Abstract
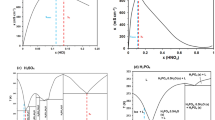
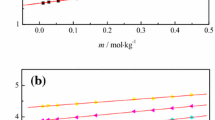
The effects of water content on physicochemical properties such as density, dynamic viscosity, and electrical conductivity of HHexen(Tf2N), composed of monoprotic N-hexylethylenediaminium as cation and bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide as anion, were studied in the temperature range T = 303.15–353.15 K. HHexen(Tf2N) was dissolved a small amount of water (up to 6.53 wt%, corresponding to w0 = [H2O]/[PIL] = 1.65) as it is a hydrophobic protic ionic liquid (PIL). The physicochemical properties of HHexen(Tf2N) were significantly influenced by its water content. The temperature dependence of the physicochemical properties at different water contents (0.50 wt%, 0.95%, 1.93%, 3.02%, 4.03%, 5.14% and 5.95%, corresponding to w0 = 0.12, 0.23, 0.47, 0.74, 1.0, 1.28 and 1.50, respectively) were studied. With an increase in the water content, the density and dynamic viscosity decreases while the electric conductivity increases in a given temperature range. The Walden lines of HHexen(Tf2N) show a good ionic character as the curves are all located in the range of ΔW = 0.5 ± 0.2 (ΔW = log101/η −log10 Λ) at different water contents. The ionicity shows an increasing trend with an increase of water content; this is evident when the water content rises to approximately 4.0% (w0 = 1.0). Additionally, HHexen(Tf2N) was used to extract Co(II) ions from an aqueous solution. Inductive coupled plasma emission spectrometry results showed that more than 99.5 wt% of Co(II) ions moved from the 100 mmol·kg−1 aqueous layer to the HHexen(Tf2N) layer (of equal volume). After extraction of the Co(II) ions, the PIL layer contained 7.90% of water (w0 = 2.0).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patil, A.B., Mahadeo, B.B.: Brønsted acidity of protic ionic liquids: a modern ab initio valence bond theory perspective. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 26020–26025 (2016)
Piekart, J., Łuczak, J.: Transport properties of aqueous ionic liquid microemulsions: influence of the anion type and presence of the co-surfactant. Soft Matter 11, 8992–9008 (2015)
Ullah, Z., Bustam, M.A., Man, Z., Muhammad, N., Khan, A.S.: Synthesis, characterization and the effect of temperature on different physicochemical properties of protic ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 5, 71449–71461 (2015)
Jacquemin, J., Husson, P., Padua, A.A.H., Majer, V.: Density and viscosity of several pure and water-saturated ionic liquids. Green Chem. 8, 172–180 (2006)
Cohen, D.T., Zhang, C., Fadzen, M., Mijalis, A.J., Hie, L., Johnson, K.D., Shriver, Z., Plante, O., Miller, S.J., Buchwald, S.L., Pentelute, B.L.: A chemoselective strategy for late-stage functionalization of complex small molecules with polypeptides and proteins. Nat. Chem. 11, 78–85 (2019)
Singh, A.P., Gardas, R., Senapati, S.: How water manifests the structural regimes in ionic liquids. Soft Matter 13, 2348–2361 (2017)
He, Z., Alexandridis, P.: Nanoparticles in ionic liquids: interactions and organization. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 18238–18261 (2015)
Wippermann, K., Giffin, J., Kuhri, S., Lehnert, W., Korte, C.: The influence of water content in a proton-conducting ionic liquid on the double layer properties of the Pt/PIL Interface. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 24706–24723 (2017)
Singh, A.P., Gardas, R., Senapati, S.: Divergent trend in density versus viscosity of ionic liquid/water mixtures: a molecular view from guanidinium ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 25037–25048 (2015)
Walst, K.J., Yunis, R., Bayley, P.M., MacFarlane, D.R., Ward, C.J., Wang, R., Curnow, O.J.: Synthesis and physical properties of tris(dialkylamino)cyclopropenium bistriflamide ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 5, 39565–39579 (2015)
Er, H., Xu, Y., Zhao, H.: Properties of mono-protic ionic liquids composed of hexylammonium and hexylethylenediaminium cations with trifluoroacetate and bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide anions. J. Mol. Liq. 276, 379–384 (2019)
Walden, P.: Molecular weights and electrical conductivity of several fused salts. Bull. Acad. Sci. St. Petersburg 1800, 405–422 (1914)
Greaves, T.L., Drummond, C.J.: Protic ionic liquids: properties and applications. Chem. Rev. 108, 206–237 (2008)
Kellkar, M.S., Maginn, E.J.: Effect of temperature and water content on the shear viscosity of the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide as studied by atomistic simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 18, 4867–4876 (2007)
Takemura, S., Kawakami, S., Harada, M., Iida, M.: Solvation structure of a copper(II) ion in protic ionic liquids comprising N-hexylethylenediamine. Inorg. Chem. 53, 9667–9678 (2014)
