Abstract
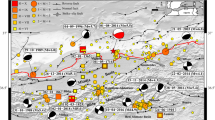
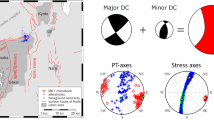
The central area of the Ionian Sea is dominated by the Cephalonia Transform Fault Zone (CTFZ) with a pronounced dextral strike-slip component of motion. The CTFZ has two main segments: the Lefkada Segment (LS) in the north and the Cephalonia Segment (CS) in the south. On 14 August 2003 an Mw 6.2 earthquake ruptured the Lefkada Segment and produced extensive damage, especially to the western coast of the island. Teleseismic waveform modelling revealed the multiple source character of the mainshock, which occurred as three sub-events along a ∼N12∘E line. The first sub-event occurred at a depth of about 15 km, followed 2.5 s later by the second and largest sub-event at a depth of 11 km and the third sub-event 14 s after the second at a depth of 15 km. The total moment from the body waves of this sequence is about 22.3×1017 Nt m (Mw 6.2) with a source duration of ∼15 s. The rupture started at the northern part of the Lefkada fault Segment and propagated southwards. The second and third sub-events are located at 7 and 40 km to the south-east in respect to the first sub-event. The focal mechanisms of the two strongest sources indicate strike-slip faulting along the NE–SW trending Lefkada segment (sub-event 2: Strike = 12∘, Dip = 81∘, Rake = 174∘; sub-event 3: Strike = 20∘, Dip = 63∘, Rake = −179∘). Moment tensor inversion applied to regional broad band waveforms obtained from the Greek National Seismographic Network provided focal mechanisms for 23 aftershocks with magnitudes ranging from Mw 3.6 to 5.4. The aftershock sequence presented spatial and temporal variation. The aftershocks were concentrated in two clusters one at the northern part of the activated area and another at the southern part. Most of them were of strike-slip character, following the major tectonic lines of the area, although low-angle thrust and reverse faulting mechanisms were also observed. Thrust and reverse type mechanisms are mainly concentrated in the northern and mainland part of the Lefkada Island which probably indicates the segmented character of the fault and probable activation of adjacent structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, H. and Jackson, J., 1987, Active tectonics of the adriatic region, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 91, 937–983.
Baker, C., Hatzfeld, D., Lyon-Caen, H., Papadimitriou, E. and Rigo, A., 1997, Earthquake mechanisms of the Adriatic Sea and western Greece, Geophys. J. Int. 131, 559–594.
Benetatos, C., Kiratzi, A., Papazachos, C. and Karakaisis, G., 2004, Focal mechanisms of shallow and intermediate depth earthquakes along the Hellenic Trench, J. Geodyn. 37, 253–296.
Dreger, D., 2002, Manual of the Time-Domain Moment Tensor Inverse Code (TDMT_INVC), Release 1.1, Berkeley Seismological Laboratory, pp. 18.
Dreger, D. and Helmberger, D., 1990, Broadband modelling of local earthquakes, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 80, 1162–1179.
Dreger, D. and Helmberger, D., 1991, Complex faulting deduced from broadband modelling of the 28 February 1990 upland earthquake (ML = 5.2), Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 81, 1129–1144.
Dreger, D. and Helmberger, D., 1993, Determination of source parameters at regional distances with single station or sparse network data, J. Geophys. Res. 98, 8107–8125.
EERI Special Earthquake Report, 2003, Preliminary observations on the August 14, 2003, Lefkada Island (western Greece) earthquake, 1–12.
Futterman, W.I., 1962, Dispersive body waves, J. Geophys. Res. 67, 5279–5291.
Hatzfeld, D., Kassaras, I., Panagiotopoulos, D., Amorese, D., Makropoulos, K., Karakaisis, G. and Coutant, O., 1995, Microseismicity and strain pattern in north-western Greece, Tectonics 14, 773–785.
Helmberger, D.V., 1974, Generalized ray theory for shear dislocation, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 64, 45–64.
ITSAK Report, 2003, The Earthquake of Lefkada 14.08.2003 and its Effects on the Built and Natural Environment, Open File Report, pp. 61 (in Greek).
Jost, M.L. and Herrmann, R., 1989, A student’s guide to and review of moment tensors, Seismol. Res. Lett. 60, 37–57.
Karakostas, V.G., Papadimitriou, E.E. and Papazachos, C.B., 2004, Properties of the 2003 Lefkada, Ionian Islands, Greece, earthquake seismic sequence and seismicity triggering, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 94, 1976–1981.
Kikuchi, M. and Kanamori, H., 1991, Inversion of complex body waves-III, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 81, 2335–2350.
Kiratzi, A. and Langston, C., 1991, Moment tensor inversion of the January 17, 1983 Kefallinia event of Ionian Islands (Greece), Geophys. J. Int. 105, 529–535.
Kiratzi, A. and Louvari E., 2001, Source parameters of the Izmit-Bolu 1999 (Turkey) earthquake sequences from teleseismic data, Annali di Geofisica 44, 33–47.
