Abstract
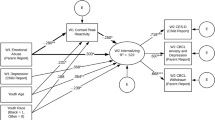
Childhood trauma is a leading early adverse environment that increases psychopathological symptoms. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia (RSA) suppression to challenges as a marker of self-regulation is found to linearly moderate the link between early adverse experiences and psychopathological symptoms, but yielding mixed findings. The present study examined the relationships between childhood trauma and internalizing and externalizing symptoms via a 1.5-year longitudinal design and the quadratic moderation effect of RSA suppression on these relationships among adolescents. In November 2021 (T1), the final sample of 275 Chinese adolescents (Mage = 12.94, SDage = 0.79; 49.82% females) completed the short form of Childhood Trauma Questionnaire and the Achenbach Youth Self-Report-2001 and underwent a speech task during which their baseline RSA and stress exposure RSA were obtained. In June 2023 (T2), 251 adolescents completed the Achenbach Youth Self-Report-2001. Results showed that childhood trauma at T1 was positively correlated with internalizing and externalizing symptoms at T1 and T2. RSA suppression to stress quadratically moderated these associations, such that adolescents with moderate rather than higher or lower RSA suppression had the least internalizing and externalizing symptoms at T1 and T2 when exposed to childhood trauma. The findings suggest that moderate RSA suppression to stress as a marker of optimal vagal regulation buffers the risk of developmental psychopathology from early adverse experiences.


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 December 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-023-01913-4
References
Achenbach, T. M., Ivanova, M. Y., Rescorla, L. A., Turner, L. V., & Althoff, R. R. (2016). Internalizing/externalizing problems: Review and recommendations for clinical and research applications. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 55(8), 647–656.
Achenbach, T. M., & Rescorla, L. A. (2001). Manual for the ASEBA School-Age Forms and Profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont Research Center for Children, Youth, & Families.
Aiken, L. S., & West, S. G. (1991). Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Beauchaine, T. P. (2001). Vagal tone, development, and Gray’s motivational theory: Toward an integrated model of autonomic nervous system functioning in psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology, 13(2), 183–214.
Beauchaine, T. P. (2015). Respiratory sinus arrhythmia: A transdiagnostic biomarker of emotion dysregulation and psychopathology. Current Opinion in Psychology, 3, 43–47.
Beauchaine, T. P., Bell, Z., Knapton, E., McDonough‐Caplan, H., Shader, T., & Zisner, A. (2019). Respiratory sinus arrhythmia reactivity across empirically based structural dimensions of psychopathology: A meta‐analysis. Psychophysiology, 56(5), e13329.
Belsky, J., & Pluess, M. (2009). Beyond diathesis stress: Differential susceptibility to environmental influences. Psychological Bulletin, 135(6), 885–908.
Bernstein, D. P., Stein, J. A., Newcomb, M. D., Walker, E., Pogge, D., Ahluvalia, T., & Zule, W. (2003). Development and validation of a brief screening version of the Childhood Trauma Questionnaire. Child Abuse & Neglect, 27, 169–190.
Berntson, G. G., Bigger, J. T., Eckberg, D. L., Grossman, P., Kaufmann, P. G., Malik, M., & van der Molen, M. W. (1997). Heart rate variability: Origins, methods, and interpretive caveats. Psychophysiology, 34, 623–648.
Bevilacqua, L., Kelly, Y., Heilmann, A., Priest, N., & Lacey, R. E. (2021). Adverse childhood experiences and trajectories of internalizing, externalizing, and prosocial behaviors from childhood to adolescence. Child Abuse & Neglect, 112, 104890.
Bland, V. J., Lambie, I., & Best, C. (2018). Does childhood neglect contribute to violent behavior in adulthood? A review of possible links. Clinical Psychology Review, 60, 126–135.
Boschan, P. (2008). Childhood and Trauma. The American Journal of Psychoanalysis, 68, 24–32.
Boyce, W. T., & Ellis, B. J. (2005). Biological sensitivity to context: I. An evolutionary-developmental theory of the origins and functions of stress reactivity. Development and Psychopathology, 17, 271–301.
Chang, S., Hou, Q., Wang, C., Wang, M., Wang, L., & Zhang, W. (2021). Childhood maltreatment and violent delinquency in Chinese juvenile offenders: Callous-unemotional traits as a mediator. Child Abuse & Neglect, 117, 105085.
Cui, Y., Li, F., Leckman, J. F., Guo, L., Ke, X., Liu, J., & Li, Y. (2021). The prevalence of behavioral and emotional problems among Chinese school children and adolescents aged 6-16: a national survey. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 30, 233–241.
