Abstract
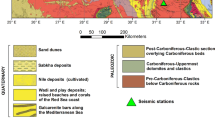
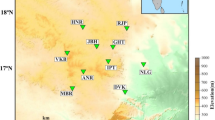
The Western Ghats (WG) is one of the great escarpments that extend ~1500 km parallel to the west coast of India in the direction of NNW-SSE. We deployed a network of seven broadband seismological stations along the WG to decipher its evolution. In the present study, we investigate the characteristics of different kinds of noises at the stations by utilizing the power spectral density (PSD) measurements. Further, the results are compared with the global standard noise models to assess the data quality. The PSD results reveal that the short period (0.1–1 s) cultural noise is more prominent at stations AGMB, SDPR and MGLI when compared to the other stations, especially during day hours of Indian Standard Time (IST) zone since these sites were in the proximity of roads. The seasonal variations are observed especially in the microseismic period range and noise levels are more prominent in the months of July to August since the western part of India experiences peak monsoon during this period. These variations are observed especially at PCH and KNUR stations as their locations were near the coastline. Furthermore, the results indicate that the noise levels are more prominent in vertical components than that of horizontal components in the microseismic period range whereas it is reversed in the short and long period ranges. Later, the results indicate that the noise levels at all the localities of stations are within the global standard noise models, which suggests that our installation of broadband seismological stations has been successful at all seven locations and has good data quality.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data can be downloadable from the following link. However, it is password protected and the password can be shared based on the request to NCESS, MoES, Govt. of India (padmarao.b@ncess.gov.in). https://1drv.ms/u/s!AsedqdTbUxUrgZMs8F2h-XH619ZAMA?e=DvlW2a
References
Abd e-l Aal AEAK (2013) Very broadband seismic background noise analysis of permanent good vaulted seismic stations. J Seismology 17:223–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-012-9308-5
Alejandro ACB, Ringler AT, Wilson DC, Anthony RE, Moore SV (2020) Towards understanding relationships between atmospheric pressure variations and long-period horizontal seismic data: a case study. Geophys J Intl 223(1):676–691. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggaa340
Anthony RE, Ringler AT, Wilson DC, Bahavar M, Koper KD (2020) How Processing Methodologies Can Distort and Bias Power Spectral Density Estimates of seismic Background Noise. Seismol Res Lett 91:1694–1706. https://doi.org/10.1785/0220190212
Ardhuin F, Gualtieri L, Stutzmann E (2015) How ocean waves rock the Earth: two mechanisms explain microseisms with periods 3 to 300 s. Geophys Res Lett 42(3):765–772. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014GL062782
Beauduin R, Lognonné P, Montagner JP, Cacho S, Karczewski JF, Morand M (1996) The effects of the atmospheric pressure changes on seismic signals or how to improve the quality of a station. Bull Seismolog Soc Am 86(6):1760–1769. https://doi.org/10.1785/BSSA0860061760
Bormann P, Wielandt E (2013) Chapter 4: Seismic signals and noise. In: Bormann P (ed) New manual of seismological observatory practice (NMSOP-2) (2012). IASPEI, GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences, Potsdam, 63. https://doi.org/10.2312/GFZ.NMSOP-2_CH4
Bormann P (2002) Seismic signal and noise, in the new manual of Seismological Observatory Practice, P. Bormann (Editor), GeoForschungsZentrum, Potsdam, Germany, 33
Bormann P (2015) Seismic Noise. In: Beer, M., Kougioumtzoglou, I., Patelli, E., Au, IK. (eds) Encyclopedia of Earthquake Engineering. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-36197-5_289-1
Bromirski PD (2009) Earth vibrations. Science 324(5930):1026–1027. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1171839
Cessaro RK (1994) Sources of primary and secondary microseisms. Bull Seismolog Soc Am 84(1):142–148.
