Abstract
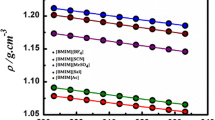
Three imidazole anion-functionalized ionic liquids (IFILs) with tributylethylphosphonium ([P4442]+) cation and imidazolate ([Im]−), 4-methylimidazolate ([4-MeIm]−), or 4-bromimidazolate ([4-BrIm]−) anions were prepared to study the effect of physicochemical properties on CO2 absorption behavior. Density (ρ), viscosity (η), and speed of sound (u) of the studied IFILs were measured, and molecular volume (Vm), standard entropy (S0), lattice energy (UPOT), and isentropic compressibility coefficient (κs) were calculated accordingly. CO2 absorption behavior of [P4442][Im] at T = 313.15–333.15 K and p = 0.2 and 1 bar was investigated as an example. The results show that with the increase of temperature, ρ, η, u, and UPOT decrease, while Vm, S0, and κs increase, due to a decrease in electrostatic interaction correspondingly. The orders of ρ, u, η, Vm, and S0 values are as follows: [P4442][Im] < [P4442][4-MeIm] < [P4442][4-BrIm], while UPOT and κs are in reverse order. Interestingly, CO2 capture capacity of IFILs is approximately linear with η or κs. Due to low η and high κs, CO2 absorption capacity of [P4442][Im] is almost independent of temperature and partial pressure, as high as 0.90 mol CO2/mol IL at 333.15 K and 0.2 bar, indicating that [P4442][Im] has potential applications for CO2 absorption at high temperature and low pressure.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fu, X., Tang, X., Chen, T., Xu, Y., Luo, X., Lu, Y., Wang, X., Qin, D., Zhang, L.: Understanding of the interactions between azole-anion-based ionic liquids and 2-methyl-3-butyn-2-ol from the experimental perspective: the cage effect. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 24, 12550–12562 (2022)
Liu, J., Tang, X., Lu, H., Xu, Y.: Insight into the interactions between azole-anion-based ionic liquids and propargylic alcohol: influence on the carboxylative cyclization of propargylic alcohol with carbon dioxide. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 9, 5050–5060 (2021)
Wang, C., Luo, X., Luo, H., Jiang, D.-E., Li, H., Dai, S.: Tuning the basicity of ionic liquids for equimolar CO2 capture. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. 50, 4918–4922 (2011)
Zhao, Y., Wu, Y., Yuan, G., Hao, L., Gao, X., Yang, Z., Yu, B., Zhang, H., Liu, Z.: Azole-anion-based aprotic ionic liquids: functional solvents for atmospheric CO2 transformation into various heterocyclic compounds. Chem. Asian J. 11, 2735–2740 (2016)
Candia-Lomelí, M., Covarrubias-Garcia, I., Aizpuru, A., Arriaga, S.: Preparation and physicochemical characterization of deep eutectic solvents and ionic liquids for the potential absorption and biodegradation of styrene vapors. J. Hazard. Mater. 441, 129835 (2023)
Chen, T., Wu, X., Xu, Y.: Effects of the structure on physicochemical properties and CO2 absorption of hydroxypyridine anion-based protic ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 362, 119743 (2022)
Zema, Z.A., Chen, T., Shu, H., Xu, Y.: Tuning the CO2 absorption and physicochemical properties of K+ chelated dual functional ionic liquids by changing the structure of primary alkanolamine ligands. J. Mol. Liq. 344, 117983 (2021)
Shi, G., Zhao, H., Chen, K., Lin, W., Li, H., Wang, C.: Efficient capture of CO2 from flue gas at high temperature by tunable polyamine-based hybrid ionic liquids. AIChE J. 66, e16779 (2020)
Wenny, M.B., Molinari, N., Slavney, A.H., Thapa, S., Lee, B., Kozinsky, B., Mason, J.A.: Understanding relationships between free volume and oxygen absorption in ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B. 126, 1268–1274 (2022)
Ramkumar, V., Gardas, R.L.: Thermophysical properties and carbon dioxide absorption studies of guanidinium-based carboxylate ionic liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 64, 4844–4855 (2019)
García-Gutiérrez, P., Jacquemin, J., Mccrellis, C., Dimitriou, I., Taylor, S.F.R., Hardacre, C., Allen, R.W.K.: Techno-economic feasibility of selective CO2 capture processes from biogas streams using ionic liquids as physical absorbents. Energy Fuels 30, 5052–5064 (2016)
He, Y., Wang, J., Chen, T., Xu, Y.: Effects of substituents on carbon capture properties of imidazole anion-functionalized ionic liquids. Energy Environ. Prot. 36, 60–65 (2022). (in Chinese)
Krishnan, A., Gopinath, K.P., Vo, D.V.N., Malolan, R., Nagarajan, V.M., Arun, J.: Ionic liquids, deep eutectic solvents and liquid polymers as green solvents in carbon capture technologies: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 18, 2031–2054 (2020)
Yang, J., Lu, X., Gui, J., Xu, W.: A new theory for ionic liquids—The interstice Model Part 1. The density and surface tension of ionic liquid EMISE. Green. Chem. 6, 541–543 (2004)
Ma, D., Zhu, C., Fu, T., Ma, Y., Yuan, X.: Performance and pressure drop of CO2 absorption into task-specific and halide-free ionic liquids in a microchannel. AIChE J. 68,(2022)
Chen, J., Chen, L., Xu, Y.: Properties of pure 1, 1, 3, 3-tetramethylguanidine imidazole ionic liquid and its binary mixtures with alcohols at T = (293.15 to 313.15) K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 88, 110–120 (2015)
Wang, J., Li, Y., Guo, C., Zhao, Y., Tong, J.: Viscosity and electrical conductivity of ether-functionalized ionic liquids-[C1OC2mim][OAc], [C1OC2mim][Pro] and [C2OC2mim][Pro]. J. Mol. Liq. 349, 118200 (2022)
