The highest electrical conductivity sensitivity belongs to the acetone exposure, whereas the MIBK exposure shows the lowest value, as a result of the smaller acetone size. The sensitivity of the composite is higher than that of pure zeolite Y by an order magnitude. For the cyclic interval, the electrical conductivity response decreases with increasing number of the interval due to the interaction between the active site and ketone vapors. The response of samples is irreversible as evidenced by FTIR.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heeger AJ, Diaz-Gracia MA (1998) Semiconducting polymers as a material for photonic device. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 3:16–22
Jung YS, Jung W, Tuller HL, Ross CA (2008) Nanowire conductive polymer gas sensor patterned using self assembled block copolymer lithography. Nano Lett 8:3777–3780
Vijaya JJ, Kenedy LJ, Sekaran G, Bayhan M, William M (2008) Preparation and VOC gas sensing properties of Sr(II)-added copper aluminate spinel composites. Sensors Actuators B Chem 134:604–612
Gao JF, Yan DX, Huang HD, Zeng XB, Zhang WQ, Li ZM (2011) Tunable positive liquid coefficient of an anisotropically conductive carbon nanotube-polymer composite. J Polym Res 18:2239–2243
Tang L, Li Y, Xu K, Hou X, Lv Y (2008) Sensitive and selective acetone sensor based on its cataluminescence from Nano-La2O3 surface. Sensors Actuators B Chem 132:243–249
Mori M, Nishimura H, Itagaki Y, Sadaoka Y (2009) Potentiometric VOC detection in air using 8YSZ-based oxygen sensor modified with SmFeO3 catalytic layer. Sensors Actuators B Chem 142:141–146
Montserral V, Joaquin C, Albert C, Albert C, Ramon MJ, Jesus S (2007) Gas detection with SnO2 sensors modified by zeolite films. Sensors Actuators B Chem 124:99–110
Benvenho ARV, Li RWC, Gruber J (2009) Polymeric electronic gas sensor for determining alcohol content in automotive fules. Sensors Actuators B Chem 136:173–176
Li RWC, Ventura L, Gruber J, Kawano Y, Carvalho LRF (2008) A selective conductive polymer–beasd sensor for volatile halogenated organic compounds (VHOC). Sensors Actuators B Chem 131:646–651
Ruangchuay L, Sirivat A, Schwank J (2004) Electrical conductivity response of polypyrrole to acetone vapor: effect of dopant anions and interaction mechanisms. Synth Met 140:15–21
Ruangchuay L, Sirivat A, Schwank J (2004) Selective conductivity response of polypyrrole-based sensor on flammable chemicals. React Funct Polym 6:11–22
Ruangchuay L, Sirivat A, Schwank J (2008) Polypyroole and its composites with 3A zeolite and polyamide 6 as sensors for four chemicals in lacquer thinner. React Funct Polym 68:1646–1651
Thongchai N, Kunanuruksapong R, Niamlang S, Wannatong L, Sirivat A, Wongkasenjit S (2009) Interactions between CO and poly(p-phenylene vinylene) as induced by ion-exchanged zeolites. Mater 2:2259–2275
Jalkane T, Tuura J, Makila E, Salonen J (2010) Electro-optical porous silicon gas sensor with enhance selectivity. Sensors Actuators B Chem 147:100–104
Chang CJ, Lin CK, Chen CC, Chen YC, Kuo EH (2011) Gas sensor with porous three dimensional framework using TiO2/Polymer double shell hollow microsphere. Thin Solid Films 520:1546–1553
Hung ST, Chang CJ, Hsu CH, Chu BH, Lo CF, Hsu CC, Pearton SJ, Holzworth MR (2012) Sn02 functionalized AlGaN/GaNhigh electron mobility transistor for hydrogen sensing application. Int J Hydrogen Energy 37:13783–13788
Chang JC, Hung ST, Lin CK, Chen CY, Kuo EH (2010) Selective growth of ZnO nanorods for gas sensors using ink-jet printing and hydrothermal processes. Thin Solid Films 519:1693–1698
