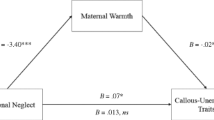
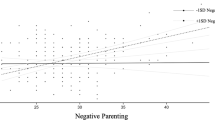
Abstract
Callous-unemotional (CU) traits (i.e., lack of empathy/guilt, uncaring attitudes) are believed to be a developmental antecedent to adult psychopathy and identify antisocial youth at risk for severe and persistent aggression. The psychosocial histories of antisocial and aggressive individuals with psychopathic traits are characterized by abusive or unaffectionate parenting; however, there is a gap in the literature regarding the unique impact of these factors on adolescent offenders. The purpose of the present study was to examine the contribution of maternal warmth and affection (i.e., care) to dimensions of CU traits and aggression, after accounting for the influence of various types of childhood maltreatment. We investigated this aim in a sample of 227 urban male adolescent offenders housed in residential facilities. Results indicated that low maternal care was significantly associated with greater total CU traits and uncaring and callousness dimensions, even after controlling for the effects of various types of childhood abuse and neglect. Furthermore, there was a significant interaction between CU traits and care, such that aggression was highest among youths scoring high on CU traits who were exposed to low levels of maternal care. These findings draw attention to the importance of maternal bonding to CU traits and related aggressive behaviors among antisocial youth.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baer, J. C., & Martinez, C. D. (2006). Child maltreatment and insecure attachment: A meta-analysis. Journal of Reproductive and Infant Psychology, 24(3), 187–197. doi:10.1080/02646830600821231.
Barker, E. D., Oliver, B. R., Viding, E., Salekin, R. T., & Maughan, B. (2011). The impact of prenatal maternal risk, fearless temperament and early parenting on adolescent callous-unemotional traits: A 14-year longitudinal investigation. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 52(8), 878–888. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02397.x.
Bernstein, D. P., Fink, L., Handelsman, L., & Foote, J. (1994). Initial reliability and validity of a new retrospective measure of child abuse and neglect. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 151(8), 1132–1136.
Blair, R. J. R. (1995). A cognitive developmental approach to morality: Investigating the psychopath. Cognition, 57(1), 1–29. doi:10.1016/0010-0277(95)00676-P.
Bowlby, J. (1969). Disruption of affectional bonds and its effects on behavior. Canada’s Mental Health Supplement, 59, 12.
Caputo, A. A., Frick, P. J., & Brodsky, S. L. (1999). Family violence and juvenile sex offending: The potential mediating role of psychopathic traits and negative attitudes toward women. Criminal Justice and Behavior, 26(3), 338–356. doi:10.1177/0093854899026003004.
Chaffin, M., Funderburk, B., Bard, D., Valle, L. A., & Gurwitch, R. (2011). A combined motivation and parent–child interaction therapy package reduces child welfare recidivism in a randomized dismantling field trial. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 79(1), 84–95. doi:10.1037/a0021227.
Chaffin, M., Silovsky, J. F., Funderburk, B., Velle, L., Brestan, E. V., Balachova, T., et al. (2004). Parent-child interaction therapy with physically abusive parents: Efficacy for reducing future abuse reports. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 72(3), 500–510. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.72.3.500.
Cornell, A. H., & Frick, P. J. (2007). The moderating effects of parenting styles in the association between behavioral inhibition and parent-reported guilt and empathy in preschool children. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 36(3), 305–318. doi:10.1080/15374410701444181.
Dadds, M. R., Jambrak, J., Pasalich, D., Hawes, D. J., & Brennan, J. (2011). Impaired attention to the eyes of attachment figures and the developmental origins of psychopathy. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 52(3), 238–245. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02323.x.
Edens, J. F., Skopp, N. A., & Cahill, M. A. (2008). Psychopathic features moderate the relationship between harsh and inconsistent parental discipline and adolescent antisocial behavior. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 37(2), 472–476. doi:10.1080/15374410801955938.
Enns, M. W., Cox, B. J., & Clara, I. I. (2002). Parental bonding and adult psychopathology: Results from the US National Comorbidity Survey. Psychological Medicine, 32(6), 997–1008. doi:10.1017/S0033291702005937.
Essau, C. A., Sasagawa, S., & Frick, P. J. (2006). Callous-unemotional traits in a community sample of adolescents. Assessment, 13(4), 454–469. doi:10.1177/1073191106287354.
