Abstract
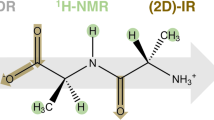
The pK a values of the peptide derived from the immunoglobulin binding protein G, Ac-Asp-Asp-Ala-Thr-Lys-Thr-NH2 (Dag1), and its derivative Ac-Asp-Asp-(meta-aminobenzoic acid)-Lys-Thr-NH2 (Dag1_M), were measured using potentiometric titrations in the temperature range from 25 to 50 °C. The heat capacity profiles for both systems were determined by differential scanning calorimetry in the temperature range 10–90 °C and CD measurements were made at nine different temperatures.To decrease the mobility of the peptide under study (Dag1), and to ensure a better stability of its structure (better stiffness), the amino acids from the turn region of Dag1 (Ala3 and Thr4) in the original sequences were replaced by the meta-aminobenzoic acid (MABA) residue, which acts as a β-mimetic. The results obtained in this work suggest that the charged residues present in both sequences (Asp1, Asp2 and Lys5) are in similar environments in both peptides. Therefore, the shapes of the dominant conformations of Dag1 and Dag1_M should be similar to each other; specifically, both peptides probably have a bent structure. Negative bands in the CD spectra are present at 195 and 215 nm for Dag1 and Dag1_M, respectively, which are characteristic of a statistical coil conformation. The pK a values for charged amino acids (two Asp and one Lys) at t = 25 °C in both sequences are very similar, which suggests that the environments for those ionizable groups are similar.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Searle, M.S., Williams, D.H., Packman, L.C.: A short linear peptide derived from the N-terminal sequence of ubiquitin folds into a water-stable non-native beta-hairpin. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2, 999–1006 (1995)
Dill, K.A.: Dominant forces in the protein folding. Biochemistry 29, 7133–7155 (1990)
Kim, P.S., Baldwin, R.L.: Intermediates in the folding reactions of small proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 59, 631–660 (1990)
Karplus, M., Weaver, D.L.: Protein folding dynamics: the diffusion-collision model and experimental data. Protein Sci. 3, 650–668 (1994)
Brown, J.E., Klee, W.A.: Helix-coil transition of the isolated amino terminus of ribonuclease. Biochemistry 10, 470–476 (1971)
Silverman, D.N., Kotelchuck, D., Taylor, G.T., Scheraga, H.A.: Nuclear magnetic resonance study of the N-terminal fragment of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 150, 757–766 (1972)
Jimnez, M.A., Herranz, J., Nieto, J.L., Rico, M., Santoro, J.: 1H NMR and CD evidence of the folding of the isolated ribonuclease 50–61 fragment. FEBS Lett. 221, 320–324 (1987)
Jimnez, M.A., Rico, M., Herranz, J., Santoro, J., Nieto, J.L.: 1H-NMR assignment and folding of the isolated ribonuclease 21–42 fragment. Eur. J. Biochem. 175, 101–109 (1988)
Dyson, H.J., Merutka, G., Waltho, J.P., Lerner, R.A., Wright, P.E.: Folding of peptide fragments comprising the complete sequence of proteins. Models for initiation of protein folding. I. Myohemerythrin. J. Mol. Biol. 226, 795–817 (1992)
Kuroda, Y.: Residual helical structure in the C-terminal fragment of cytochrome c. Biochemistry 32, 1219–1224 (1993)
Munoz, V., Serrano, L., Jimnez, M.A., Rico, M.: Structural analysis of peptides encompassing all alpha-helices of three alpha/beta parallel proteins: Che-Y, flavodoxin and P21-ras: implications for alpha-helix stability and the folding of alpha/beta parallel proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 4, 648–669 (1995)
Blanco, F.J., Serrano, L.: Folding of protein G B1 domain studied by the conformational characterization of fragments comprising its secondary structure elements. Eur. J. Biochem. 230, 634–649 (1995)
Park, S.H., Shalongo, W., Stellwagen, E.: Residue helix parameters obtained from dichroic analysis of peptides of defined sequence. Biochemistry 32, 7048–7053 (1993)
Marqusee, S., Robbins, V.H., Baldwin, R.L.: Unusually stable helix formation in short alanine-based peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 5286–5290 (1989)
Grimsley, G.R., Shaw, K.L., Fee, L.R., Alston, R.W., Huyghues-Despointes, B.M.P., Thurlkill, R.L., Scholtz, J.M., Pace, C.N.: Increasing protein stability by altering long-range coulombic interactions. Protein Sci. 8, 1843–1849 (1999)
Perl, D., Mueller, U., Heinemann, U., Schmid, F.X.: Two exposed amino acid residues confer thermostability on a cold shock protein. Nat. Struct. Biol. 7, 380–383 (2000)
Huyghues-Despointes, B.M., Qu, X., Tsai, J., Scholtz, J.M.: Terminal ion pairs stabilize the second beta-hairpin of the B1 domain of protein G. Proteins 63, 1005–1017 (2006)
de Alba, E., Blanco, F.J., Jimenez, M.A., Rico, M., Nieto, J.L.: Interactions responsible for the pH dependence of the beta-hairpin conformational population formed by a designed linear peptide. Eur. J. Biochem. 233, 283–292 (1995)
Ramirez Alvarado, M., Blanco, F.J., Serrano, L.: Elongation of the BH8 beta-hairpin peptide: electrostatic interactions in beta-hairpin formation and stability. Protein Sci. 10, 1381–1392 (2001)
