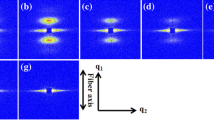
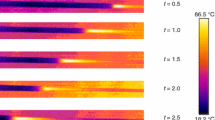
Abstract
The crystallization behavior of melt-spun poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) fibers during hot drawing process was studied by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and computer controlled electronic universal testing machine. The effects of drawing temperature and drawing speed on the crystallinity and the stress induced crystallization of PVA fibers were discussed. The results showed that the crystallization process of PVA fibers during hot drawing presented three stages: initial stage, stress induced crystallization stage and slowly increasing stage. And PVA fibers with high crystallinity can be obtained by properly increasing the drawing temperature and drawing speed, especially when the drawing temperature and speed were 453 K and 100 mm/min respectively. The stress induced crystallinity of PVA fibers during drawing process was the difference between the crystallinity of PVA fibers after drawing and after only heat treatment. At the low drawing speed, i.e. 50 mm/min, due to the strong molecular movement and orientation relaxation under high temperature, the effect of stress induced crystallization weakens with the increase of drawing temperature, the ratio between stress induced crystallinity and thermal induced crystallinity changed from 8.7%:0%(393 K) to 1.7%:5% (453 K). While at the high drawing speeds, i.e. 100 mm/min and 500 mm/min, with the decrease of available orientation relaxation time, the stress induced crystallization plays an important role during the drawing process, the ratio between stress induced crystallinity and thermal induced crystallinity were 8%:2.9% and 10.2%:0.5% at 453 K respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salamone JC (1996) Polymeric materials encyclopedia. CRC, New York, p 6998
Sakurada I (1985) Polyvinyl alcohol fiber. Dekker, New York
Finch CA (1992) Polyvinyl alcohol developments. Wiley, Chichester
Yamaura K, Kumakura R (1999) J Appl Polym Sci 77:2872
Fujiwara H, Shibayama M, Chen HJ (1989) J Appl Polym Sci 37:1403
Dai LX, Yu SY (2003) Polym Adv Technol 14:449
Kubo S, Kadla JF (2003) Biomacromolecules 4:561
Ku TH, Lin CA (2005) J Polym Res 12:23
Okazaki M, Tsujimoto T, Fujiwara N (2005) Jpn Pat 2005306901
Haralabakopoulos AA, Tsiourvas D, Paleos CM (1998) J Appl Polym Sci 69:1885
Hiroshi N, Nobuo D, Takeaki M (1998) J Polym Sci: Part A 36:3045
Piao DS, Toshio K (1982) Sen’I Gakkaishi 38:43
Lin CA, Ku TH (2008) J Mater Pro Tech 200:331
Ku T, Lin CJ (2005) Text Res 75:681
Wang R, Wang Q, Li L (2001) Polym Mater Sci Eng 17:111
Wang R, Wang Q, Li L (2003) Polym Int 52:1820
Li L, Wang Q, Wang R (2005) J Appl Polym Sci 98:774
Zhang H, Wang Q, Li L (2009) Polym Int 58:97
Chen N, Li L, Wang Q (2007) Plast Rubber Compos 36:283
Salem DR (1992) Polymer 33:3182
Kawakami D, Benjamin S, Burger C (2004) Polymer 45:905
Wang Q, Li L, Chen N (2007) Cn Pat ZL200510057435.0
Jacqueline IK (2003) Encyclopedia of polymer science and technology. Wiely, New Jersey, p 399
Salem DR (1992) Polymer 33:3189
Salem DR, Aminuddin N, Baird (2001) Structure formation in polymeric fibers. Hanser, Cincinati
Salem DR (1994) Polymer 35:771
Assender HE, Windle AH (1998) Polymer 39:4295
Hong PD, Chen JH, Wu HL (1998) J Appl Polym Sci 69:2477
Miyazaki T (2007) Macromolecules 40:8277
Acknowledgement
This research is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (50673068, 50833003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Q., Chen, N. & Wang, Q. Crystallization behavior of melt-spun poly(vinyl alcohol) fibers during drawing process. J Polym Res 17, 903–909 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-009-9382-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-009-9382-8