Kiratzi, A. and Louvari, E., 2003, Focal mechanisms of shallow earthquakes in the Aegean Sea and the surrounding lands determined by waveform modeling: A new database, J. Geodyn. 36, 251–274.
Langston, C.A. and Helmberger, D.V., 1975, A procedure for modelling shallow dislocation sources, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 42, 117–130.
Louvari, E., Kiratzi, A. and Papazachos, B., 1999, The Cephalonia transform fault and its continuation to western Lefkada Island, Tectonophysics 308, 223–236.
Louvari, E. and Kiratzi A., 2001, Source parameters of the 7 September 1999 Athens (Greece) earthquake based on teleseismic data, J. Balkan Geophys. Soc. 4, 51–60.
McCaffrey, R. and Nábělek, J., 1987, Earthquakes, gravity, and the origin of the Bali Basin: An example of nascent continental fold-and-thrust belt, J. Geophys. Res. 92, 441–460.
McCaffrey, R. and Abers, G., 1988, SYN3: A Program for Inversion of Teleseismic Body Waveform on Microcomputers, Air Force Geophysics Laboratory Technical Report, AFGL-TR-88-0099.
McCaffrey, R., Abers, G. and Zwick, P., 1991, Inversion of Teleseismic Body Waves, International Association of Seismology and Physics of the Earth’s Interior, pp. 166.
McKenzie, D., 1972, Active tectonics of the Mediterranean region, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 30, 109–185.
McKenzie, D., 1978, Active tectonics of the Alpine-Himalayan belt: The Aegean Sea and surrounding regions, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 55, 217–254.
Melis, N.S. and Tselentis, G.-A., 1998, 3-D P-wave velocity structure in western Greece determined from tomography using earthquake data recorded at the University of Patras seismic network (PATNET), PAGEOPH 152, 329–348.
Molnar, P. and Lyon-Caen, H., 1989, Fault plane solutions of earthquakes and active tectonics of the Tibetan Plateau and its margins, Geophys. J. Int. 99, 123–153.
Nábělek, J., 1984, Determination of Earthquake Source Parameters from Inversion of Body Waves, PhD Thesis, MIT.
Novotny, O., Zahradnik, J. and Tselentis, G.-A., 2001, North-western Turkey earthquakes and the crustal structure inferred from surface waves observed in Western Greece, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 91, 875–879.
Panagiotopoulos, D.G., Hatzidimitriou, P.M., Karakaisis, G.F., Papadimitriou, E.E. and Papazachos, B.C., 1985, Travel time residuals in southeastern Europe, PAGEOPH 123, 221–231.
Papadimitriou, E., 2002, Mode of strong earthquake recurrence in central Ionian Islands (Greece). Possible triggering due to Coulomb stress changes generated by the occurrence of previous strong shocks, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 92, 3293–3308.
Papadopoulos, G., Karastathis, V., Ganas, A., Pavlides, S., Fokaefs, A. and Orfanogiannaki, K., 2003, The Lefkada, Ionian Sea (Greece), shock (Mw 6.2) of 14 August 2003: Evidence for the characteristic earthquake from seismicity and ground failures, Earth Planets Space 55, 713–718.
Papazachos, B. and Papazachou, C., 2003, The Earthquakes of Greece, 3rd edn., Ziti Public, Thessaloniki, p. 286.
Papazachos, B., Scordilis, E., Panagiotopoulos, D., Papazachos, C. and Karakaisis, G., 2004, Global relations between seismic fault parameters and moment magnitude of earthquakes, Proc. of the 10th Conference of the Hellenic Geol. Union, April 15–17, 2004, Thessaloniki (in press)
Papazachos, C.B. and Kiratzi, A.A., 1996, A detailed study of active crustal in the Aegean and surrounding region, 1996, Tectonophysics 253, 129–153.
Pasyanos, E., Dreger, D. and Romanowicz, B., 1996, Towards real-time determination of regional moment tensors, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 86, 1255–1269.
Saikia, C.K., 1994, Modified frequency-wavenumber algorithm for regional seismograms using Filon’s quadrature; modelling of Lg waves in eastern North America, Geophys. J. Int. 118, 142–158.
Scordilis, E.M., Karakaisis, G.F., Karacostas, B.G., Panagiotopoulos, D.G., Comninakis, P.E. and Papazachos, B.C., 1985, Evidence for transform faulting in the Ionian Sea: The Cephalonia Island earthquake sequence of 1983, PAGEOPH 123, 388–397.
Waldhauser, F., 2001, HypoDD – A program to compute double-difference hypocenter locations, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report, 113 pp.
Zahradnik, J., Serpetsidaki, A., Sokos, E. and Tselentis, G.-A., 2003, A multiple-event interpretation of the 2003 Lefkada earthquake, http://www.emsc-csem.org/ (last visited 14 September 2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benetatos, C., Kiratzi, A., Roumelioti, Z. et al. The 14 August 2003 Lefkada Island (Greece) earthquake: Focal mechanisms of the mainshock and of the aftershock sequence. J Seismol 9, 171–190 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-005-7092-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-005-7092-1