Abstract
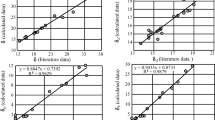
Investigation of the solubility of anthracene can yield potential models to give insights into solvent–solute systems of polyaromaric hydrocarbons (PAHs). This is important in petroleum industries and also fluorescence studies of polyaromatics in organic phases. A five parametric linear QSPR model, based structural/theoretical descriptors of solvents, and a five parametric LSER model using empirical scales, are developed to predict the Ostwald solubility coefficient of anthracene in various organic solvents. Both QSPR and LSER models obtained good prediction quality with covering 84 and 88% of data variance, respectively. The validation process of these models was done using cross validation, y-randomization and external test set. The applicability domain of the proposed model was also calculated using both a Williams plot and the standardization approach. The first model shows the role of some structural features combined with mass, charge and electronegativity of solvents in prediction of anthracene’s Ostwald solubility coefficient in organic phases. In addition, the second, alternative model based on empirical scales reveals the contributions of solvent polarity, polarizability, dielectric constant and acidity parameter to the solubility of anthracene.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PAH:
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- MLR:
-
Multiple linear regression analysis
- VIF:
-
Variance inflation factor
- AD:
-
Applicability domain
- PCA:
-
Principle component analysis
- QSPR:
-
Quantitative structure property relationship
- LSER:
-
Linear solvation energy relationship
- MAE:
-
Mean absolute error
References
Means, J.C., Wood, S.G., Hassett, J.J., Banwart, W.L.: Sorption of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons by sediments and soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 14, 1524–1528 (1980)
Ali, S.H., Al-Rashed, O.A.: Solubility of pyrene in simple and mixed solvent systems. Fluid Phase Equilib. 281, 133–143 (2009)
Powell, J.R., Voisinet, D., Salazar, A., Acree, W.E.: Solubility of pyrene in organic nonelectrolyte solvents. Comparison of observed versus predicted values based upon mobile order theory. Phys. Chem. Liq. 28, 269–276 (1994)
McCargar, J.W., Acree, W.E.: Thermochemical investigations of associated solutions: 4. Calculation of carbazole–dibutyl ether association constants from measured solubility in binary solvent mixtures. J. Pharm. Sci. 76, 572–574 (1987)
Acree, W.E., Tucker, S.A.: Solubility of anthracene in binary p-xylene + alkane and benzene + alkane solvent mixtures. Phys. Chem. Liq. 20, 31–38 (1989)
Acree, W.E., Zvaigzne, A.I., Tucker, S.A.: Thermochemical investigations of hydrogen-bonded solutions: development of a predictive equation for the solubility of anthracene in binary hydrocarbon. Fluid Phase Equilib. 92, 233–253 (1994)
Acree, W.E.: Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: binary non-aqueous systems, Part 1: solutes A–E. In: Solubility Data Series, pp. 1–44. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1995)
Acree Jr., W.E., Abraham, M.H.: Solubility predictions for crystalline nonelectrolyte solutes dissolved in organic solvents based upon the Abraham general solvation model. Can. J. Chem. 79, 1466–1476 (2001)
Acree, W.E.: Thermochemical investigations of associated solutions. Part 14.—Calculation of anthracene–butyl acetate association parameters from measured solubility data. J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. I 87, 461–464 (1991)
Roy, L.E., Hernández, C.E., Acree, W.E.: Solubility of anthracene in organic nonelectrolyte solvents. Comparison of observed versus predicted values based upon mobile order theory. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 13, 105–116 (1999)
Zhang, Q., Hu, Y., Shi, Y., Yang, Y., Cheng, L., Cao, C., Yang, W.: Thermodynamic models for determination of the solubility of dibenzothiophene in different solvents at temperatures from (278.15 to 328.15) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 59, 2799–2804 (2014)
