Abstract
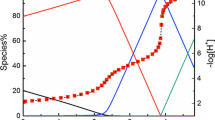
In acidic aqueous solutions, the protonation of gluconate is coupled with the lactonization of gluconic acid. With a decrease of pC H, two lactones (δ- and γ-) are sequentially formed. The δ-lactone forms more readily than the γ-lactone. In 0.1 mol⋅L−1 gluconate solutions, if pC H>2.5 then only the δ-lactone is generated. When the pC H is decreased below 2.0, formation of the γ-lactone is observed although the δ-lactone still predominates. In solutions with I=0.1 mol⋅L−1 NaClO4 and room temperature, the deprotonation constant of the carboxylic group was determined to be log 10 K a=3.30±0.02 using the NMR technique, and the δ-lactonization constant obtained by batch potentiometric titrations was log 10 K L=−(0.54±0.04). Using ESI-MS, the rate constants for the δ-lactonization and the reverse hydrolysis reaction at pC H≈5.0 were estimated to be k 1=3.2×10−5 s−1 and k −1=1.1×10−4 s−1, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yano, S.: Coordination compounds containing sugars and their derivatives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 92, 113–156 (1988)
Whitfield, D.M., Stojkovky, S., Sarka, B.: Metal coordination to carbohydrates. Structures and function. Coord. Chem. Rev. 122, 171–225 (1993)
Sawyer, D.T.: Metal-gluconate complexes. Chem. Rev. 64, 633–643 (1964)
Carper, W.R., Coffin, D.B.: NMR studies of paramagnetic metal ion interactions with gluconate and 1,5-gluconolactone. Inorg. Chimica Acta 167, 261–264 (1990)
Goroux, S., Rubini, P., Henry, B., Aury, S.: Complexes of praseodymium(III) with D-gluconic acid. Polyhedron 19, 1567–1574 (2000)
Zhernosekov, K.P., Mauerhofer, E., Getahun, G., Warwick, P., Rosch, F.: Complex formation of Tb3+ with glycolate, D-gluconate and α-isosaccharinate in neutral aqueous perchlorate solutions. Radiochim. Acta 91, 599–602 (2003)
Warwick, P., Evan, N., Hall, T., Vines, S.: Stability constants of uranium(IV)-α-isosaccharinic acid and gluconic acid complexes. Radiochim. Acta 92, 897–902 (2004)
Coccioli, F., Vicedomini, M.: On the protonation of gluconate ions and complex formation with lead(II) in acid solutions. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 40, 2103–2105 (1978)
Motekaitis, R.J., Martell, A.E.: Complexes of aluminum(III) with hydroxy carboxylic acids. Inorg. Chem. 23, 18–23 (1984)
Sawyer, D.T., Bagger, J.B.: The lactone-acid-salt equilibria for D-glucono-δ-lactone and the hydrolysis kinetics for this lactone. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 81, 5302–5306 (1959)
Combes, C.L., Birch, G.G.: Interaction of D-glucono-1,5-lactone with water. Food Chem. 27, 283–298 (1988)
Ekberg, S., Ekberg, C., Albinsson, Y.: Characterization of α-isosaccharinic acid: Lactone and carboxylic conformations. J. Solution Chem. 33, 465–477 (2004)
Pecsok, R.L., Sandera, J.: The gluconate complexes. II. The ferric-gluconate system. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 77, 1489–1494 (1955)
Wishart, D.S., Bogam, C.G., Yao, J., Abildgard, F., Dyson, H.J., Oldfield, E., Markley, J.L., Sykes, B.D.: 1H, 13C and 15N chemical shift referencing in biomolecular NMR. J. Biomol. NMR 6, 135–140 (1995)
Wishart, D.S., Nip, A.M.: Protein chemical shift analysis: a practical guide. Biochem. Cell Biol. 76, 153–163 (1998)
Bates, R.G.: Determination of pH Theory and Practice. Wiley, New York (1964)
Zanonato, P., Di Bernardo, P., Bismondo, A., Liu, G., Chen, X., Rao, L.: Hydrolysis of uranium(VI) at variable temperatures (10–85 °C). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 5515–5522 (2004)
Rao, L., Srinivasan, T.G., Garnov, A.Y., Zanonato, P., Di Bernardo, P., Bismondo, A.: Hydrolysis of neptunium(V) at variable temperatures (10–85 °C). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 68, 4821–4836 (2004)
Gans, P., Sabatini, A., Vacca, A.: Investigation of equilibria in solution. Determination of equilibrium constants with the HYPERQUAD suite of programs. Talanta 43, 1739–1753 (1996)
Hoffmann, E.D., Stroobant, V.: Mass Spectrometry, Principles and Applications, 2nd. edn. Willey, New York (2002)
Drago, R.S.: Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy-additional principles and applications. In: Physical Methods in Chemistry, pp. 252–309. Saunders, Philadelphia (1977)
Frassineti, C., Ghelli, S., Gans, P., Sabatini, A., Moruzzi, M.S., Vacca, A.: Nuclear magnetic resonance as a tool for determining protonation constants of natural polyprotic bases in solution. Anal. Biochem. 231, 374–382 (1995)
Anderson, D.E., Lu, J., McIntosh, L. Dahlquist, F.W.: In: Clore, G.M., Gronenborr, A.M. (eds.) NMR of Proteins, 258. CRC, Boca Raton (1993)
Cho, H.M., Rai, D., Hess, N.J., Xia, Y., Rao, L.: Acidity and structure of isosaccharinate in aqueous solution: a nuclear magnetic resonance study. J. Solution Chem. 32, 691–702 (2003)
Martell, A.E., Smith, R.M.: NIST critically selected stability constants of metal complexes. NIST Standard Reference Database 46 Version 6.0, developed by R.J. Motekaitis and distributed by NIST Standard Reference Data (2001)
Silva, C.O., Da Silva, E.C., Nascimento, M.A.C.: Ab initio calculations of absolute pK a values in aqueous solution II. Aliphatic alcohols, thiols, and halogenated carboxylic acids. J. Phys. Chem. A 104, 2402–2409 (2000)
Kim, H.I., Johnson, P.V., Beegle, L.W., Beauchamp, J.L., Kanik, I.: Electrospray ionization ion mobility spectrometry of carboxylate anions: ion mobilities and a mass-mobility correlation. J. Phys. Chem. A 109, 7888–7895 (2005)
Espenson, J.H.: Reversible and concurrent reactions. In: Speer, J.B., Morriss, J.M. (eds.) Chemical Kinetics and Reaction Mechanism, 2nd edn., pp. 46–69. McGraw-Hill, New York (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Gibson, P., Clark, S.B. et al. Lactonization and Protonation of Gluconic Acid: A Thermodynamic and Kinetic Study by Potentiometry, NMR and ESI-MS. J Solution Chem 36, 1187–1200 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-007-9182-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-007-9182-x