Fanti, K. A., Frick, P. J., & Georgiou, S. (2009). Linking callous-unemotional traits to instrumental and non-instrumental forms of aggression. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 31(4), 285–298. doi:10.1007/s10862-008-9111-3.
Fowles, D. C., & Kochanska, G. (2000). Temperament as a moderator of pathways to conscience in children: The contribution of electrodermal activity. Psychophysiology, 37(6), 788–795. doi:10.1017/S0048577200981848.
Frick, P. J. (2006). Developmental pathways to conduct disorder. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 15(2), 311–331. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2005.11.003.
Frick, P. J., Kimonis, E. R., Dandreaux, D. M., & Farrell, J. M. (2003). The 4 year stability of psychopathic traits in non-referred youth. Behavioral Sciences & the Law, 21(6), 713–736. doi:10.1002/bsl.568.
Frick, P. J., & White, S. F. (2008). Research review: The importance of callous-unemotional traits for developmental models of aggressive and antisocial behavior. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 49(4), 359–375. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01862.x.
Gao, Y., Raine, A., Chan, F., Venables, P. H., & Mednick, S. A. (2010). Early maternal and paternal bonding, childhood physical abuse and adult psychopathic personality. Psychological Medicine: A Journal of Research in Psychiatry and the Allied Sciences, 40(6), 1007–1016. doi:10.1017/S0033291709991279.
George, D., & Mallery, P. (2003). SPSS for Windows step by step: A simple guide and reference. 11.0 update (4th ed.). Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Gretton, H. M., Hare, R. D., & Catchpole, R. E. H. (2004). Psychopathy and offending from adolescence to adulthood: A 10-year follow-up. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 72(4), 636–645. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.72.4.636.
Hare, R. (1993). Without conscience. The disturbing world of the psychopaths among us. New York: Pocket Books.
Hare, R. D. (2003). Hare psychopathy checklist-revised (PCL-R): 2nd edition, technical manual. Toronto: Multi-Health Systems.
Hawes, D. J., & Dadds, M. R. (2005). The treatment of conduct problems in children with callous-unemotional traits. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 73(4), 737–741. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.73.4.737.
Hawes, D. J., Dadds, M. R., Frost, A. D. J., & Hasking, P. A. (2011). Do childhood callous-unemotional traits drive change in parenting practices? Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 40(4), 507–518. doi:10.1080/15374416.2011.581624.
Hipwell, A. E., Pardini, D. A., Loeber, R., Sembower, M., Keenan, K., & Stouthamer-Loeber, M. (2007). Callous-unemotional behaviors in young girls: Shared and unique effects relative to conduct problems. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 36(3), 293–304. doi:10.1080/15374410701444165.
Hoeve, M., Dubas, J. S., Eichelsheim, V. I., van der Laan, P. H., Smeenk, W., & Gerris, J. R. M. (2009). The relationship between parenting and delinquency: A meta-analysis. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37(6), 749–775. doi:10.1007/s10802-009-9310-8.
Holmbeck, G. N. (2002). Post hoc probing of significant moderational and mediational effects in studies of pediatric populations. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 27(1), 87–96.
Huizinga, D., Thornberry, T., Knight, K., & Lovegroove, P. (2007). Disproportionate minority contact in the juvenile justice system: A study of differential minority arrest/referral to court in three cities. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Justice.
Jackson-Newsom, J., Buchanan, C. M., & McDonald, R. M. (2008). Parenting and perceived maternal warmth in European American and African American adolescent. Journal of Marriage and Family, 70(1), 62–75.
Jang, K. L., Stein, M. B., Taylor, S., Asmundson, G. J. G., & Livesley, W. J. (2003). Exposure to traumatic events and experiences: Aetiological relationships with personality function. Psychiatry Research, 120(1), 61–69. doi:10.1016/S0165-1781(03)00172-0.
Jones, A. P., Laurens, K. R., Herba, C. M., Barker, G. J., & Viding, E. (2009). Amygdala hypoactivity to fearful faces in boys with conduct problems and callous-unemotional traits. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 166(1), 95–102. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2008.07071050.
Kimbrel, N. A., Nelson-Gray, R. O., & Mitchell, J. T. (2007). Reinforcement sensitivity and maternal style as predictors of psychopathology. Personality and Individual Differences, 42(6), 1139–1149. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2006.06.028.
