Abstract
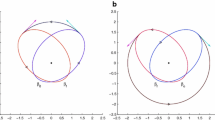
The problem of planar optimal impulsive transfer between ellipses in a Newtonian gravitational field with the final time- free is approached through a transformation of variables. New necessary conditions for optimal Bi-Elliptic Transfers are presented in terms of these transformed variables. The work is applied to examples in which the apses of the ellipses are aligned. The Generalized Hohmann, Bi-Elliptic and Bi-Parabolic Transfers are discussed. An example is presented that shows that Bi-Elliptic Transfer cannot be optimal if the final time is free. The approach can also be applied to determine optimality of transfers for other aligned configurations. This project is then changed to a fixed final time minimization problem. For this problem, it is found that there is a one-to-one correspondence between the final time and the apogee of the transfer ellipse. It is shown from this fact that there can be optimal Bi-Elliptic Transfers if the final time is fixed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hohmann, W.: Die Erreichbarkeit der Himmelskoerper, Oldenbourg, Munich (1925), The Attainability of Heavenly bodies NASA Tech. Translation F-44 (1960)
Oberth, H.: Wege Zur Raumschiffahrt. R. Oldenbourg, Munich (1929)
Lawden, D.F.: Minimal rocket trajectories. J. Am. Rocket Soc. 23, 360–382 (1953)
Lawden, D.F.: Stationary rocket trajectories. Quart. J. Mech. 7, 488–504 (1954)
Lawden, D.F.: Optimal Trajectories for Space Navigation. Butterworths, London (1963)
Shternfeld, A.: Soviet Space Sciences, pp. 109–111. Basic Books Inc, New York (1959)
Hoelker, R. F., and Silber, R.: The bi-elliptical transfer between co-planar circular orbits. In: Proceedings of the 4th symposium on ballistic missile and space technology, Los Angeles (1959)
Edelbaum, T.N.: Some extensions of the Hohmann transfer maneuver. J. Am. Rocket Soc. 29, 864–865 (1959)
Edelbaum, T.N.: How many impulses? Astronaut. Aeronaut. 5, 64–69 (1967)
Bell, D.J.: Optimal space trajectories. A review of published work. Aeronaut. J. R. Aeronaut. Soc. 72, 141–146 (1968)
Robinson, A.C.: A survey of methods and results in the determination for fuel-optimal space maneuvers. In: A.A.S. Paper 68-091, AAS/AIAA ... Specialist Conference (1968)
Gobetz, F.W., Doll, J.R.: A survey of impulse trajectories. AIAA J. 7, 801–834 (1969)
Breakwell, J.V.: Minimum impulse transfer, Preprint 63-416, AIAA Astrodynamics Conference, New Haven, Aug 19–23 (1963)
Kechician, J.A.: Optimal transfer between close near-circular orbits. Ph.D Thesis, Stanford University (1977)
Marec, J.P.: Optimal Space Trajectories. Elsevier, New York (1979)
Avandario, P., Mortari, D.: A closed-form solution to the minimum \(\Delta V_{tot}^2\) Lambert’s problem. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 106, 25–37 (2010)
Zhang, G., Zhou, D., Mortari, D.: Optimal two-impulse rendezvous using constrained multiple-revolution lambert solutions. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 110, 199–215 (2011)
Carter, T., Humi, M.: A new approach to optimal impulsive rendezvous near circular orbit. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 112, 385–426 (2012)
Carter, T., Brient, J.: Linearized impulsive rendezvous problem. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 86, 553–584 (1995)
Carter, T.: Optimal impulsive space trajectories based on linear equations. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 70, 277–297 (1991)
Neustadt, L.: Optimization, a moment problem, and nonlinear programming. SIAM J. Control 2, 33–53 (1964)
Prussing, J.: Optimal impulsive linear systems: sufficient conditions and maximum number of impulses. J. Astronaut. Sci. 43, 195–206 (1995)
Ting, L.: Optimum orbital transfers by several impulses. Asronaut. Acta 6, 256–261 (1960)
Kirilink, E., Zaborsky, S.: Optimal bi-elliptic transfer between two generic coplanar elliptical orbits. Acta Astronaut. 139, 996–1000 (2017)
Carter, T., Humi, M.: Two-impulse, bi-parabolic, and bi-elliptical transfers between coplanar elliptical orbits. Acta Astronaut. 177, 158–171 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jason L. Speyer.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carter, T., Humi, M. Generalized Hohmann, Bi-Parabolic and Bi-Elliptic Planar Impulsive Transfer Using Transformed Variables. J Optim Theory Appl 189, 117–135 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-021-01824-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-021-01824-z