Abstract
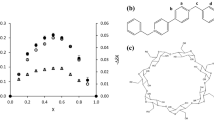
Long chain calix[4]arene ethers have been examined for aggregation in nonaqueous solvents by using UV-vis molecular absorbance spectroscopy. It has been observed that tetraalkylated (alkyl = hexadecyl and octadecyl, respectively) calix[4]arene ethers tend to aggregate in chloroform and tetrahydrofuran, possibly via π–π stacking interactions of the phenyl moieties, and the aggregation process appears to be facilitated by the alkyl chains. The analogous dialkylated compounds do not show any self-aggregation, plausibly due to strong hydrogen bonding between the –OH and the –O– of calix aryl ether which seems to disrupt the aggregation process. Addition of the anionic surfactant sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS) appears to hinder the aggregation process in nonpolar chloroform but the same surfactant facilitates aggregation in the polar tetrahydrofuran. The cationic surfactant (cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide) and the nonionic surfactant (Brij-35) have no effect on this aggregation process. Unexpectedly, SDS induces aggregation of dialkylated calix[4]arene ethers in chloroform. It has been observed that the aggregated form of the tetraalkylated calix[4]arene ethers tend to increase the dimerization efficiency of cationic dyes (pinacyanol chloride and methylene blue) in chloroform.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin, O.M., Mecozzi, S.: Synthesis and pH-dependent self-assembly of semifluorinated calix[4]arenes. Tetrahedron 63, 5539–5547 (2007)
Shivanyuk, A., Saadioui, M., Broda, F., Thondorf, I., Vysotsky, M.O., Rissanen, K., Kolehmainen, E., Böhmer, V.: Sterically and guest controlled self-assembly of calix[4]arene derivatives. Chem. Eur. J. 10, 2138–2148 (2004)
Kotz, J., Kosmella, S., Beitz, T.: Self-assembled polyelectrolyte systems. Prog. Polym. Sci. 26, 1199–1232 (2001)
Forster, S., Plantenberg, T.: From self-organizing polymers to nanohybrid and biomaterials. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 41, 688–714 (2002)
Hunter, R.J.: Foundations of Colloid Science, vol. 1. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1987)
Israelachvili, J.N.: Intermolecular and Surface Forces. Academic Press, Orlando (1985)
Rosen, M.J.: Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (1989)
Tanford, C.: The Hydrophobic Effect: Formation of Micelles and Biological Membranes, 2nd edn. Kriger, Malabar (1991)
Myers, D.: Surfactant Science and Technology, 2nd edn. VCH, New York (1992)
Evans, D.F., Wennerström, H.: The Colloidal Domain: Where Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Technology Meet, 2nd edn. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim (1999)
Gutsche, C.D.: In: Stoddart, J.F. (ed.) Calixarenes: Monographs in Supramolecular Chemistry. Royal Society of Chemistry, London (1989)
Gutsche, C.D.: Calixarenes: An Introduction, 2nd edn. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge (2008)
Chawla, H.M., Srinivas, K.: Molecular diagnostics: synthesis of new chromogenic calix[8]arenes as potential reagents for detection of amines. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 2593–2594 (1994)
Kubo, Y., Maruyama, S., Ohhara, N., Nakamura, M., Tokita, S.S.: Molecular recognition of butylamines by a binaphtyl-derived chromogenic calix[4]crown. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1727–1728 (1995)
Chawla, H.M., Srinivas, K.: Synthesis of new chromogenic calix[4]arenes bridged at the upper rim through bisazophenyl linkages. J. Org. Chem. 61, 8464–8467 (1996)
Pandey, S., Ali, M., Bishnoi, A., Azam, A., Pandey, S., Chawla, H.M.: Quenching of pyrene fluorescence by calix[4]arene and calix[4]resorcinarenes. J. Fluoresc. 18, 533–539 (2008)
Pandey, S., Azam, A., Pandey, S., Chawla, H.M.: Novel dansyl-appended calix[4]arene frameworks: fluorescence properties and mercury sensing. Org. Biomol. Chem. 7, 269–279 (2009)
Venkatesan, N.: Studies on calix[n]arenes based molecular receptors. Ph.D. Thesis, IIT, New Delhi (2000)
Diamond, D., Mckervey, M.A.: Calix[4]arene-based sensing agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 25, 15–24 (1996)