Kimonis, E. R., Frick, P. J., & Barry, C. T. (2004). Callous-unemotional traits and delinquent peer affiliation. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 72(6), 956–966. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.72.6.956.
Kimonis, E. R., Frick, P. J., Munoz, L. C., & Aucoin, K. J. (2008a). Callous-unemotional traits and the emotional processing of distress cues in detained boys: Testing the moderating role of aggression, exposure to community violence, and histories of abuse. Development and Psychopathology, 20(2), 569–589. doi:10.1017/S095457940800028X.
Kimonis, E. R., Frick, P. J., Skeem, J. L., Marsee, M. A., Cruise, K., Munoz, L. C., et al. (2008b). Assessing callous-unemotional traits in adolescent offenders: Validation of the inventory of callous-unemotional traits. International Journal of Law and Psychiatry, 31(3), 241–252. doi:10.1016/j.ijlp.2008.04.002.
Kochanska, G. (1997). Multiple pathways to conscience for children with different temperaments: From toddlerhood to age 5. Developmental Psychology, 33(2), 228–240. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.33.2.228.
Kosson, D. S., Cyterski, T. D., Steuerwald, B. L., Neumann, C. S., & Walker-Matthews, S. (2002). The reliability and validity of the psychopathy checklist: Youth version (PCL:YV) in nonincarcerated adolescent males. Psychological Assessment, 14(1), 97–109. doi:10.1037/1040-3590.14.1.97.
Kroneman, L. M., Hipwell, A. E., Loeber, R., Koot, H. M., & Pardini, D. A. (2011). Contextual risk factors as predictors of disruptive behavior disorder trajectories in girls: The moderating effect of callous-unemotional features. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 52(2), 167–175. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02300.x.
Lau, A. S., McCabe, K. M., Yeh, M., Garland, A. F., Hough, R. L., & Landsverk, J. (2003). Race/ethnicity and rates of self-reported maltreatment among high-risk youth in public sectors of care. Child Maltreatment, 8(3), 183–194. doi:10.1177/1077559503254141.
Levenson, M. R., Kiehl, K. A., & Fitzpatrick, C. M. (1995). Assessing psychopathic attributes in a noninstitutionalized population. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 68(1), 151–158. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.68.1.151.
Marsee, M. A., Barry, C. T., Childs, K. K., Frick, P. J., Kimonis, E. R., Munoz, L., et al. (2011). Assessing the forms and functions of aggression using self-report: Factor structure and invariance of the peer conflict scale in youth. Psychological Assessment, 23(3), 792–804. doi:10.1037/a0023369.
McCartney, M., Duggan, C., Collins, M., & Larkin, E. P. (2001). Are perceptions of parenting and interpersonal functioning related in those with personality disorder? Evidence from patients detained in a high secure setting. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 8(3), 191–197. doi:10.1002/cpp.289.
McCord, W. M., & McCord, J. (1956). Psychopathy and delinquency. New York, NY: Grune & Stratton.
Meier, M. H., Slutske, W. S., Arndt, S., & Cadoret, R. J. (2008). Impulsive and callous traits are more strongly associated with delinquent behavior in higher risk neighborhoods among boys and girls. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 117(2), 377–385. doi:10.1037/0021-843X.117.2.377.
Muñoz, L. C., Pakalniskiene, V., & Frick, P. J. (2011). Parental monitoring and youth behavior problems: Moderation by callous-unemotional traits over time. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 20(5), 261–269. doi:10.1007/s00787-011-0172-6.
O’Neill, M. L., Lidz, V., & Heilbrun, K. (2003). Adolescents with psychopathic characteristics in a substance abusing cohort: Treatment process and outcomes. Law and Human Behavior, 27(3), 299–313. doi:10.1023/A:1023435924569.
Obradović, J., Pardini, D. A., Long, J. D., & Loeber, R. (2007). Measuring interpersonal callousness in boys from childhood to adolescence: An examination of longitudinal invariance and temporal stability. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 36(3), 276–292. doi:10.1080/15374410701441633.
Oxford, M., Cavell, T. A., & Hughes, J. N. (2003). Callous/unemotional traits moderate the relation between ineffective parenting and child externalizing problems: A partial replication and extension. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 32(4), 577–585. doi:10.1207/S15374424JCCP3204_10.
