Abstract
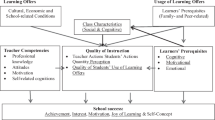
Classroom teaching is a main frontier of the implementation of new curricular ideas in China. The study reported in this article is concerned with the effectiveness of system of classroom teaching (SCT) in chemistry lessons. According to the Systems Science theory, we took a macroscopic view on the SCT, arguing that SCT is a hierarchy of system, which includes class system, plate system, unit system, and primitive system. In this study, we focused on primitive system of classroom teaching (PrS)—the lowest level in a SCT. Using focus group interviews, this study investigated the variables related to the effectiveness of PrS. We found a total of 21 such variables. To identify the main factors underlying the effectiveness of PrS, we further used exploratory factor analysis and confirmatory factor analysis. We found five main factors: rational use of time, quality of teaching behavior chain, match degree, quality of using resource and technology, and rationality of primitive content. Based on these findings, we constructed an evaluation scale for assessing the effectiveness of primitive system of chemistry classroom teaching.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alton-Lee A (2003) Quality teaching for diverse students in schooling: Best evidence synthesis. Retrieved from http://www.educationcounts.govt.nz/publications/series/2515/5959
Angelo T, Cross P (1993) Classroom assessment techniques: a handbook for college teachers. Josse Bass Higher and Adult Education: Jossey-Bass, San Francisco
Baker JA (1999) Teacher-student interaction in Urban at-risk classrooms: differential behavior, relationship quality, and student satisfaction with school. Elem Sch J 100(1):57–70
Birch SH, Ladd GW (1997) The teacher-child relationship and children’s early school adjustment. J Sch Psychol 35(1):61–79. doi:10.1016/s0022-4405(96)00029-5
Byrom E, Bingham M (1998) Factors influencing the effective use of technology for teaching and learning: lessons learned from the SEIR-TEC intensive site schools. SERVE, Greensboro, NC
Cameron M (2002) Peer influences on learning. Set 3:36–40
Chickering AW, Ehrmann SC (1996) Implementing the seven principles: technology as lever. AAHE Bull 49(3):3–7
Çimer A (2007) Effective teaching in science: a review of literature. J Turk Sci Educ 4(1):20
Clark LA, Watson D (1995) Constructing validity: basic issues in objective scale development. Psychol Assess 7(3):309–319
Cui Y (2009) Effective teaching. East China Normal University Press, Shanghai (in Chinese)
Darling-Hammond L (2000) Teacher quality and student achievement: a review of state policy evidence. Educ Policy Anal Arch 8(1). Retrieved from http://epaa.asu.edu/ojs/article/view/392
Davis EA, Petish D, Smithey J (2006) Challenges new science teachers face. Rev Educ Res 76(4):607–651. doi:10.3102/00346543076004607
Delandshere G (2002) Assessment as inquiry. Teach Coll Rec 104(7):1461–1484
Dowing L, Harland D (2001) Critical factors in the effective use of technology. Walden University. Retrieved from http://www.dowlingcentral.com/gradschool/Edu6420/project1.html
Ebel RL (1954) Procedures for the analysis of classroom tests. Educ Psychol Measur 14(2):352–364. doi:10.1177/001316445401400215
Ferketich S (1991) Focus on psychometrics. Aspects of item analysis. Res Nurs Health 14(2):165–168. doi:10.1002/nur.4770140211
Findley WG (1956) A rationale for evaluation of item discrimination statistics. Educ Psychol Measur 16(2):175–180. doi:10.1177/001316445601600201
Floden RE (2001) Research on effects of teaching. In: Richardson V (ed) Handbook of research on teaching, 4th edn. American Educational Research Association, Washington, DC, pp 3–16
Glynn SM, Taasoobshirazi G, Brickman P (2009) Science Motivation Questionnaire: construct validation with nonscience majors. J Res Sci Teach 46(2):127–146. doi:10.1002/tea.20267
Goldhaber D, Anthony E (2007) Can teacher quality be effectively assessed? National Board Certification as a Signal of Effective Teaching. Rev Econ Stat 89(1):134–150. doi:10.1162/rest.89.1.134
Gorsuch RL (1983) Factor analysis, 2nd edn. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, NJ
Gorsuch RL (2003) Factor analysis. In: Schinka JA, Velicer WF (eds) Handbook of psychology: research methods in psychology. John Wiley, Hoboken, NJ
Guadagnoli E, Velicer WF (1988) Relation of sample size to the stability of component patterns. Psychol Bull 103(2):265–275
Gurney P (2007) Five factors for effective teaching. N Z J Teach Work 4(2):89–98
Haycock K (1998) Good teaching matters: how well-qualified teachers can close the gap. Thinking K 16(3):2
He X (2007) Reflect on the effectiveness of classroom teaching under the background of new curriculum. Teach Learn Ref Middle Sch Chem (in Chinese)
Henson RK, Roberts JK (2006) Use of exploratory factor analysis in published research. Educ Psychol Measur 66(3):393–416. doi:10.1177/0013164405282485