Fang, X., Fry, D. A., Ji, K., Finkelhor, D., Chen, J., Lannen, P., & Dunne, M. P. (2015). The burden of child maltreatment in China: a systematic review. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 93, 176–185C.
Fanti, K. A., Eisenbarth, H., Goble, P., Demetriou, C., Kyranides, M. N., Goodwin, D., & Cortese, S. (2019). Psychophysiological activity and reactivity in children and adolescents with conduct problems: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 100, 98–107.
Fortunato, C. K., Gatzke‐Kopp, L. M., & Ram, N. (2013). Associations between respiratory sinus arrhythmia reactivity and internalizing and externalizing symptoms are emotion specific. Cognitive Affective and Behavioral Neuroscience, 13, 238–251.
Fu, W., Yao, S., Yu, H., Zhao, X., Li, R., Li, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2005). Initial reliability and validity of Childhood Trauma Questionnaire (CTQ-SF) applied in Chinese college students. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 13, 40–42.
Graziano, P., & Derefinko, K. (2013). Cardiac vagal control and children’s adaptive functioning: A meta-analysis. Biological Psychology, 94, 22–37.
Huffman, L. G., Oshri, A., & Caughy, M. (2020). An autonomic nervous system context of harsh parenting and youth aggression versus delinquency. Biological Psychology, 156, 107966.
Infurna, M. R., Reichl, C., Parzer, P., Schimmenti, A., Bifulco, A., & Kaess, M. (2016). Associations between depression and specific childhood experiences of abuse and neglect: A meta-analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders, 190, 47–55.
Ji, H., & Lü, W. (2021). Childhood abuse and social anxiety symptoms among young adults: Moderating role of respiratory sinus arrhythmia suppression to social stress. Child Abuse & Neglect, 117, 105118.
Lang, P. J., Bradley, M. M., & Cuthbert, B. N. (2005). International affective picture system (IAPS): Affective rating of pictures and instruction manual. Gainesville, FL: University of Florida Center for Research in Psychophysiology.
Li, Z., Sturge-Apple, M. L., Martin, M. J., & Davies, P. T. (2019). Interactive effects of family instability and adolescent stress reactivity on socioemotional functioning. Developmental Psychology, 55(10), 2193.
Lü, W., & Wang, Z. (2017). Physiological adaptation to recurrent social stress of extraversion. Psychophysiology, 54, 270–278.
Lü, W., Wang, Z., & You, X. (2016). Physiological responses to repeated stress in individuals with high and low trait resilience. Biological Psychology, 120, 46–52.
Lü, W., Xing, W., Hughes, B. M., & Wang, Z. (2018). Extraversion and cardiovascular responses to recurrent social stress: effect of stress intensity. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 131, 14–151.
Marcovitch, S., Leigh, J., Calkins, S. D., Leerks, E. M., O’Brien, M., & Blankson, A. N. (2010). Moderate vagal withdrawal in 3.5-year-old children is associated with optimal performance on executive function tasks. Developmental Psychobiology, 52(6), 603–608.
McElroy, E., Shevlin, M., Murphy, J., & McBride, O. (2018). Co-occurring internalizing and externalizing psychopathology in childhood and adolescence: a network approach. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 27(11), 1449–1457.
Mclaughlin, K. A., Alves, S., & Sheridan, M. A. (2014). Vagal regulation and internalizing psychopathology among adolescents exposed to childhood adversity. Developmental Psychobiology, 56, 1036–1051.
Miller, J. W., Stromeyer, W. R., & Schwieterman, M. A. (2013). Extensions of the Johnson-Neyman technique to linear models with curvilinear effects: Derivations and analytical tools. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 48, 267–300.
Monroe, S. M., & Simons, A. D. (1991). Diathesis-stress theories in the context of life stress research: Implications for the depressive disorders. Psychological Bulletin, 110, 406–425.
Muniz, C. N., Fox, B., Miley, L. N., Delisi, M., Cigarran, G. P., & Birnbaum, A. (2019). The effects of adverse childhood experiences on internalizing versus externalizing outcomes. Criminal Justice and Behavior, 46(4), 568–589.
Obradović, J., Bush, N. R., Stamperdahl, J., Adler, N. E., & Boyce, W. T. (2010). Biological sensitivity to context: the interactive effects of stress reactivity and family adversity on socioemotional behavior and school readiness. Child Development, 81(1), 270–289.