Watanabe, M., Nakayama, C., Yasuda, H., Harada, M., Iida, M.: Interactions of nickel(II) ions in protic ionic liquids comprising N-hexyl(or N-2-ethtylhexyl)ethylenediamines. J. Mol. Liq. 214, 77–85 (2016)
Grishina, E.P., Ramenskaya, L.M., Gruzdev, M.S., Kraeva, O.V.: Water effect on physicochemical properties of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium based ionic liquids with inorganic anions. J. Mol. Liq. 117, 267–272 (2013)
Watanabe, M., Takemura, S., Kawakami, S., Syouno, E., Kurosu, H., Harada, M., Iida, M.: Sites of protonation and copper(II) complexation in protic ionic liquids comprised of N-hexylethylenediaminium cation. J. Mol. Liq. 183, 50–58 (2013)
Bruno, A.J., Chaberek, S., Martell, A.E.: The preparation and properties of N-substituted ethylenediaminetriacetic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 12, 2723–2728 (1956)
Iida, M., Kawakami, S., Syouno, E.: Hua, Er: properties of ionic liquids containing silver(I) or protic alkylethylenediamine cations with a bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl) amide anion. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 356, 630–638 (2011)
Er, H., Wang, H.: Properties of protic ionic liquids composed of N-alkyl (= hexyl, octyl and 2-ethylhexyl) ethylenediaminum cations with trifluoromethanesulfonate and trifluoroacetate anion. J. Mol. Liq. 220, 649–656 (2016)
Dupont, J.: On the solid, liquid and solution structural organization of imidazolium ionic liquids. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 15, 341–350 (2004)
Zhang, Q.G., Li, Q., Liu, D., Zhang, X.Y., Lang, X.S.: Density, dynamic viscosity, electrical conductivity, electrochemical potential window, and excess properties of ionic liquid N-butyl-pyridinium dicyanamide and binary system with propylene carbonate. J. Mol. Liq. 249, 1097–1106 (2018)
Oswal, S.L., Desai, H.S.: Studies of viscosity and excess molar volume of binary mixtures 2. Butylamine + 1-alkanol mixtures at 303.15 and 313.15 K. Fluid Phase Equilib. 161, 191–204 (1999)
Das, D., Messaâdi, A., Barhoumi, Z., Ouerfelli, N.: The relative reduced Redlich–Kister equations for correlating excess properties of N,N-dimethylacetamide + water binary mixtures at temperatures from 298.15 K to 318.15 K. J. Solution Chem. 41, 1555–1574 (2012)
Liu, Z., Hua, Er, Liu, R., Ji, J.L.: Water effects on physicochemical properties of protic ionic liquid with N-hexylamine as cation and bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide as anion. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. (2020). https://doi.org/10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2020-0940
Xu, W., Cooper, E.I., Angell, C.A.: Ionic liquids: ion mobilities, glass temperatures, and fragilities. J. Phys. Chem. B 25, 6170–6178 (2003)
Xu, W., Angell, C.A.: Solvent-free electrolytes with aqueous solution-like conductivities. Science 302, 422–425 (2003)
Liu, Q.S., Liu, J., Liu, X.X., Zhang, S.T.: Density, dynamic viscosity, and electrical conductivity of two hydrophobic functionalized ionic liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 90, 39–45 (2015)
Schreiner, C., Zugmann, S., Hartl, R., Gores, H.J.: Fractional Walden rule for ionic liquids: examples from recent measurements and a critique of the so-called ideal KCl line for the Walden plot. J. Chem. Eng. Data 5, 1784–1788 (2010)
Iida, M., Baba, C., Inoue, M., Yoshida, H., Taguchi, E., Furusho, H.: Ionic liquids of bis(alkylethylenediamine)silver(I) salts and the formation of silver(0) nanoparticles from the ionic liquid system. Chem. Eur. J. 14, 5047–5056 (2008)
MacFarlane, D.R., Forsyth, M., Izgorodin, E.I.A., Abbot, A.P., Annat, G., Fraser, K.: On the concept of ionicity in ionic liquid. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 4962–4967 (2009)
Liu, Q.S., Li, P.P., Welz-Biermann, U., Chen, J., Liu, X.X.: Density, dynamic viscosity and electrical conductivity of pyridinium-based hydrophobic ionic liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 66, 88–94 (2013)
Yoshizawa, M., Xu, W., Angell, C.A.: Ionic liquids by proton transfer: vapor pressure, conductivity, and the relevance of ΔpKa from aqueous solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 15411–15419 (2003)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Foundation of Ningxia Higher Education (Project Number: NGY2020063). We are also grateful to Prof. Masayasu Iida of Nara Women’s University for the helpful discussion. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, E., Liu, Z. & Qin, L. Effects of Water Content on Physicochemical Properties of a Protic Ionic Liquid with Monoprotic N-Hexylethylenediaminium as Cation and Bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) Imide as Anion. J Solution Chem 50, 503–516 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-021-01067-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-021-01067-6