Howard ME (2008) Effective teachers’ perceptions of the impact of the multiple dimensions of teaching on student success in the elementary classroom (Order No. 3310953, The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill). ProQuest Dissertations and Theses, pp 167–n/a. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com/docview/304530855?accountid=12840
Jones, B. F. (1995). New times demand new ways of learning. Retrieved from http://www.netc.org/cdrom/plug_in/html/newtimes.htm
Kaplan D (2000) Structural equation modeling: foundations and extensions. SAGE Adv Quant Tech Soc Sci Seri 10. ISBN 0-7619-1407-2
Kaplan LS, Owings WA (2001) Teacher quality and student achievement: recommendations for principals. NASSP Bull 85(628):64–73. doi:10.1177/019263650108562808
Kendall MG (1938) A new measure of rank correlation. Biometrika 30(1/2):81–93
Lahue-McCully M (2012) Traditional teaching strategies and effective teaching strategies in connection to student achievement: a comparison in one school district’s high school English classrooms. Doctoral dissertation. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com/docview/1019055700
Lange A, Lehmann IJ, Mehrens WA (1967) Using item analysis to improve tests. J Educ Meas 4(2):65–68. doi:10.1111/j.1745-3984.1967.tb00572.x
Lee M-H, Johanson RE, Tsai C–C (2008) Exploring Taiwanese high school students’ conceptions of and approaches to learning science through a structural equation modeling analysis. Sci Educ 92(2):191–220. doi:10.1002/sce.20245
Legendre P (2005) Species associations: the Kendall coefficient of concordance revisited. J Agric Biol Environ Stat 10(2):226–245. doi:citeulike-article-id:201411
Legendre P (2010) Coefficient of concordance. In: N Salkind (ed) Encyclopedia of research design. SAGE Publications, Inc., Thousand Oaks, CA, pp 165–170. doi:10.4135/9781412961288.n55
Liu J (2008) Complexity: a philosophical view. Hunan Science and Technology Press, ChangSha, China (in Chinese)
Lv X, Wang Y (2007) Classroom instructional strategies of the training of students scientific quality in American science education. Studies in Foreign Education (in Chinese)
Mainous GA (1993) Factor analysis as a tool in primary care research. Fam Pract 10(3):330–336. doi:10.1093/fampra/10.3.330
Miao D (2010) Essentials of systems science, 3rd edn. China Renmin University Press, BeiJing (in Chinese)
Ministry of Education (2003) Chemistry curriculum standard of general senior secondary school. People’s Education Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Nokelainen P (2007) Introduction to structural equation modeling. Retrieved from http://www.uta.fi/arkisto/aktk/lectures/sem_en/pdf/1999_pn.pdf
Norman MM (2000) The human side of school technology. Educ Digest 65(7):45–52
Nunnally JC, Bernstein IH, Berge JMT (1967) Psychometric theory, vol 2. McGraw-Hill, New York
Oesterle M (2008) Student perceptions of effective teaching. Doctoral dissertation, Arizona State University. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com/docview/304686040
People’s Education Press, CMRI (2004) High school curriculum standard textbook: chemistry (Module 1). People’s Education Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Peterson PL, Fennema E (1985) Effective teaching, student engagement in classroom activities, and sex-related differences in learning mathematics. Am Educ Res J 22(3):309–335
Pianta RC (1999) Enhancing relationships between children and teachers. American Psychological Association, Washington, DC
Preece PF, Skinner NC (1999) The national assessment in science at Key Stage 3 in England and Wales and its impact on teaching and learning. Assess Educ Princ Pol Pract 6(1):11–25
Prosser M, Trigwell K (1997) Relations between perceptions of the teaching environment and approaches to teaching. Br J Educ Psychol 67(1):25–35. doi:10.1111/j.2044-8279.1997.tb01224.x
Reise SP, Wallar NG, Comrey AL (2000) Factor analysis and scale revision. Psychol Assess 12(3):287–297. doi:10.1037//1040-3590.12.3.287
Rui LJC, Yoau-chau J, Shi H (2010) The relationship between teacher quality and teaching effectiveness perceived by students from industrial vocational high schools. Arts Sci 1:167–187
Salkind NJ (ed) (2007) Encyclopedia of measurement and statistics, vol 1–3. SAGE Publications, Inc., Thousand Oaks, CA. doi:10.4135/9781412952644
Schumacker RE, Lomax RG (2004) A beginner’s guide to structural equation modeling, 2nd edn. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah, NJ
Seidel T, Shavelson RJ (2007) Teaching effectiveness research in the past decade: the role of theory and research design in disentangling Meta-Analysis results. Rev Educ Res 77(4):454–499
Shelly RW (2000) From literacy to fluency in instructional technology: taking your staff to the next level. NASSP Bull 84(614):61–70. doi:10.1177/019263650008461408
Smith K (1995) Strategies for effective teaching a handbook for teaching assistants. Retrieved from http://www.engr.wisc.edu/services/elc/strategies.pdf
Song Q (2004) On teaching effectiveness. Curric Teach Mater Method 24(10):25–29 (in Chinese)