Peng, Y., Yang, X., & Wang, Z. (2021). Parental marital conflict and growth in adolescents’ externalizing problems: The role of respiratory sinus arrhythmia. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 1-14.
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., & Lee, J. Y., et al. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(5), 879–903.
Porges, S. W. (2007). The polyvagal perspective. Biological Psychology, 74, 116–143.
Radell, M. L., Abo Hamza, E. G., Daghustani, W. H., Perveen, A., & Moustafa, A. A. (2021). The impact of different types of abuse on depression. Depression Research and Treatment, 2021, 6654503.
Rudd, K. L., Alkon, A., & Yates, T. M. (2017). Prospective relations between intrusive parenting and child behavior problems: Differential moderation by parasympathetic nervous system regulation and child sex. Physiology & Behavior, 180, 120–130.
Scully, C., McLaughlin, J., & Fitzgerald, A. (2020). The relationship between adverse childhood experiences, family functioning, and mental health problems among children and adolescents: A systematic review. Journal of Family Therapy, 42(2), 291–316.
Skowron, E. A., Cipriano-Essel, E., Gatzke‐Kopp, L. M., Teti, D. M., & Ammerman, R. T. (2014). Early adversity, RSA, and inhibitory control: Evidence of children’s neurobiological sensitivity to social context. Developmental Psychobiology, 56(5), 964–978.
Tabachnick, A. R., Moore, C., Raby, K. L., Goldstein, A., Zajac, L., & Dozier, M. (2021). Respiratory sinus arrhythmia as a moderator of early maltreatment effects on later externalizing problems. Development and Psychopathology, 33(3), 821–831.
Tanzer, M., Salaminios, G., Morosan, L., Campbell, C., & Debbané, M. (2021). Self-blame mediates the link between childhood neglect experiences and internalizing symptoms in low-risk adolescents. Journal of Child & Adolescent Trauma, 14, 73–83.
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. (1996). Heart rate variability: Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Circulation, 93, 1043–1065.
Thomson, N. D., Kevorkian, S., Blair, J., Farrell, A., West, S. J., & Bjork, J. M. (2021). Psychophysiological underpinnings of proactive and reactive aggression in young men and women. Physiology & Behavior, 242, 113601.
Tucker, D., Poulsen, C., & Luu, P. (2015). Critical periods for the neurodevelopmental processes of externalizing and internalizing. Development and Psychopathology, 27(2), 321–346.
Ugarte, E., Miller, J. G., Weissman, D. G., & Hastings, P. D. (2023). Vagal flexibility to negative emotions moderates the relations between environmental risk and adjustment problems in childhood. Development and Psychopathology, 35(3), 1051–1068.
Vaughn-Coaxum, R. A., Dhawan, N., Sheridan, M. A., Hart, M. J., & Weisz, J. R. (2020). Dimensions of adversity in association with adolescents’ depression symptoms: Distinct moderating roles of cognitive and autonomic function. Development and Psychopathology, 32(3), 817–830.
Wang, Z., Lü, W., & Qin, R. (2013). Respiratory sinus arrhythmia is associated with trait positive affect and positive emotional expressivity. Biological Psychology, 93, 190–196.
Watters, E. R., & Wojciak, A. S. (2020). Childhood abuse and internalizing symptoms: Exploring mediating & moderating role of attachment, competency, and self-regulation. Children and Youth Services Review, 117, 105305.
Wei, X., & Lü, W. (2023). Childhood trauma and internalizing and externalizing behavior problems among adolescents: Role of executive function and life events stress. Journal of Adolescence, 95(4), 740–750.
Young-Southward, G., Svelnys, C., Gajwani, R., Bosquet Enlow, M., & Minnis, H. (2020). Child maltreatment, autonomic nervous system responsivity, and psychopathology: current state of the literature and future directions. Child Maltreatment, 25(1), 3–19.
Zhou, H., & Long, L. (2004). Statistical remedies for common method biases. Advances in Psychological Science, 12(6), 942–950.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32171066) awarded to Wei Lü.
Data Sharing and DeclarationThe datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.Y. participated in the study design, conducted the statistical analysis, and drafted the article; L.W. conceived of the study, participated in its design and coordination, reviewed and provided the guidance of revision of the article. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Lü, W. Nonlinear Moderation Effect of Vagal Regulation on the Link between Childhood Trauma and Adolescent Internalizing and Externalizing Symptoms. J. Youth Adolescence 53, 217–228 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-023-01860-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-023-01860-0