Abstract
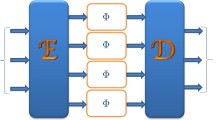
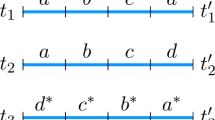
Kraus representation of quantum information transfer channels is widely used in practice. We present examples of Kraus decompositions for channels that possess the covariance property with respect to the maximal commutative group of unitary operators. We show that in some problems (for example, the problem on the estimate of the minimal output entropy of the channel), the choice of a Kraus representation with nonminimal number of Kraus operators is relevant. We also present certain algebraic properties of noncommutative operator graphs generated by Kraus operators for the case of quantum channels that demonstrate the superactivation phenomenon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. G. Amosov, “On Weyl channels being covariant with respect to the maximum commutative group of unitaries,” J. Math. Phys., 48, No. 1, 2104–2117 (2007).
G. G. Amosov, “The strong superadditivity conjecture holds for the quantum depolarizing channel in any dimension,” Phys. Rev. A, 75, No. 6, 060304 (2007).
G. G. Amosov, “On estimating the output entropy of the tensor product of a phase-damping channel and an arbitrary channel,” Probl. Pered. Inform., 49, No. 3, 32–39 (2013).
G. G. Amosov, “Estimating the output entropy of a tensor product of two quantum channels,” Teor. Mat. Fiz., 182, No. 3, 453–464 (2015).
G. G. Amosov and I. Yu. Zhdanovskii, “Structure of the algebra generated by a noncommutative operator graph which demonstrates the superactivation phenomenon for zero-error capacity,” Mat. Zametki, 99, No. 6, 929–932 (2016).
G. G. Amosov and I. Yu. Zhdanovsky, “On the noncommutative deformation of the operator graph corresponding to the Klein group,” J. Math. Sci., 215, No. 6, 659–676 (2016).
C. H. Bennett, C. A. Fuchs, and J. A. Smolin, “Entanglement-enhanced classical communication on a noisy quantum channel,” in: Quantum Communication, Computing and Measurement, Plenum Press, New York (1997), pp. 79–88.
M. D. Choi, “Completely positive linear maps on complex matrices,” Lin. Alg. Appl., 10, 285–290 (1975).
M. D. Choi and E. G. Effros, “Injectivity and operator spaces,” J. Funct. Anal., 24, No. 2, 156–209 (1977).
T. S. Cubitt, J. Chen, and A. W. Harrow, “Superactivation of the asymptotic zero-error classical capacity of a quantum channel,” IEEE Trans. Inform. Theor., 57, No. 12, 8114–8126 (2011); arXiv:0906.2547 (2009).
R. Duan, Super-activation of zero-error capacity of noisy quantum channels, arXiv:0906.2527 (2009).
A. S. Holevo, Probabilistic and Statistical Aspects of Quantum Theory [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1980).
A. S. Holevo, “Quantum coding theorems,” Usp. Mat. Nauk, 53, No. 6, 193–230 (1998).
A. S. Holevo, “The capacity of the quantum channel with general signal states,” IEEE Trans. Inform. Theor., 44, No. 1, 269–273 (1998).
A. S. Holevo, “On complementary channels and the additivity problem,” Probab. Theory. Appl., 51, 133–143 (2005).
A. S. Holevo, Quantum Channel, System, Information, De Gryuter, Berlin–Boston (2012).
A. S. Holevo and M. E. Shirokov, “On Shor’s channel extension and constrained channels,” Commun. Math. Phys., 249, 417–430 (2004).
C. King, “Additivity for unital qubit channels,” J. Math. Phys., 43, No. 10, 4641–4653 (2002).
C. King, “The capacity of the quantum depolarizing channel,” IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 49, No. 1, 221–229 (2003).
M. Kontsevich and A. Rosenberg, “Noncommutative smooth spaces,” in: Gelfand Mathematical Seminars, 1996–1999, Birkhäuser, Boston (2000), pp. 85–108.
M. Nathanson and M. B. Ruskai, “Pauli diagonal channels constant on axes,” J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 40, 8171–8204 (2007).
M. B. Ruskai, S. Szarek, and E. Werner, “An analysis of completely positive trace-preserving maps on 2 × 2 matrices,” Lin. Alg. Appl., 347, 159–187 (2002).
M. E. Shirokov, “On channels with positive quantum zero-error capacity having vanishing n-shot capacity,” Quantum Inf. Process., 14, No. 8, 3057–3074 (2015).
P. W. Shor, “Scheme for reducing decoherence in quantum computer memory,” Phys. Rev. A, 52, R2493–R2496 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Itogi Nauki i Tekhniki, Seriya Sovremennaya Matematika i Ee Prilozheniya. Tematicheskie Obzory, Vol. 138, Quantum Computing, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amosov, G.G. Algebraic Methods of the Study of Quantum Information Transfer Channels. J Math Sci 241, 109–116 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10958-019-04411-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10958-019-04411-w
Keywords phrases
- quantum channel
- Kraus decomposition
- minimal output entropy
- noncommutative operator graph
- quantum channel capacity with zero error