Steven J (1996) Applied multivariate statistics for the social science, 3rd edn. Erlbaum, Mahwah, NJ
Sun Y (2008) A study on the effective classroom teaching standards. Educational Science Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Tabachnick BG, Fidell L (2000) Using multivariate statistics, 4th edn. Allyn&Bacon, Boston
Tang Y (2003) Discussion of teaching communication effectiveness. J Chin Soc Educ 6:35–37 (in Chinese)
Thompson B (2004) Exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis: understanding concepts and applications. American Psychological Association, Washington, DC
Von Bertalanffy L (1950) An outline of general system theory. Br J Philos Sci 1:134–165. doi:10.1093/bjps/I.2.134
Wang X (2000) Classroom behavior difference research on effective teaching and inefficient teaching. Educ Theory Pract 20(9):50–53 (in Chinese)
Wang C (2005) The research of developing the scientific literacy of students in the chemistry teaching process of senior middle school. Master’s thesis. Retrieved from http://epub.cnki.net/kns/default.htm
Wenglinsky H (2000) How teaching matters bringing the classroom back into discussions of teacher quality. Retrieved from http://www.ets.org/Media/Research/pdf/PICTEAMAT.pdf
Wolk S (2001) The benefits of exploratory time. Educ Lead 59(2):56–59
Wu M (2011) Structural equation modeling—operation and application of using AMOS. Chong Qing University Press, Chong Qing (in Chinese)
Yao L (2004) The elementary approach to the implications of effective teaching. Mod Univ Educ 5:10–13 (in Chinese)
Zhao Z (2002) Optimizing students mood—effective teaching strategy. People’s Educ 5:45–46 (in Chinese)
Zheng C (2006) New chemistry curriculum and teaching. Graduated College of Northeast Normal University, Changchun (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Initial Hypothesized Assessing Instrument
Appendix: Initial Hypothesized Assessing Instrument
Evaluation scale of effectiveness of primitive system of classroom teaching (ESEPrSCT)
Items | StD | D | SiD | SiA | A | StA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1. Rich and innovative of this selective content material | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
2. This content is appropriate to reflect the curriculum standards and textbooks | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
3. This generated content is reasonable | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
4. The breadth and depth of this content is in students’ zone of proximal development | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
5. No unreasonable deepen and widen to this content | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
6. Using time properly according to characteristics of this content | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
7. Compact and appropriate speed of the teaching process | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
8. No waste time on the lack of clarity | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
9. No waste time on the unreasonable generation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
10. No waste time on making mistake or re-presentation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
11. Teacher can well manage the type of this teaching behavior chain | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
12. The type of this teaching behavior chain is consistent with the learning characteristics of students | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
13. The type of this teaching behavior chain is consistent with the characteristics of this content | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
14. The type of this teaching behavior chain is consistent with the school resources | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
15. Choosing proper material object (or model, writing on the blackboard, multimedia, etc.) to assist students’ understanding | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
16. Participating fully in teaching and learning activities (discussion, communication, question–answer, etc.) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
17. Selecting experimental material properly to attract students’ attention | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
18. Summarizing properly in an opportune moment | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
19. Question designed lead to students’ effective thinking | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
20. Teacher–student and student–student communicate fully with each other | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
21. Encouraging students to self-evaluation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, C., Fu, L. & He, P. Development of an Instrument for Assessing the Effectiveness of Chemistry Classroom Teaching. J Sci Educ Technol 23, 267–279 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-013-9459-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-013-9459-3