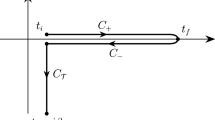
The bimodal Bose–Hubbard model is studied. The application of the Quantum Inverse Method allows us to calculate the time-dependent correlation functions of the model. Form-factors of the bosonic creation and annihilation operators in the wells are expressed in the determinantal form.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Milburn, J. Corney, E. Wright, and D. Walls, “Quantum dynamics of an atomic Bose–Einstein condensate in a double-well potential,” Phys. Rev., A 55, 4318 (1997).
D. Witthaut, F. Trimborn, and S. Wimberger, “Dissipation induced coherence of a two-mode Bose–Einstein condensate,” Phys. Rev. Lett., 101, 200402 (2008).
E. Boukobza, M. Chuchem, D. Cohen, and A. Vardi, “Phase-diffusion dynamics in weakly coupled Bose–Einstein condensates,” Phys. Rev. Lett., 102, 180403 (2009).
T. Pudlik, H. Hennig, D. Witthaut, and D. Campbell, “Dynamics of entanglement in a dissipative Bose–Hubbard dimer,” Phys. Rev., A 88, 063606 (2013).
F. Trimborn, D. Witthaut, V. Kegel, and H. J. Korsch, “Nonlinear Landau–Zener tunneling in quantum phase space,” New J. Phys., 12, 053010 (2010).
I. Tikhonenkov, M. G. Moore, and A. Vardi, “Robust sub-shot-noise measurement via Rabi–Josephson oscillations in bimodal Bose–Einstein condensates,” Phys. Rev., A 83, 063628 (2011).
M. Chuchem, K. Smith-Mannschott, M. Hiller, T. Kottos, A. Vardi, and D. Cohen, “Quantum dynamics in the bosonic Josephson junction,” Phys. Rev., A 82, 053617 (2010).
V. Giovannetti, S. Lloyd, and L. Maccone, “Quantum-enhanced measurements: beating the standard quantum limit,” Science, 306, 1330 (2004).
D. Jaksch, H.-J. Briegel, J. Cirac, C. Gardiner, and P. Zoller, “Entanglement of atoms via cold controlled collisions,” Phys. Rev. Lett., 82, 1975 (1999).
L. D. Faddeev, “Quantum completely integrable models of field theory,” in: 40 Years in Mathematical Physics, World Sci. Ser. 20th Century Math., vol. 2, World Sci., Singapore (1995), pp. 187–235.
P. P. Kulish and E. K. Sklyanin, “Quantum spectral transform method. Recent developments,” Lecture Notes Phys., 151, Springer (1982), pp. 61–119.
V. Z. Enol’skii, V. B. Kuznetsov, and M. Salerno, “On the quantum inverse scattering method for the DST dimer,” Phys., D 68, 138 (1993).
J. Links and K. Hibberd, “Bethe ansatz solutions of the Bose–Hubbard dimer,” SIGMA 2, Paper 095 (2006).
R. Orús, S. Dusuel, and J. Vidal, “Equivalence of critical scaling laws for many-body entanglement in the Lipkin–Meshkov–Glick model,” Phys. Rev. Lett., 101, 025701 (2008).
N. M. Bogoliubov, R. K. Bullough, and J. Timonen, “Exact solution of generalised Tavis-Cummings models in quantum optics,” J. Phys. A, 29, 6305 (1996).
N. M. Bogoliubov and P. P. Kulish, “Exactly solvable models of quantum nonlinear optics,” J. Math. Sci., 192, 14 (2013).
V. E. Korepin, N. M. Bogoliubov, and A. G. Izergin, Quantum Inverse Scattering Method and Correlation Functions, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge (1993).
I. G. Macdonald, Symmetric Functions and Hall Polynomials, Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford (1995).
N. A. Slavnov, “Calculation of scalar products of wave functions and form factors in the framework of the algebraic Bethe ansatz,” Theor. Math. Phys, 79, 502 (1989).
N. Kitanine, J. M. Maillet, and V. Terras, “Form factors of the XXZ Heisenberg spin-1/2 finite chain,” Nucl. Phys., B 516, 647 (1999).
V. E. Korepin, “Calculation of norms of Bethe wave functions,” Comm. Math. Phys., 86, 391 (1982).
M. Hillery and M. Zubairy, “Entanglement conditions for two-mode states,” Phys. Rev. Lett., 96, 050503 (2006).
Q. He, M. Reid, T. Vaughan, C. Gross, M. Oberthaler, and P. Drummond, “Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen entanglement strategies in two-well Bose–Einstein condensates,” Phys. Rev. Lett., 106, 120405 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to P. P. Kulish on his 70th birthday
Translated from Zapiski Nauchnykh Seminarov POMI, Vol. 433, 2015, pp. 65–77.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bogoliubov, N.M. Time-Dependent Correlation Functions for the Bimodal Bose–Hubbard Model. J Math Sci 213, 662–670 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10958-016-2730-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10958-016-2730-4