Duncan, D.M., Cockayne, J.S.: Application of calixarene ionophores in PVC based ISEs for uranium detection. Sens. Actuators B 73, 228–235 (2001)
Li, D., Yang, X., McBranch, D.: Molecular architecture of calixarenes and their self-assembled mono- and multi-layers for nonlinear optical (NLO) applications. Synth. Met. 86, 1949–1950 (1997)
Arimori, S., Nagasaki, T., Shinkai, S.: Tailor-making of desired assemblies from well-designed monomers: use of calix[4]arene conformers as building blocks. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1, 887–889 (1993)
Arimori, S., Nagasaki, T., Shinkai, S.: Self-assembly of tetracationic amphiphiles bearing a calix[4]arene core. Correlation between the core structure and the aggregation properties. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, 679–683 (1995)
Ikeda, A., Shinkai, S.: Metal-induced aggregation-deaggregation equilibrium change in calix[4]arene-appended bisfullerenes. Chem. Lett. 803–804 (1996)
Lee, M., Lee, S.J., Jiang, L.H.: Stimuli responsible supramolecular nanocapsules from amphiphilic calixarene assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 12724–12725 (2004)
Omar, O., Ray, A.K., Hassan, A.K.: Resorcinol calixarenes (resorcinarenes): Langmuir-Blodgett films and optical properties. Supramol. Sci. 4, 417–421 (1997)
Markowitz, M.A., Janout, V., Castner, D.G., Regen, S.L.: Perforated monolayers: design and synthesis of porous and cohesive monolayers from mercurated calix[n]arenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 111, 8192–8200 (1989)
Tani, T.: In: Kobayashi, T. (ed.) J-Aggregates. World Scientific, Singapore (1996)
West, W., Pearce, S.: The dimeric state of cyanine dyes. J. Phys. Chem. 69, 1894–1903 (1965)
Patil, K., Pawar, R., Talap, P.: Self-aggregation of methylene blue in aqueous medium and aqueous solutions of Bu4NBr and urea. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2, 4313–4317 (2002)
Bauer, L.J., Gutsche, C.D.: Calixarenes. 15. The formation of complexes of calixarenes with neutral organic molecules in solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 107, 6063–6069 (1985)
Munch, J.H., Gutsche, C.D.: p-tert-butylcalix[8]arene [preparation]. Org. Synth. 68, 234–237 (1990)
Gutsche, C.D., Iqbal, M., Steward, D.: Calixarenes. 19. Syntheses procedures for p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene. J. Org. Chem. 51, 742–745 (1986)
Creaven, B.S., Deasy, M., Gallagher, J.F., Mcginley, J., Murry, B.A.: Unusual cone conformation retention in calix[4]arenes. Tetrahedron 57, 8883–8887 (2001)
Verboom, W., Durie, A., Egberink, R.J.M., Asfari, Z., Reinhoudt, D.N.: Ipso nitration of p-tert-butylcalix[4]arenes. J. Org. Chem. 57, 1313–1316 (1992)
Clark, T.E., Makha, M., Raston, C.L., Sobolev, A.L.: Supersized bilayers based on an o-alkyl substituted calix[4]arene. Cryst. Eng. Commun. 8, 707–711 (2006)
Arora, V.: Studies directed towards development of new molecular diagnostics. Ph.D. Thesis, IIT, New Delhi (2004)
Jaime, C., Mendoza, J.D., Prados, P., Nieto, P.M., Sanchez, C.: 13C NMR chemical shifts. A single rule to determine the conformation of calix[4]arenes. J. Org. Chem. 56, 3372–3376 (1991)
Mukherjee, P., Gumkowski, M.J., Chan, C.C., Sharma, R.: Determination of critical micellization concentrations of perfluorocarboxylates using ultraviolet spectroscopy: some unusual counterion effects. J. Phys. Chem. 94, 8832–8835 (1990)
Saha, A., Nayak, S.K., Chottopadhaya, S., Mukherjee, A.K.: Evidence of reverse micellization of a calix[4]arene through a study of its charge transfer and host-guest complexation with [60]fullerene. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 7688–7693 (2004)
Sabaté, R., Gallardo, M., Estelrich, J.: Location of pinacyanol in micellar solutions of N-alkyl trimethylammonium bromide surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 233, 205–210 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, S., Kar, J.R., Azam, A. et al. Competitive Self and Induced Aggregation of Calix[4]arene Ethers and Their Interaction with Pinacyanol Chloride and Methylene Blue in Nonaqueous Media. J Solution Chem 39, 107–120 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-009-9489-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-009-9489-x