Abstract
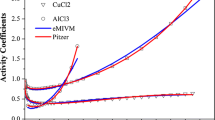
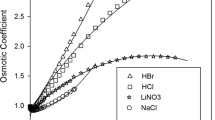
In this work, the electrolyte molecular interaction volume model (eMIVM) and the optimized model (eMIVM-ET) were used to fit the activity coefficients and osmotic coefficients of 47 single electrolyte solutions containing Ni2+, Co2+ and Cu2+, respectively, and the activity coefficients and osmotic coefficients of 10 two electrolyte solutions containing Ni2+, Co2+ and Cu2+ were predicted. The results indicate that the average deviation and average relative error fitted by the two models are: the activity coefficients of eMIVM are 0.0548 and 7.22%, the osmotic coefficients are 0.0307 and 5.06%, the activity coefficients of eMIVM-ET are 0.0326 and 3.78%, and the osmotic coefficients are 0.0276 and 4.73%, respectively; the average deviation and relative error predicted by the two models are: the activity coefficients of eMIVM are 0.2331 and 41.64% , the osmotic coefficients are 0.2590 and 21.1%, the activity coefficients of eMIVM-ET are 0.1340 and 24.88%, and the osmotic coefficients are 0.1139 and 9.11% respectively. This shows that the prediction effect of eMIVM-ET is better than that of eMIVM, so eMIVM-ET can be used as an alternative thermodynamic prediction model.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(i\) :
-
The component of the electrolyte solution
- \(*\) :
-
Represents asymmetry
- \(x_{i}\) :
-
The mole fraction of the component
- \(A_{\phi }\) :
-
Debye-Hückel parameter
- \(M_{s}\) :
-
Molecular weight of solvent
- \(\rho\) :
-
Nearest distance parameter
- \(I_{x}\) :
-
Ionic strength
- \(z_{i}\) :
-
Charge number of the ion
- \(\gamma_{ \pm }^{ * }\) :
-
Average activity coefficient in mole fraction
- \(r_{i}\) :
-
Radius of the ion in the solution(nm)
- \(\gamma_{ \pm m}^{ * }\) :
-
Average activity coefficient in mass molar concentration
- S D :
-
Deviation of the system
- ARD :
-
Relative error of the system (%)
References
Moggia, E.: Generalized Quasi-Random Lattice model for electrolyte solutions: Mean activity and osmotic coefficients, apparent and partial molal volumes and enthalpies. Fluid Phase Equilib. 479, 69–84 (2018)
Dan, W., Yang, Y.Y., Zhang, X.P., Sang, S.H.: Mean activity coefficients of NaCl in NaCl–CdCl2–H2O ternary system at 298.15 K by potential difference method. J. Chem. Eng. Data 61, 3027–3033 (2016)
Shekarri, H., Mousavi, S.S.: Measurement and modeling of osmotic coefficients of aqueous solution of ionic liquids using vapor pressure osmometry method. Fluid Phase Equilib. 279, 73–79 (2009)
Noguchi, D., Takeda, O., Abe, T., Zhu, H.M., Sugimoto, S.: Determination of activity of RE (RE = Nd and Dy) in molten RE-Fe-B alloys by the electromotive force method. Thermochim. Acta 709, 179–161 (2022)
Wang, W.: Determination of activity coefficient of electrolyte solution. J. Hubei Norm. Coll. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 25, 104–106 (2005)
Dai, H., Tao, D.P.: A statistical thermodynamic model with strong adaptability for liquid mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilib. 473, 154–165 (2018)
Pitzer, K.S.: Thermodynamics of electrolytes. I. Theoretical basis and general equations. J. Phys. Chem. 77, 268–277 (1973)
Pitzer, K.S., Kim, J.J.: Thermodynamics of electrolytes. IV. Activity and osmotic coefficients for mixed electrolytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 96, 5701–5707 (1974)
Kim, H.T., Frederick, W.J.: Evalution of Pitzer ion interaction parameters of aqueous electrolytes at 25°C. 1. Single Salt parameters. J. Chem. Eng. Data 33, 177–184 (1988)
Das, B.: Pitzer ion interaction parameters of single aqueous electrolytes at 25°C. J. Solution Chem. 33, 33–45 (2004)