Yang P, Ye X, Lau C, Liu X, Lu J (2007) Design of efficient zeolite materials for n-Hexane. Anal Chem 79:1425–1432
Varsani P, Afonja A, Williams DE, Parkin IP, Binions R (2011) Zeolite-modified WO3 gas sensors-enhanced detection of NO2. Sensors Actuators B Chem 160:475–482
Yimlamai I, Niamlang S, Chanthaanont P, Kunanuruksapong R, Changkhamchom S, Sirivat A (2011) Electrical conductivity response and sensitivity of ZSM-5, Y and mordernite zeolite towards ethanol vapor. Ion 17:607–615
Li X, Dutta PK (2010) Interaction of dimethylmethylphosphonate with zeolite Y: impedance-based sensor for detecting nerve agent stimulus. J Phys Chem C 114:7986–7994
Soontornworajit B, Wannatong L, Hiamtup P, Niamlang S, Chotpattananont D, Sirivat A, Schwank J (2007) Induced interaction between polypyrrole and SO2 via molecularsieve 13X. Mater Sci Eng B 15:78–86
Kamonsawas J, Sirivat A, Niamlang S, Hormnirun P, Prissanaroon-Ouijai W (2010) Electrical conductivity response of poly (phenylene vinylene)/zeolite composites exposed to ammonium nitrate. Sens 10:5590–5603
Thuwachaosoan K, Chottananont D, Sirivat A, Rujiravanit R, Schwank JW (2007) Electrical conductivity responses and interactions of poly(3-thiopheneacetic acid)/zeolites L, modernite, beta and H2. Mater Sci Eng B 140:23–30
Ahlskog M, Reghu M, Noguchi T, Ohnishi T (1997) Doping and conductivity studies on poly (p-phenylene vinylene). Synth Met 89:11–15
Wessling RA, Zimmerman RG (1968) Polyelectrolytes from bis-sulfonium salts. U.S. Patent 3:401
McKeen JC, Davis ME (2009) Conductivity of Mo-and divalent cation in the microporous zincosilicate VPI9. J Phys Chem C 113:9870–9877
Scott MA, Katehleen AC, Dutta PK (2003) Handbook of zeolite science and technology. Marcel Dekker, New York
Florian J, Kubelkova L (1994) Proton transfer between H-Zeolite and adsorbed acetone or acetonitrile: quantum chemical and FTIR study. J Phy Chem 98:8734–8741
Panov AG, Fripiat JJ (1998) An infared study of acetone and mesityl oxide adsorption on acid catalyst. Langmuir 14:3788–3796
Biaglow AI, Gorte RJ, David W (1993) Molecular motions and 13C chemical shift anisotropy of acetone adsorbed inH-ZSM-5 zeolite. J Phys Chem 97:7135–7137
Martins AVG, Berlier G, Bisio C, Coluccia S, Pastore HO, Marchese L (2008) Quantification of bronsed sites in microporous catalysts by a combined FTIR and NH3-TPD study. J Phys Chem C 112:7120–7139
Fameth WE, Gorte RJ (1995) Methods for characterizing zeolite acidicity. Chem Rev 95:615–635
Jian HZH, Ying W, Yuan C, Xiao SW (1998) Dispersion of potassium nitrate and the resulting basicity on alumina and zeolite NaY. J Chem Soc 94:1163–1169
Boekfa B, Pantu P, Prosbt M, Limtrakul J (2010) Adsorption and tautomerization reaction of acetone on acidic zeolites: the confinement effect in different types of zeolites. J Phys Chem C 114:15061–15067
Hoost TE, Laframboise KA, Otto K (1996) Infrared study of acetone and nitrogen oxides on Cu-ZSM-5. Catal Lett 37:153–156
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial supports from the Conductive and Electroactive Polymers Research Unit of Chulalongkorn University, the Thailand Research Fund (TRF-BRG, TRF-RTA, PHD/0026/2553), and the Royal Thai Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamonsawas, J., Sirivat, A. & Hormnirun, P. Poly(p-phenylene vilnylene)/zeolite Y composite as a ketone vapors sensor: effect of alkaline cation. J Polym Res 19, 20 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-012-0020-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-012-0020-5