Mu, L., He, H.: Prediction of standard absolute entropies for gaseous organic compounds. Chemom Intell. Lab. Syst. 112, 41–47 (2012)
Zhang, D., Li, B., Hong, M., Kong, Y., Tong, J.: Synthesis and characterization of physicochemical properties of new ether-functionalized amino acid ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 304, 112718 (2020)
Wang, J., Jiang, H., Liu, Y., Hu, Y.: Density and surface tension of pure 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium L-lactate ionic liquid and its binary mixtures with water. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 43, 800–804 (2011)
Glasser, L.: Lattice and phase transition thermodynamics of ionic liquids. Thermochim. Acta 421, 87–93 (2004)
Wu, K., Chen, Q., He, C.: Speed of sound of ionic liquids: Database, estimation, and its application for thermal conductivity prediction. AIChE J. 60, 1120–1131 (2014)
Keshapolla, D., Srinivasarao, K., Gardas, R.L.: Influence of temperature and alkyl chain length on physicochemical properties of trihexyl- and trioctylammonium based protic ionic liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 133, 170–180 (2019)
Das, I., Swami, K.R., Gardas, R.L.: Influence of alkyl substituent on thermophysical properties and CO2 absorption studies of diethylenetriamine-based ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 371, 121114 (2023)
Zhang, X., Bao, D., Huang, Y., Dong, H., Zhang, X., Zhang, S.: Gas–liquid mass-transfer properties in CO2 absorption system with ionic liquids. AIChE J. 60, 2929–2939 (2014)
Sánchez, L.G., Meindersma, G.W., De Haan, A.B.: Kinetics of absorption of CO2 in amino-functionalized ionic liquids. Chem. Eng. J. 16, 1104–1115 (2011)
Zhang, S., Wang, X., Yao, J., Li, H.: Electron paramagnetic resonance studies of the chelate-based ionic liquid in different solvents. Green Energy Environ. 5, 341–346 (2020)
Huang, Y., Cui, G., Zhao, Y., Wang, H., Li, Z., Dai, S., Wang, J.: Preorganization and cooperation for highly efficient and reversible capture of low-concentration CO2 by ionic liquids. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 13293–13297 (2017)
Suo, X., Fu, Y., Do-Thanh, C.L., Qiu, L.-Q., Jiang, D.-E., Mahurin, S.M., Yang, Z., Dai, S.: CO2 chemisorption behavior in conjugated carbanion-derived ionic liquids via carboxylic acid formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 21658–21663 (2022)
Gutowski, K.E., Maginn, E.J.: Amine-functionalized task-specific ionic liquids: A mechanistic explanation for the dramatic increase in viscosity upon complexation with CO2 from molecular simulation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 14690–14704 (2008)
Luo, X., Fan, X., Shi, G., Li, H., Wang, C.: Decreasing the viscosity in CO2 capture by amino-functionalized ionic liquids through the formation of intramolecular hydrogen bond. J. Phys. Chem. B. 120, 2807–2813 (2016)
Goodrich, B.F., de la Fuente, J.C., Gurkan, B.E., Lopez, Z.K., Price, E.A., Huang, Y., Brennecke, J.F.: Effect of water and temperature on absorption of CO2 by amine-functionalized anion-tethered ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B. 115, 9140–9150 (2011)
Brennecke, J.F., Gurkan, B.E.: Ionic liquids for CO2 capture and emission reduction. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 1, 3459–3464 (2010)
Wang, C., Guo, Y., Zhu, X., Cui, G., Li, H., Dai, S.: Highly efficient CO2 capture by tunable alkanolamine-based ionic liquids with multidentate cation coordination Chem. Commun. 48, 6526–6528 (2012)
Yang, Z.-Z., Jiang, D.-E., Zhu, X., Tian, C., Brown, S., Do-Thanh, C.L., He, L.-N., Dai, S.: Coordination effect-regulated CO2 capture with an alkali metal onium salts/crown ether system. Green Chem. 16, 253–258 (2014)
Shu, H., Xu, Y.: Tuning the strength of cation coordination interactions of dual functional ionic liquids for improving CO2 capture performance. Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control. 94, 102934 (2020)
Shiflett, M.B., Niehaus, A.M.S., Yokozeki, A.: Separation of N2O and CO2 using room-temperature ionic liquid [bmim][BF4]. J. Phys. Chem. B. 115, 3478–3487 (2011)
Shiflett, M.B., Drew, D.W., Cantini, R.A., Yokozeki, A.: Carbon dioxide capture using ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate. Energy Fuels. 24, 5781–5789 (2010)
Bates, E.D., Mayton, R.D., Ntai, I., Davis, J.H.: CO2 capture by a task-specific ionic liquid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 926–927 (2002)
Qu, Y., Lan, J., Chen, Y., Sun, J.: Amino acid ionic liquids as efficient catalysts for CO2 capture and chemical conversion with epoxides under metal/halogen/cocatalyst/solvent-free conditions. Sustain. Energy Fuels. 5, 2494–2503 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 21978172) and Undergraduate Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of Shaoxing University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW, YH, and TC performed the experiments. YX: wrote the manuscript and BC wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., He, Y., Chen, T. et al. Insight into the Effect of Physicochemical Properties on CO2 Absorption Behavior of Imidazole Anion-Functionalized Ionic Liquids. J Solution Chem 52, 1255–1272 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-023-01314-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-023-01314-y