Olsen, K.A., Fesinmeyer, R.M., Stewart, J.M., Andersen, N.H.: Hairpin folding rates reflect mutation within and remote from the turn region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 15483–15487 (2005)
Muňoz, V., Henry, E.R., Hofrichter, J., Eaton, W.A.: A statistical mechanical model for beta-hairpin kinetics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 5872–5879 (1998)
Dinner, A.R., Lazaridis, T., Karplus, M.: Understanding beta-hairpin formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 9068–9073 (1996)
Skwierawska, A., Makowska, J., Ołdziej, S., Liwo, A., Scheraga, H.A.: Mechanism of formation of the C-terminal β-hairpin of the B3 domain of the immunoglobulin binding protein G from Streptococcus. I. Importance of hydrophobic interactions in stabilization of β-hairpin structure. Proteins 75, 931–953 (2009)
Skwierawska, A., Żmudzińska, W., Ołdziej, S., Liwo, A., Scheraga, H.A.: Mechanism of formation of the C-terminal beta-hairpin of the B3 domain of the immunoglobulin binding protein G from Streptococcus. II. Interplay of local backbone conformational dynamics and long-range hydrophobic interactions in hairpin formation. Proteins 76, 637–654 (2009)
Lewandowska, A., Ołdziej, S., Liwo, A., Scheraga, H.A.: Mechanism of formation of the C-terminal β-hairpin of the B3 domain of the immunoglobulin binding protein G from Streptococcus. III. Dynamics of long-range hydrophobic interactions. Proteins 78, 723–737 (2010)
Lewandowska, A., Ołdziej, S., Liwo, A., Scheraga, H.A.: Mechanism of formation of the C-terminal β-hairpin of the B3 domain of the immunoglobulin-binding protein G from Streptococcus. IV. Implication for the mechanism of folding of the parent protein. Biopolymers 93, 469–480 (2010)
Makowska, J., Bagińska, K., Liwo, A., Chmurzyński, L., Scheraga, H.A.: Acidic-basic properties of three alanine-based peptides containing acidic and basic side chains: comparison between theory and experiment. Biopolymers 90, 724–732 (2008)
Makowska, J., Bagińska, K., Skwierawska, A., Liwo, A., Chmurzyński, L., Scheraga, H.A.: Influence of charge and size of terminal amino-acid residues on local conformational states and shape of alanine-based peptides. Biopolymers 90, 772–782 (2008)
Makowska, J., Żmudzińska, W., Uber, D., Chmurzyński, L.: NMR study of the influence of charged residues on β-hairpin formation. Protein J. (2014). doi:10.1007/s10930-014-9585-7
Chung, Y.J., Christianson, L.A., Stanger, H.E., Powell, D.R., Gellman, S.H.: A β-peptide reverse turn that promotes hairpin formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 20, 10555–10556 (1998)
Von Roedern, E.G., Lohof, E., Hessler, G., Hoffmann, M., Kessler, H.: Synthesis and conformational analysis of linear and cyclic peptides containing sugar amino acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 10156–10167 (1996)
Kostrowicki, J., Liwo, A.: A general method for the determination of the stoichiometry of unknown species in multicomponent systems from physicochemical measurements. Comput. Chem. 11, 195–210 (1987)
Kostrowicki, J., Liwo, A.: Determination of equilibrium parameters by minimization of an extended sum of squares. Talanta 37, 645–650 (1990)
Albert, A., Serjeant, E.P.: The Determination of Ionization Constants. Chapman and Hall, London (1984)
Plotnikov, V., Rochalski, A., Brandts, M., Brandts, J.F., Williston, S., Frasca, V., Lin, L.N.: An autosampling differential scanning calorimeter instrument for studying molecular interactions. Assay. Drug. Dev. Technol. 1, 83–90 (2002)
Makowska, J., Bagińska, K., Makowski, M., Jagielska, A., Liwo, A., Kasprzykowski, F., Chmurzyński, L., Scheraga, H.A.: Assessment of two theoretical methods to estimate potentiometric-titration curves of peptides: comparison with experiment. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 4451–4458 (2006)
Rodante, F., Fantauzzi, F., Catalani, G.: Thermodynamics of dipeptides in water. VI. Calorimetric determination of enthalpy changes of dissociation processes in water of the free α-carboxyl and α-amino groups in a series of dipeptides. Comparison of these processes for two series of dipeptides. Thermochim. Acta 311, 43–49 (1998)
Hermans Jr, J., Scheraga, H.A.: Structural studies of ribonuclease. VI. Abnormal ionizable groups. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 83, 3293–3300 (1961)
Derrick, J.P., Wigley, D.B.: The third IgG-binding domain from Streptococcal protein-G—An analysis by X-ray crystallography of the structure alone and in a complex with Fab. J. Mol. Biol. 243, 906–918 (1994)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Polish National Science Center (UMO-2011/01/D/ST4/04497) and by a grant for Young Scientists 2013 from the University of Gdansk BMN 538-8232-B01813.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makowska, J., Uber, D. & Chmurzyński, L. Thermodynamical Studies of an Example Peptide Containing Metaaminobenzoic Acid (MABA) that Promotes Bends in Proteins. J Solution Chem 44, 223–236 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-015-0307-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-015-0307-3