Abstract
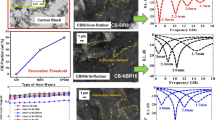
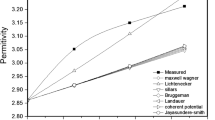
The study presents the effect that elastomeric matrices different in their chemical nature (a non-polar and crystallizing natural rubber and a polar and non-crystallizing acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber) have upon the dynamic mechanical and dielectric properties of the composites comprising different amounts of conductive carbon black. Dynamic mechanical thermal analysis (DMTA) and Dielectric thermal analysis (DETA) are the techniques used for studying the structure-properties relationships of the composites. The experimental results show that the matrices studied and their specific properties have a great impact upon both the dynamic mechanical and dielectric parameters of the composites based on them. The chemical nature, structure and specific characteristics of the matrix affect the storage modulus, glass transition temperature, elasticity behavior, high-elasticity, energy dispersion, dielectric permittivity and DETA tan δ of the composites investigated. The matrix effect dominates at lower filler amounts and determines the properties of the composites.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shaw M, MacKnight W (2005) Introduction to polymer viscoelasticity. Wiley, New York
Lobo H, Bonilla H (eds.) (2003) Handbook of polymer analyses, Dekker
Dang Z-M, Song H-T, Lin Y-Q, Ma L-J (2009) High and low dielectric permittivity polymer-based nanobybrid dielectric films. J Phys Conf Ser 152:012047
Gabbott P (ed) (2008) Principles and application of thermal analyses. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford
Ferry JD (1980) Viscoelastic properties of polymers. Wiley, New York
Heinrich G (2011) advanced rubber composites (Advances in Polymer Science, 239). Springer, Heidelberg
Fritzsche J, Das A, Jurk R, Stöckelhuber KW, Heinrich G, Klüppel M (2008) Relaxation dynamics of carboxylated nitrile rubber filled with organomodified nanoclay. Express Polym Lett 2:373–377
Das A, Costa FR, Wagenknecht U, Heinrich G (2008) Nanocomposites based on chloroprene rubber: Effect of chemical nature and organic modification of nanoclay on the vulcavizate properties. Eur Polym J 44:3456–3465
Das A, Jurk R, Stöckelhuber KW, Engelhardt T, Fritzsche J, Klüppel M, Heinrich G (2008) Nanoalloy based on clays: intercalated-exfoliated layered silicate in high performance elastomer. J Macromol Sci Chem 45:144–150
Eisenberg A, Hird B, Moore RB (1990) A new multiplet-cluster model for the morphology of random ionomers. Macromolecules 23:4098–4107
Heinrich G, Klüppel M (2002) Recent advances in the theory of filler networking in elastomers. Adv Polym Sci 160:1–44
Thomas S, Stephen R (eds) (2010) Rubber nanocomposites. Wiley, Singapore
Angellier H, Molina-Boisseau S, Dufresne A (2005) Mechanical properties of waxy maize starch nanocrystal reinforced natural rubber. Macromolecules 38:9161–9170
Gatos KG, Sawanis NS, Apostolov AA, Thomann R, Karger-Kocsis J (2004) Nanocomposite formation in Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)/Organo-Montmorillonite as a function of the intercalant type. Macromol Mater Eng 289:1079–1086
Wang Y, Zhang H, Wu Y, Yang J, Zhang L (2005) Preparation and properties of natural rubber/rectorite nanocomposites. Eur Polym J 41:2776–2783
Kalgaonkar RA, Jog JP (2008) Molecular dynamics of copolyester/clay nanocomposites as investigated by viscoelastic and dielectric analysis. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 46:2539–2555
Rao YQ, Pochan JM (2007) Mechanics of polymer-clay nanocomposites. Macromolecules 40:290–299
Hernandez MC, Suarez N, Martinez LA, Fejoo JL, Monaco SL, Salazar N (2008) Effects of nanoscale dispersion in the dielectric properties of poly(vinyl alcohol)-bentonite nanocomposites. Phys Rev E77:051801
Page KA, Adachi K (2006) Dielectric relaxation in montmorillonite/polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 47:6406–6410
Psarras GC, Gatos KG, Karger-Kocsis J (2007) Dielectric properties of layered silicate-reinforced natural and polyurethane rubber nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 106:1405–1411
Wan NY, Chin KP, Saad CS (2010) Comparison of epoxidised natural rubber (enr) 37.5 and enr 25/enr 50 physical blend: specialty polymer for “green tyre” application. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng 11:012004
Small W, Wilson TS (2010) Crystallization behavior of virgin TR-55 silicone rubber measured using dynamic mechanical thermal analysis with liquid nitrogen cooling, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, LLNL-TR-426277
Ghadir M, Zimonyi E, Nagy J (1994) Thermal investigation of silicone rubber containing imide-siloxane copolymers. Thermal Anal Calorimetry 41:1019–1029
Pandey AK, Setua DK (2006) Raw material and applications–study of damping behavior of rubber- plastic blend. Kautsch Gummi Kunstst 59:45–4
Boye WM, Terrill E (2011) Structure–property analysis of unfilled polyisoprene (IR) vulcanizates characterized by mechanical and rheological measurements, Rubber World, Aug. 22–27
Niedermeier CW Carbon blacks for electrically conductive rubber products, Evonik (Degussa), Technical report TR 812
Gozdiff M (2001) Acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber. In: Dick JS (ed) Rubber technology: compounding and testing for performance, 1st edn. Hanser Publishers, Munich, pp 193–201
Kornev A (2005) Technology of elastomeric materials, Istek, Moscow, (in Russian)
Dick JS (ed) (2001) Rubber technology, Hamser, Munich
Varghese S, Karger-Kocsis J, Gatos KG (2003) Melt compounded epoxidized natural rubber/layered silicate nanocomposites: structure-properties relationships. Polymer 44:3977–3983
Ramier J, Gauthier C, Chazeau L, Stelandre L, Guy L (2007) Payne effect in silica-filled styrene–butadiene rubber: influence of surface treatment. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys 45:286–298
Wolf S, Wang M (1993) Carbon black reinforcements of the elastomers, In Carbon black, 2nd Edition, Marcel Dekker, New York
Acknowledgments
The present research is a result of an international collaboration program between University of Tabuk, Tabuk, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and the University of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy, Sofia, Bulgaria. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the University of Tabuk.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Hartomy, O.A., Al-Ghamdi, A.A., Al-Solamy, F. et al. Influence of matrices chemical nature on the dynamic mechanical and dielectric properties of rubber composites comprising conductive carbon black. J Polym Res 19, 16 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-012-0016-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-012-0016-1