Ruelle, P., Sarraf, E., Kesselring, U.W.: Prediction of carbazole solubility and its dependence upon the solvent nature. Int. J. Pharm. 104, 125–133 (1994)
Monárrez, C.I., Stovall, D.M., Woo, J.H., Taylor, P., Acree, W.E.: Solubility of xanthene in organic nonelectrolyte solvents: comparison of observed versus predicted values based upon mobile order theory. Phys. Chem. Liq. 40, 703–714 (2002)
Franck, H.-G., Stadelhofer, J.W.: Anthracene—production and uses. In: Industrial Aromatic Chemistry, pp. 343–361. Springer, Berlin (1988)
Diaz, A.: Analytical applications of 1,10-anthraquinones: A review. Talanta 38, 571–588 (1991)
He, Z.-H., He, M.-F., Ma, S.-C., But, P.P.-H.: Anti-angiogenic effects of rhubarb and its anthraquinone derivatives. J. Ethnopharmacol. 121, 313–317 (2009)
Honarasa, F., Yousefinejad, S., Nasr, S., Nekoeina, M.: Structure–electrochemistry relationship in non-aqueous solutions: Predicting the reduction potential of anthraquinones derivatives in some organic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 212, 52–57 (2015)
Yousefinejad, S., Hemmateenejad, B.: Chemometrics tools in QSAR/QSPR studies: a historical perspective. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 149, 177–204 (2015)
Dearden, J.C.: The history and development of quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSARs). Int. J. Quant. Struct. Relationships 1, 1–44 (2016)
Roy, K., Kar, S., Das, R.N.: Understanding the Basics of QSAR for Applications in Pharmaceutical. Academic Press, Tokyo (2015)
Katritzky, A.R., Oliferenko, A.A., Oliferenko, P.V., Petrukhin, R., Tatham, D.B., Maran, U., Lomaka, A., Acree, W.E.: A general treatment of solubility. 1. The QSPR correlation of solvation free energies of single solutes in series of solvents. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 43, 1794–1805 (2003)
Yousefinjead, S., Honarasa, F., Chaabi, M.: New relationship models for solvent–pyrene solubility based on molecular structure and empirical properties. New J. Chem. 40, 10197–10207 (2016)
Abraham, M.H., Grellier, P.L., McGill, R.A.: Determination of olive oil–gas and hexadecane–gas partition coefficients, and calculation of the corresponding olive oil–water and hexadecane–water partition coefficients. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 797–803 (1987)
Mauri, A., Consonni, V., Pavan, M., Todeschini, R.: Dragon software: an easy approach to molecular descriptor calculations. MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 56, 237–248 (2006)
Katritzky, A.R., Fara, D.C., Kuanar, M., Hur, E., Karelson, M.: The classification of solvents by combining classical QSPR methodology with principal component analysis. J. Phys. Chem. A 109, 10323–10341 (2005)
Golbraikh, A., Tropsha, A.: Predictive QSAR modeling based on diversity sampling of experimental datasets for the training and test set selection. Mol. Divers. 5, 231–243 (2002)
Yousefinejad, S., Honarasa, F., Solhjoo, A.: On the solubility of ferrocene in nonaqueous solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 61, 614–621 (2016)
Gramatica, P.: On the development and validation of QSAR models. In: Reisfeld, B., Mayeno, A.N. (eds.) Computational Toxicology, pp. 499–526. Humana Press, New York (2013)
Gramatica, P.: External evaluation of QSAR models, in addition to cross-validation: verification of predictive capability on totally new chemicals. Mol. Inform. 33, 311–314 (2014)
Tetko, I.V., Livingstone, D.J., Luik, A.I.: Neural network studies. 1. Comparison of overfitting and overtraining. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 35, 826–833 (1995)
Ojha, P.K., Mitra, I., Das, R.N., Roy, K.: Further exploring rm2 metrics for validation of QSPR models. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 107, 194–205 (2011)
Roy, K., Mitra, I., Kar, S., Ojha, P.K., Das, R.N., Kabir, H.: Comparative studies on some metrics for external validation of QSPR models. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 52, 396–408 (2012)