Pardini, D. A., Lochman, J. E., & Powell, N. (2007). The development of callous-unemotional traits and antisocial behavior in children: Are there shared and/or unique predictors? Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 36(3), 319–333. doi:10.1080/15374410701444215.
Pardini, D. A., & Loeber, R. (2007). Interpersonal and affective features of psychopathy in children and adolescents: Advancing a developmental perspective. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 36(3), 269–275. doi:10.1080/15374410701441575.
Parker, G. (1989). The parental bonding instrument: Psychometric properties reviewed. Psychiatric Developments, 4, 317–335.
Parker, G., Tupling, H., & Brown, L. B. (1979). A parental bonding instrument. British Journal of Medical Psychology, 52(1), 1–10. doi:10.1111/j.2044-8341.1979.tb02487.x.
Pasalich, D. S., Dadds, M. R., Hawes, D. J., & Brennan, J. (2011). Do callous-unemotional traits moderate the relative importance of parental coercion versus warmth in child conduct problems? An observational study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 52(12), 1308–1315. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02435.x.
Roose, A., Bijttebier, P., Decoene, S., Claes, L., & Frick, P. J. (2010). Assessing the affective features of psychopathy in adolescence: A further validation of the Inventory of Callous and Unemotional traits. Assessment, 17(1), 44–57. doi:10.1177/1073191109344153.
Sedlak, A. J., McPherson, K., & Das, B. (2010). Fourth national incidence study of child abuse and neglect (NIS-4): Supplementary analyses of race differences in child maltreatment rates in the NIS-4. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Children and Families.
Seto, M. C., & Lalumière, M. L. (2010). What is so special about male adolescent sexual offending? A review and test of explanations using meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 136(4), 526–575. doi:10.1037/a0019700.
Steinberg, L. (2001). We know some things: Parent-adolescent relationships in retrospect and prospect. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 11(1), 1–19.
Thombs, B. D., Bennett, W., Ziegelstein, R. C., Bernstein, D. P., Scher, C. D., & Forde, D. R. (2007). Cultural sensitivity in screening adults for a history of childhood abuse: Evidence from a community sample. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 22(3), 368–373.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Children and Families. Administration on Children, Youth and Families, Children’s Bureau. Child Maltreatment 2009 [Online]. Available at: http://www.acf.hhs.gov/programs/cb/pubs/cm09/cm09.pdf. Accessed August 27, 2012.
Viding, E., Jones, A. P., Frick, P. J., Moffitt, T. E., & Plomin, R. (2008). Heritability of antisocial behaviour at 9: Do callous-unemotional traits matter? Developmental Science, 11(1), 17–22. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7687.2007.00648.x.
Weiler, B. L., & Widom, C. S. (1996). Psychopathy and violent behaviour in abused and neglected young adults. Criminal Behaviour and Mental Health, 6(3), 253–271. doi:10.1002/cbm.99.
Wootton, J. M., Frick, P. J., Shelton, K. K., & Silverthorn, P. (1997). Ineffective parenting and childhood conduct problems: The moderating role of callous-unemotional traits. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65(2), 301–308. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.65.2.292.b.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the University of South Florida. EK conceived of the study and its design and coordinated and contributed major portions of the writing and statistical analysis and interpretation of the data for the initial draft of the manuscript and its revision; BC performed and wrote up results of statistical analyses and contributed to their interpretation as well as substantial writing of the initial draft of the manuscript; AH participated in collecting the study data, performed a portion of the statistical analyses and contributed to their interpretation, as well as writing sections of the initial draft of the results section of the manuscript; KD participated in the coordination and collection of study data, as well as contributing sections of the writing for the initial draft of the method section of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. We thank Melissa Harrison and Vimbai Mudimu for managing the project and research assistants, Jessica Branch, Nicole Graham, Cailey Miller, Edward Perin, and Aaron Stewart for their assistance with data collection. We also thank the youth who participated in this study and the facility staff who facilitated data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimonis, E.R., Cross, B., Howard, A. et al. Maternal Care, Maltreatment and Callous-Unemotional Traits Among Urban Male Juvenile Offenders. J Youth Adolescence 42, 165–177 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-012-9820-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-012-9820-5