Abstract
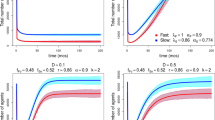
Neutral models aspire to explain biodiversity patterns in ecosystems where species difference can be neglected and perfect symmetry is assumed between species. Voter-like models capture the essential ingredients of the neutral hypothesis and represent a paradigm for other disciplines like social studies and chemical reactions. In a system where each individual can interact with all the other members of the community, the typical time to reach an absorbing state with a single species scales linearly with the community size. Here we show, by using a rigorous approach based on a large deviation principle and confirming previous approximate and numerical results, that in a mean-field heterogeneous voter model the typical time to reach an absorbing state scales exponentially with the system size.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hubbell, S.P.: The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Monographs in population biology. Princeton University Press, Princeton (2008)
Volkov, I., Banavar, J.R., Hubbell, S.P., Maritan, A.: Neutral theory and relative species abundance in ecology. Nature 424(2), 1035–1037 (2003)
Azaele, S., Pigolotti, S., Banavar, J.R., Maritan, A.: Dynamical evolution of ecosystems. Nature 444, 926–928 (2006)
Vallade, M., Houchmandzadeh, B.: Analytical solution of a neutral model of biodiversity. Phys. Rev. E 68(6), 061902 (2003)
Alonso, D., Etienne, R.S., McKane, A.J.: The merits of neutral theory. Trends Ecol. Evol. 21(8), 451–457 (2006)
Chave, J.: Neutral theory and community ecology. Ecol. Lett. 7, 241–253 (2004)
Liggett, T.M.: Interacting Particle Systems. Springer, Dordrecht (2005)
Al Hammal, O., Chaté, H., Dornic, I., Muñoz, M.A.: Langevin description of critical phenomena with two symmetric absorbing states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230601 (2005)
Kimura, M., Takahata, N.: Population Genetics, Molecular Evolution, and the Neutral Theory: Selected Papers. Evolutionary biology. University of Chicago Press, Chicago (1995)
M. Henkel, H. Hinrichsen, and S. Lübeck. Non-equilibrium Phase Transitions. Volume I: Absorbing phase transitions. Theoretical and Mathematical Physics. Springer / Canopus, (2008)
Dornic, I., Chaté, H., Chave, J., Hinrichsen, H.: Critical coarsening without surface tension: the universality class of the voter model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 045701 (2001)
Durrett, R., Levin, S.A.: Stochastic spatial models: a user’s guide to ecological applications. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 343(1305), 329–350 (1994)
Castellano, C., Fortunato, S., Loreto, V.: Statistical physics of social dynamics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 591–646 (2009)
Blythe, R.A., McKane, A.J.: Stochastic models of evolution in genetics, ecology and linguistics. J. Stat. Mech.: Theory Exp. 2007(07), P07018 (2007)
Pigolotti, S., Cencini, M.: Coexistence and invasibility in a two-species competition model with habitat-preference. J. Theor. Biol. 265(4), 609–617 (2010)
Borile, C., Maritan, A., Muñoz, M.A.: The effect of quenched disorder in neutral theories. J. Stat. Mech.: Theory Exp. 2013(04), P04032 (2013)
Tilman, D., May, R.M., Lehman, C.L., Nowak, M.A.: Habitat destruction and the extinction debt. Nature 371, 65–66 (1994)
Masuda, N., Gibert, N., Redner, S.: Heterogeneous voter models. Phys. Rev. E 82, 010103 (2010)
Masuda, N., Redner, S.: Can partisan voting lead to truth? J. Stat. Mech.: Theory Exp. 2011(02), L02002 (2011)
Krapivsky, P.L., Redner, S., Ben-Naim, E.: A Kinetic View of Statistical Physics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Ódor, G.: Universality In Nonequilibrium Lattice Systems: Theoretical Foundations. World Scientific, Singapore (2008)
Tilman, D.: Niche tradeoffs, neutrality, and community structure: a stochastic theory of resource competition, invasion, and community assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101(30), 10854–10861 (2004)
Adler, P.B., HilleRisLambers, J., Levine, J.M.: A niche for neutrality. Ecol. Lett. 10(2), 95–104 (2007)
Lambert, A.: Population dynamics and random genealogies. Stoch. Models 24(S1), 45–163 (2008)
Ethier, S.N., Kurtz, T.G.: Markov Processes: Characterization and Convergence. Wiley, Hoboken (2009)
Freidlin, M.I., Wentzell, A.D.: Random Perturbations of Dynamical Systems. Springer, Dordrecht (2012)
Den Hollander, F. Large deviations. Am. Math. Soc., 2008.
Touchette, H.: The large deviation approach to statistical mechanics. Phys. Rep. 478(1), 1–69 (2009)
Bovier, A.: Eur. Math. Soc. Zurich. Metastability: a potential theoretic approach. International Congress of Mathematicians III, 499–518 (2006)
Bianchi, A., Bovier, A., Ioffe, D.: Sharp asymptotics for metastability in the random field Curie-Weiss model. Electron. J. Probab. 14(53), 1541–1603 (2009)
J. T. Cox and A. Greven. The finite systems scheme: an abstract theorem and a new example. Measure-valued processes, stochastic partial differential equations, and interacting systems (Montreal, PQ, 1992), 55?67, In: CRM Proceeding Lecture Notes, 5, American Mathematical Society , Providence, RI, 1994.
Greven, A., Limic, V., Winter, A.: Representation theorems for interacting Moran models, interacting Fisher-Wright diffusions and applications. Electron. J. Probab. 10(39), 1286–1356 (2005)
Budhiraja, A., Dupuis, P., Maroulas, V.: Variational representations for continuous time processes. Ann. Inst. Henri Poincaré Probab. Stat. 47(3), 725–747 (2011)
Falcone, M. Numerical solution of dynamic programming equations. Appendix A. In: Bardi, M., and Capuzzo-Dolcetta, I. Optimal Control and Viscosity Solutions of Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman Equations. Birkhäuser, 1997.
Kushner, H.J., Dupuis, P.: Numerical Methods for Stochastic Control Problems in Continuous Time. Springer, dordrecht (2001)
Hanggi, P.: Escape from a metastable state. J. Stat. Phys. 42(1–2), 105–148 (1986)
Durrett, R.: Coexistence in stochastic spatial models. Ann. Appl. Probab. 19, 477–496 (2009)
McClain, C.R., Barry, J.P.: Habitat heterogeneity, disturbance, and productivity work in concert to regulate biodiversity in deep submarine canyons. Ecology 91(4), 964–976 (2010)
Acknowledgments
AM acknowledges Cariparo foundation for financial support. We thank Miguel Muñoz for useful discussions, comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borile, C., Pra, P.D., Fischer, M. et al. Time to Absorption for a Heterogeneous Neutral Competition Model. J Stat Phys 156, 119–130 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-014-0989-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-014-0989-8
Keywords
- Voter Model with disorder
- Neutral models of biodiversity
- Large deviations
- Stochastic dynamics with quenched disorder