Roy, K., Chakraborty, P., Mitra, I., Ojha, P.K., Kar, S., Das, R.N.: Some case studies on application of “rm2” metrics for judging quality of quantitative structure–activity relationship predictions: Emphasis on scaling of response data. J. Comput. Chem. 34, 1071–1082 (2013)
Roy, K., Das, R.N., Ambure, P., Aher, R.B.: Be aware of error measures. Further studies on validation of predictive QSAR models. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 152, 18–33 (2016)
Rücker, C., Rücker, G., Meringer, M.: y-Randomization and its variants in QSPR/QSAR. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 47, 2345–2357 (2007)
Eriksson, L., Jaworska, J., Worth, A.P., Cronin, M.T.D., McDowell, R.M., Gramatica, P.: Methods for reliability and uncertainty assessment and for applicability evaluations of classification- and regression-based QSARs. Environ. Health Perspect. 111, 1361–1375 (2003)
Craney, T.A., Surles, J.G.: Model-dependent variance inflation factor cutoff values. Qual. Eng. 14, 391–403 (2002)
Yousefinejad, S., Honarasa, F., Montaseri, H.: Linear solvent structure–polymer solubility and solvation energy relationships to study conductive polymer/carbon nanotube composite solutions. RSC Adv. 5, 42266–42275 (2015)
Todeschini, R., Consonni, V., Gramatica, P.: Chemometrics in QSAR. In: Tauler, R., Walczak, B., Brown, S.D. (eds.) Comprehensive Chemometrics: Chemical and Biochemical Data Analysis. Elsevier B.V, Amsterdam (2009)
Yousefinejad, S., Honarasa, F., Abbasitabar, F., Arianezhad, Z.: New LSER model based on solvent empirical parameters for the prediction and description of the solubility of buckminsterfullerene in various solvents. J. Solution Chem. 42, 1620–1632 (2013)
Yousefinejad, S., Hemmateenejad, B.: A chemometrics approach to predict the dispersibility of graphene in various liquid phases using theoretical descriptors and solvent empirical parameters. Colloids Surfaces, A 441, 766–775 (2014)
Kamlet, M.J., Taft, R.W.: Linear solvation energy relationships. Part 1. Solvent polarity–polarizability effects on infrared spectra. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 337–341 (1979)
Taft, R.W., Abboud, J.-L.M., Kamlet, M.J., Abraham, M.H.: Linear solvation energy relations. J. Solution Chem. 14, 153–186 (1985)
Fawcett, W.R.: Acidity and basicity scales for polar solvents. J. Phys. Chem. 97, 9540–9546 (1993)
Abe, T.: Improvements of the empirical π* solvent polarity scale. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn 63, 2328–2338 (1990)
Pincock, R.E.: Effects of nonpolar solvents on an ionic reaction. The ionic decomposition of tert-butylperoxy formate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 86, 1820–1826 (1964)
Brooker, L.G.S., Craig, A.C., Heseltine, D.W., Jenkins, P.W., Lincoln, L.L.: Color and constitution. XIII. Merocyanines as solvent property indicators. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 87, 2443–2450 (1965)
Todeschini, R., Consonni, V.: Molecular Descriptors for Chemoinformatics. WILEY-VCH, Weinheim (2009)
Kamlet, M.J., Abboud, J.L.M., Taft, R.W.: An examination of linear solvation energy relationships. In: Taft, R.W. (ed.) Progress in Physical Organic Chemistry, vol. 13, pp. 485–630. Wiley, Hoboken (1981)
Gemperline, P. (ed.): Practical Guide to Chemometrics. Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton (2006)
Netzeva, T.I., Worth, A.P., Aldenberg, T., Benigni, R., Cronin, M.D., Gramatica, P., Jaworska, J.S., Kahn, S., Klopman, G.A.C., Myatt, G., Nikolova-Jeliazkova, N., Patlewicz, G.Y., Perkins, R.: Current status of methods for defining the applicability domain of (quantitative) structure–activity relationships. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2, 1–19 (2005)
Roy, K., Kar, S., Ambure, P.: On a simple approach for determining applicability domain of QSAR models. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 145, 22–29 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yousefinejad, S., Honarasa, F., Nekoeinia, M. et al. Investigation and Modeling of the Solubility of Anthracene in Organic Phases. J Solution Chem 46, 352–373 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-017-0568-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-017-0568-0