Abstract
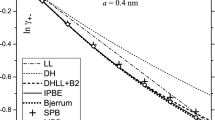
The expression for Gibbs energy of electrolyte solutions has been derived taking into account the contribution of interactions of the hydrated shells of ions. It is in good agreement with data for the dependence of the hydration number on concentration. The contribution of different interactions to the activity coefficient depending on concentration has been analyzed. The possibility of determining parameters which characterize the composition of hydrated shells of individual atoms from experimental data has been considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Damaskin, B.B., Petrij, O.A., Chirlina, G.A.: In: Electrochemistry, p. 623. Khimia, Moscow (2000)
Onori, G.: The hydration of potassium chloride in aqueous solution. Acoust. Lett. 11, 187–193 (1988)
Onori, G.: Ionic hydration in sodium chloride solution. J. Chem. Phys. 1(89), 510–516 (1988)
Afanasiev, V.N.: The verified analysis of an activity coefficient of solvent in liquid-phase solutions of electrolytes. Rep. Acad. Sci. RF 402, 231–235 (2005)
Afanasiev, V.N., Ustinov, A.N.: The verified analysis of hydration of electrolytes. J. Struct. Chem. 46, 463–471 (2005)
Afanasiev, V.N., Ustinov, A.N., Vashurina, I.Yu.: Acoustic study of solvent coordination in the hydration shells of potassium iodide. J. Solution Chem. 35, 1477–1491 (2006)
Afanasiev, V.N., Zaitsev, A.A., Tunina, E.J., Ustinov, A.N.: The adiabatic compressibility and structural parameters of hydration of strong electrolytes. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 79, 1239–1244 (2005)
Afanasiev, V.N., Zaitsev, A.A.: Features of a structural condition of solvent in solutions of electrolytes. J. Struct. Chem. 47, 94–101 (2006)
Landau, L.D., Lifshits, E.M.: In: Statistical Physics, vol. VI, p. 583. Nauka, Moscow (1976)
Dwait, G.B.: In: Tables of Integrals and Other Mathematical Formulas, p. 226. Nauka, Moscow (1966)
Robinson, R., Stokes, R.: In: Electrolyte Solutions, p. 646. Inostrannaya Literatura, Moscow (1953)
Krasnov, K.S.: In: Physical Chemistry. Krasnov, p. 687. Nauka, Moscow (1982)
CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Electronic version of the 81st edition, http://www.lib.utexas.edu/indexes/titles.html?id=103
Kittel, Ch.: In: Introduction to a Solid State Physics. Phys. and Math. Literature, p. 520. Mir, Moscow (1966)
Huang, K.: In: Statistical Mechanics. Phys. and Math. Literature, p. 520. Mir, Moscow (1966)
Mikulin, G.I.: In: Questions of Physical Chemistry of Electrolyte Solutions, p. 417. Khimia, Leningrad (1968)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaitsev, A.A., Afanasiev, V.N. The Development of the Theory of Strong Electrolyte Solutions. J Solution Chem 37, 1425–1436 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-008-9312-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-008-9312-0