Cooley J, Tukey J (1965) An algorithm for machine calculation of complex Fourier series. Mathematics of computing, reprinted 1972. Digital signal processing. IEEE Press, New York, NY, 223-227
De la Torre TL, Sheehan AF (2005) Broadband seismic noise analysis of the Himalayan Nepal Tibet seismic experiment. Bull Seismolog Soc Am 95(3):1202–1208
Elouai D, Abd el Aal, A. e.-A. K. (2016) Ambient seismic noise levels: a survey of the permanent and temporary seismographic networks in Morocco. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.4934.5525
Frankinet B, Lecocq T, Camelbeeck T (2021) Wind-induced seismic noise at the Princess Elisabeth Antarctica Station. The Cryosphere 15:5007–5016. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-15-5007-2021
Hasselmann K (1963) A statistical analysis of the generation of microseisms. Rev Geophys 1(2):177. https://doi.org/10.1029/RG001i002p00177
Huang B, Xue M, Guo Z, Song W (2022) Exploring the deep ocean single-frequency microseisms southwest of Japan in northern Philippine Sea. Geophys Res Lett 49:2021097444. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GL097444
Jana N, Singh C, Biswas R, Grewal N, Singh A (2017) Seismic noise analysis of broadband stations in the Eastern Ghat Mobile Belt of India using power spectral density. Geomatics Natural Hazards and Risk 8(2):1622–1630. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2017.1365777
Kroner C, Jahr T, Kuhlmann S, Fischer KD (2005) Pressure-induced noise on horizontal seismometer and strainmeter records evaluated by finite element modelling. Geophys J Int 161:167–178
Longuet-Higgins MS, Jeffreys H (1950) A theory of the origin of microseisms. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London - Series A: Mathematical and Physical Sciences 243(857):1–35. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.1950.0012
McNamara D, Buland RP (2004) Ambient noise levels in continental United States. Bull Seismolog Soc Am 94:1517–1527
McNamara D, Hutt C, Gee L, Benz HM, Buland R (2009) A method to establish seismic noise baselines for automated station assessment. Seismolog Res Lett 80:628–637
McNamara D, Boaz RI (2006) Seismic Noise Analysis system using power spectral density probability density functions: A stand-alone software package. US Geological Survey, Open-File Report
Peterson J (1993) Observations and modelling of seismic background noise. US Geological Survey, Open-File Report: 93-322
Rastin S, Unsworth C, Gledhill K, McNamara D (2012) A detailed noise characterization and sensor evaluation of the north island of New Zealand using the PQLX data quality control system. Bull Seismolog Soc Am 102:98–113. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120110064
Ringdal F, Bungum H (1977) Noise level variation at NORSAR and its effect on detectability. Bull Seismolog Soc Am 67(2):479–492
Romanowicz B (2021) Surface Waves. In: Gupta, H.K. (eds) Encyclopedia of Solid Earth Geophysics. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58631-7_143
Steffen H (2006) The importance of instrument location on barometric pressure induced noise. Bull Inf Mar ́ees Terrestres,141,11293–11302
Stutzmann E, Roult G, Astiz L (2000) GEOSCOPE station noise levels. Bull Seismolog Soc Am 90(3):690–701
Uthaman M, Singh C, Singh A et al (2022) Spatial and temporal variation of the ambient noise environment of the Sikkim Himalaya. Sci Rep 12:274. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-04183-x
Webb SC (1998) Broadband seismology and noise under the ocean. Rev Geophys 36(1):105–142
Webb SC, Lee WHK (2002) Seismic noise on land and on the seafloor. Intl Geophys Series 81(A):305–318
Wielandt E (2002) Seismometry. Intl Geophys Series 81:283–304
Wielandt E (2012) Seismic sensors and their calibration. In New Manual of Seismological Observatory Practice 2 (NMSOP-2), P. Bormann (Editor), Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum GFZ, 1-51
Willmore PL (Ed.) (1979) Manual of Seismological Observatory Practice. World Data Center A for Solid Earth Geophysics, Report SE-20, September 1979, Boulder, Colorado, 165
Wilson D, Leon J, Aster RC, Ni J (2002) Broadband Seismic Background Noise at Temporary Seismic Stations Observed on a Regional Scale in the Southwestern United States. Bull Seismolog Soc Am 92(8):3335–3342. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120010234
Withers MM, Aster RC, Young CJ, Chael EP (1996) High-frequency analysis of seismic background noise as a function of wind speed and shallow depth. Bull Seismolog Soc Am 86(5):1507–1515
Young CJ, Chael EP, Withers MM, Aster RC (1996) A comparison of the high-frequency (> 1 Hz) surface and subsurface noise environment at three sites in the United States. Bull Seismolog Soc Am 86(5):1516–1528
Zürn W, Widmer R (1995) On noise reduction in vertical seismic records below 2 mHz using local barometric pressure. Geophys Res Lett 22(24):3537–3540. https://doi.org/10.1029/95GL03369
Zürn W, Exß J, Steffen H, Kroner C, Jahr T, Westerhaus M (2007) On reduction of long-period horizontal seismic noise using local barometric pressure. Geophys J Intl 171(2):780–796. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03553.x
Acknowledgements
We sincerely acknowledge the Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, for supporting this project under the core program of the National Centre for Earth Science Studies (NCESS). We thank the editor and reviewers for their thoughtful comments, which significantly improved the quality of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, under the core program of the National Centre for Earth Science Studies (NCESS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Krishna Jha: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation.
B. Padma Rao: conceptualization, data curation, investigation, methodology, validation, visualization, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing.
Sribin C: data curation
Silpa S: data curation
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
I, on the behalf of all the authors, give my consent to publish the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jha, K., B, P.R., C, S. et al. Analysis of seismic noise of broadband seismological stations installed along the Western Ghats. J Seismol 27, 325–342 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-023-10138-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-023-10138-8