Zhang, C.Y., Xing, Y.B., Tao, D.P.: A two-parameter theoretical model for predicting the activity and osmotic coefficients of aqueous electrolyte solutions. J. Solution Chem. 49, 659–694 (2020)
Shi, J.D., Wu, H.Y., Li, H., et al.: Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics and influencing factors of heavy metals in surface soil of China: based on bibliometric analysis. Environ. Ecol. 4, 1–7 (2022)
Ge, F., Li, M.M., Ye, H., Zhao, B.X.: Effective removal of heavy metal ions Cd2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Cu2+from aqueous solution by polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 211, 251–256 (2012)
Wl, W., Zeng, D., Zhou, H., Wu, X.F., Yin, X.: Solubility isotherms of gypsum, hemihydrate, and anhydrite in the ternary systems CaSO4 + MSO4 + H2O (M = Mn Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) at T=298.1 K to 373.1 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 60, 3024–3032 (2015)
Zhang, C., Xing, Y.B., Tao, D.P.: Prediction of activity and osmotic coefficients of fission product systems CsOH + CsX (X = Cl, Br, I) at 298.15 K. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 323, 773–784 (2020)
Pitzer, K.S.: Electrolytes: from dilute solutions to fused salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 102, 2902–2906 (1980)
Tao, D.P.: A new model of thermodynamics of liquid mixtures and its application to liquid alloys. Thermochim. Acta 363, 105–113 (2000)
Tao, D.P.: Basic features and applications of molecular interaction volume model. J. Kunming Univ. Sci. Technol. (Sci. Technol.) 29, 15–22 (2004)
Dai, H., Tao, D.P.: Application of the molecular interaction volume model (MIVM) and its modified form to organic vapor-liquid equilibria. Fluid Phase Equilib. 484, 74–81 (2019)
Marcus, Y.: Ionic volumes in solution. Biophys. Chem. 124, 200–207 (2006)
Tao, D.P.: The universal characteristics of a thermodynamic model to conform to the Gibbs-Duhem equation. Sci. Rep. 6, 35792 (2016)
Spah, M., Spah, D.C., Park, J.J., Song, H.J., Park, K., Park, J.W.: Thermodynamic transfer study of various metal chlorides from water to formamide and dimethylformamide by EMF measurements. Fluid Phase Equilib. 272, 75–83 (2008)
Downes, C.J.: Thermodynamics of mixed electrolyte solutions: the systems H2O−NaCl−CoCl2 and H2O−CaCl2−CoCl2 at 25°C. J. Solution Chem. 4, 191–204 (1975)
Pournaghdy, M., Aghaie, H., Monajjemi, M., Giahi, M., Bagherinia, M.A.: Thermodynamic investigation of the ternary mixed electrolyte (CoCl2 + CoSO4 + H2O) system by EMF measurements at T = 298.15 K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 42, 1494–1499 (2010)
Pitzer, K.S.: Thermodynamic properties of aqueous solutions of bivalent sulphates. J. Chem. Soc. 68, 101–113 (1972)
Ghalami-Choobar, B.: Thermodynamic study of the ternary mixed electrolyte (NaCl + NiCl2 + H2O) system: application of Pitzer model with higher-order electrostatic effects. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 43, 901–907 (2011)
Arvand, M., Ghalami-Choobar, B., Moghimi, M., Zanjianchi, M.A., Bagherinia, M.A.: Thermodynamic investigation of the ternary mixed electrolyte (NiCl2 + NiSO4 + H2O) system by potentiometric method at T=298.15 K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 41, 916–922 (2009)
Rard, J.A.: Isopiestic investigation of water activities of aqueous NiCl2 and CuCl2 solutions and the thermodynamic solubility product of NiCl2·6H2O at 298.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 37, 433–442 (1992)
Guendouzi, M.E.L., Mounir, A., Dinane, A.: Water activity, osmotic and activity coefficients of aqueous solutions of Li2SO4, Na2SO4, K2SO4, (NH4)2SO4, MgSO4, MnSO4, NiSO4, CuSO4, and ZnSO4 at T=298.15K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 35, 209–220 (2003)
Albright, J.G., Rizzo, P.: Isopiestic determination of the osmotic and activity coefficients of Cu(NO3)2(aq) at the temperature 298.15 K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 30, 327–352 (1998)
Wei, X.Q., Sang, S.H., Ma, X.C., Gao, Y.Y., Lei, N.F.: Thermodynamic study of the ternary system KCl–CuCl2–H2O at 298.15 K by the electromotive force method. J. Chem. Eng. Data 64, 5349–5355 (2019)
Yang, H.T., Zeng, D.W., Voigt, W., Chen, Y.F., Zhou, Q.B.: Isopiestic measurements on aqueous solutions of heavy metal sulfates: MSO4 + H2O (M = Mn Co, Ni, Cu, Zn). 2. T=373.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 61, 3406–3412 (2016)
Yang, H.T., Zeng, D.W., Voigt, W., Hefter, G., Liu, S.J., Chen, Q.Y.: Isopiestic measurements on aqueous solutions of heavy metal sulfates: MSO4 + H2O (M = Mn Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) 1. T = 323.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 59, 97–102 (2014)
Ma, X.C., Li, X.P., He, X.F., Sang, S.H., Lei, N.F., Nie, Z.: Thermodynamic study of the NaCl-CuCl2-H2O ternary system at 298.15 K by the electromotive force method. J. Chem. Eng. Data 64, 90–97 (2019)
Yi, X., Hu, J.G., Zhang, W.L., Zhang, X.Y., Sun, M., Liu, S.J.: Isopiestic measurements of osmotic and activity coefficients of NiCl2-NH4Cl-H2O systems at 308.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 63, 3136–3144 (2018)
Spah, M., Spah, D.C., Lee, J., Song, H.J., Park, J.W.: Thermodynamic determination of solvation potentials of divalent metal chlorides (MCl2) in iso-dielectric media by EMF measurements. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 41, 598–603 (2009)
Spah, M., Spah, D.C., Jun, S.Y., Lee, S.M., Song, H.J., Won-Gun, K., Park, J.W.: Thermodynamic determination of solvation potentials of various metal chlorides by (1,4-dioxane + water) mixtures through EMF measurements. Fluid Phase Equilib. 279, 17–27 (2009)
Ghalami-Choobar, B.N., Mahmoodi, N., Nasiri-Louhesara, T.: Potentiometric determination of activity coefficients for NiCl2 in water + glucose mixtures at 298.15K. Phys. Chem. Liq. 49, 673–683 (2011)
Bagherini, M.A., Pournaghdi, M.: Determination and modeling of activity coefficients of cobalt chloride in the (water plus ethanol) mixed solvent system by potentiometric method at 298.15 K. J. Mol. Liq. 199, 339–343 (2014)
Sardroodi, J.J., Seyedahmadian, S.M., Sadr, M.H., Kazemi, Y.: Isopiestic study of the solutions of MnCl2, CoCl2 and NiCl2 in methanol and ethanol at 298.15 K. Fluid Phase Equilib. 240, 114–121 (2006)
Zafarani-Moattar, M.T., Sardroodi, J.J.: Isopiestic and volumetric study of CuCl2 + ethanol at 25°C. J. Chem. Eng. Data 48, 308–313 (2003)
Sang, S.H., Wei, X.Q., Ma, X.C., Gao, Y.Y., Lei, N.F., Cui, R.Z.: Activity coefficient measurements in the ternary system NaNO3-Cu(NO3)2–H2O at 298.15 K by the cell potential method. J. Chem. Eng. Data 66, 1255–1263 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No.51464022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SZ participated in all the work of the whole thesis CX participated in the model optimization work YL participated in the mapping work of Figs.1–4. DT participated in the guidance of this research.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, S., Xu, C., Lu, Y. et al. Prediction of Thermodynamic Properties of Ni2+, Co2+, Cu2+ Electrolyte Solutions by eMIVM-ET. J Solution Chem 52, 1273–1288 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-023-01315-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-023-01315-x